| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 25g |
|
||
| 50g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
HSV-2 ( IC50 = 11.3 μg/mL ); HSV-1 ( IC50 = 9.3 μg/mL )
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:阿糖腺苷和阿昔洛韦对野生型有协同作用。阿糖腺苷能够抑制 HSV 和 VZV 的阿昔洛韦耐药/TK 缺陷突变体,因为它被细胞激酶磷酸化为其活性阿糖腺苷三磷酸形式,并且不依赖于病毒 TK 的激活。单独的阿糖腺苷和阿昔洛韦 (ACV) 对 Vero 细胞中 HSV-1 斑块形成具有浓度依赖性抑制作用。阿糖腺苷与酸性蛋白结合多糖(APBP)联合对 Vero 细胞中 HSV-1 噬斑形成具有协同作用。阿糖腺苷直接作用于水痘带状疱疹病毒 (VZV) 和双链 DNA 病毒(包括人类腺病毒)的 DNA 聚合酶。阿糖腺苷特异性抑制11型腺病毒复制,体外无明显细胞毒性。阿糖腺苷对早期蛋白质的合成作用较小,但对 DNA 复制后的蛋白质合成作用较大。阿糖腺苷是一种抗病毒药物,对疱疹病毒、痘病毒、某些弹状病毒、嗜肝病毒和 RNA 肿瘤病毒具有活性。阿糖腺苷在体外和体内也具有抗痘苗病毒的活性。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
阿糖腺苷快速脱氨基为主要代谢物 9-β-D-阿拉伯呋喃糖基次黄嘌呤 (Ara-Hx)。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Systemetic absorption of vidarabine should not be expected to occur following ocular administration and swallowing lacrimal secretions. Vira-A is rapidly deaminated to arabinosylhypoxanthine (Ara-Hx), the principal metabolite. ...Because of the low solubility of Vira-A, trace amounts of both Vira-A and Ara-Hx can be detected in the aqueous humor only if there is an epithelial defect in the cornea. If the cornea is normal, only trace amounts of Ara-Hx can be recovered from the aqueous humor. Systemic absorption of Vira-A should not be expected to occur following ocular administration and swallowing lacrimal secretions. Vidarabine is poorly absorbed following oral, im, or SC administration. Following iv administration of vidarabine, 75-87% of the dose is rapidly deaminated by adenosine deaminase to ara-hypoxanthine. Ara-hypoxanthine also possesses antiviral activity but substantially less than that of vidarabine. Following slow iv administration of vidarabine 10 mg/kg in adults, peak plasma concentrations of the drug range from 0.2-0.4 ug/mL and peak plasma concentrations of ara-hypoxanthine range from 3-6 ug/mL. Plasma concentrations of vidarabine and ara-hypoxanthine are higher and more prolonged in patients with renal impairment. Vidarabine and ara-hypoxanthine are widely distributed into body tissues and fluids and readily cross the blood-brain barrier. In patients with normal meninges, ara-hypoxanthine concentrations in the CSF are about 33-35% of concurrent plasma concentrations. Vidarabine crosses the placenta in animals. It is not known if vidarabine is distributed into milk. ... Vidarabine is 20-30% bound and ara-hypoxanthine is 0-3% bound to plasma proteins. Vidarabine and ara-hypoxanthine are excreted mainly by the kidneys. Within 24 hours following iv administration of vidarabine 15 mg/kg in patients with normal renal function, 1-3% of the dose is excreted in urine as vidarabine and 41-53% of the dose is excreted as ara-hypoxanthine. There is no evidence of fecal excretion of the drug or metabolite. Metabolism / Metabolites In laboratory animals, vidarabine is rapidly deaminated in the gastrointestinal tract to Ara-Hx. In laboratory animals, Vira-A is rapidly deaminated in the gastrointestinal tract to arabinosylhypoxanthine (Ara-Hx). Vidarabine is rapidly deaminated, possibly within the cornea, by adenosine deaminase to ara-hypoxanthine. Ara-hypoxanthine also possesses antiviral activity but substantially less than that of vidarabine. Biological Half-Life The plasma half-life of vidarabine in adults with normal renal function is 1.5 hr, and the plasma half-life of ara-hypoxanthine is 3.3 hr. |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
24-38% Interactions Although an interaction has not been clearly established, concurrent administration of vidarabine and allopurinol has been associated with tremors, anemia, nausea, pain, and pruritus in some patients. Animal and in vitro studies suggest that allopurinol may interfere with the metabolism of vidarabine. Acyclovir and vidarabine both exhibit anti-herpetic activity. Because different mechanisms of action of vidarabine and acyclovir have been reported, /the authors/ analyzed their combined anti-herpetic activity on plaque formation of herpes simplex virus (HSV)-1, HSV-2, and varicella-zoster virus (VZV) by isobolograms. The results indicate that acyclovir and vidarabine have a synergistic effect on wild type HSV-1, HSV-2, and VZV. ... Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mouse iv 442 mg/kg LD50 Mouse sc 5086 mg/kg LD50 Mouse ip 3057 mg/kg LD50 Mouse oral 7800 ug/kg For more Non-Human Toxicity Values (Complete) data for VIDARABINE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
||
| 参考文献 | |||
| 其他信息 |
Vidarabine is a white to off-white crystalline powder. (NTP, 1992)
Adenine arabinoside is a purine nucleoside in which adenine is attached to arabinofuranose via a beta-N(9)-glycosidic bond. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent, a bacterial metabolite and a nucleoside antibiotic. It is a purine nucleoside and a beta-D-arabinoside. It is functionally related to an adenine. A nucleoside antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces antibioticus. It has some antineoplastic properties and has broad spectrum activity against DNA viruses in cell cultures and significant antiviral activity against infections caused by a variety of viruses such as the herpes viruses, the vaccinia VIRUS and varicella zoster virus. Vidarabine has been reported in Streptomyces antibioticus, Streptomyces herbaceus, and other organisms with data available. Vidarabine Anhydrous is an anhydrous form of vidarabine, a nucleoside analog with activity against herpes simplex virus and varicella zoster virus. Vidarabine is converted to a monophosphate by viral thymidine kinase and is further modified to a triphosphate form by host enzymes. Vidarabine triphosphate directly inhibits DNA polymerase and also acts as a chain terminator in DNA replication. Vidarabine is a nucleoside analog with activity against herpes simplex virus and varicella zoster virus. Vidarabine is converted to a monophosphate by viral thymidine kinase and is further modified to a triphosphate form by host enzymes. Vidarabine triphosphate directly inhibits DNA polymerase and also acts as a chain terminator in DNA replication. A nucleoside antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces antibioticus. It has some antineoplastic properties and has broad spectrum activity against DNA viruses in cell cultures and significant antiviral activity against infections caused by a variety of viruses such as the herpes viruses, the VACCINIA VIRUS and varicella zoster virus. Drug Indication For treatment of chickenpox - varicella, herpes zoster and herpes simplex Mechanism of Action Vidarabine stops replication of herpes viral DNA in 2 ways: 1) competitive inhibition of viral DNA polymerase, and consequently 2) incorporation into and termination of the growing viral DNA chain. Vidarabine is sequentially phosphorylated by kinases to the triphosphate ara-ATP, which is the active form of vidarabine that acts as both an inhibitor and a substrate of viral DNA polymerase. By acting as a substrate for viral DNA polymerase, ara-ATP competitively inhibits dATP leading to the formation of ‘faulty’ DNA. Ara-ATP can also be incorporated into the DNA strand to replace many of the adenosine bases, resulting in the disruption of DNA synthesis. The antiviral mechanism of action has not been established. Vidarabine appears to interfere with the early steps of viral DNA synthesis. The antiviral mechanism of vidarabine is incompletely understood, but vidarabine is an inhibitor of viral DNA synthesis. Cellular enzymes phosphorylate vidarabine to the triphosphate, which inhibits viral DNA polymerase activity in a manner that is competitive with deoxyadenosine triphosphate. Vidarabine triphosphate is incorporated into both cellular and viral DNA, where it may act as a chain terminator. Vidarabine triphosphate also inhibits ribonucleoside reductase, RNA polyadenylation, and S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (SAHH), an enzyme involved in transmethylation reactions. Therapeutic Uses A nucleoside antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces antibioticus. It has some antineoplastic properties and has broad spectrum activity against DNA viruses in cell cultures and significant antiviral activity against infections caused by a variety of viruses such as the herpes viruses, the VACCINIA VIRUS and varicella zoster virus Vidarabine has been shown to possess antiviral activity against the following viruses in vitro: Herpes simplex types 1 and 2; vaccinia, varicella-zoster. Except for rhabdovirus and oncornavirus, vidarabine does not display in vitro antiviral activity against other RNA or DNA viruses, including adenovirus. /EXPTL THER/ When adenovirus causes hemorrhagic cystitis in immunocompromised patients, vidarabine is used for its treatment because therapeutic choice is limited. Although vidarabine has been reported to be effective for these patients, its therapeutic basis has not yet been established. Vidarabine dose-dependently inhibited viral replication as assessed by a yield reduction assay. Viral protein synthesis was dose-dependently inhibited by vidarabine but not at all by acyclovir, and the degree of inhibition by vidarabine was different for each of the viral proteins, ranging from 0-40% of the untreated control. These results indicated the specificity and mechanism of action of vidarabine against adenovirus. The concentration of vidarabine and its metabolite in the bladder is suggested to exhibit effective anti-adenoviral activity in suppressing the replication of adenovirus. Thus, /the authors conclude that their/ results support vidarabine therapy as a possible candidate for adenovirus-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in immunocompromised patients. /EXPTL THER/ In the present study, effectiveness of topical vidarabine or subsequent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) administration was examined against persistent genital human papillomavirus (HPV) infection after local surgery. Thirty patients underwent local eradication treatment of uterine cervical intra-epithelial neoplasia (CIN) and stage Ia1 uterine cervical cancers. HPV typing was performed by PCR-RFLP analysis. HPV infection was detected pre-operatively in 29 of 30 patients. Of these, HPV was still present in the 20 patients within two months after the therapy. Topical administration of vidarabine or subsequent 5-FU once a week for four weeks was performed to the post-operative persistent HPV-positive cases. HPV infection was abolished in 1 of 10 (10%) with topical vidarabine, and in 2 of 4 vidarabine-resistant cases (50%) with topical 5-FU. Topical vidarabine or 5-FU treatment is beneficial for HPV-positive cases after local surgical excision. For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for VIDARABINE (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Vidarabine has been classified as a potential teratogen and should be used with caution during pregnancy (use only for strong clinical indication in absence of suitable alternative). Hallucinosis has been reported with excessive (as opposed to therapeutic) doses /of Vidarabine/. Vidarabine should be used only under the close supervision of an ophthalmologist. Concurrent topical application of vidarabine and a corticosteroid is contraindicated in superficial herpes simplex keratitis. Although concomitant application of vidarabine and a corticosteroid may be of benefit in severe infections, corticosteroids should be used with caution and the patient must be observed closely because of the risk of accelerating the spread of the infection. If a topical corticosteroid is administered concurrently with vidarabine, the possibility of corticosteroid induced adverse ocular effects, including increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma, and cataract formation, must be considered. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for VIDARABINE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Vidarabine is a synthetic purine nucleoside analogue with in vitro and in vivo inhibitory activity against herpes simplex virus types 1 (HSV-1), 2 (HSV-2), and varicella-zoster virus (VZV). The inhibitory activity of Vidarabine is highly selective due to its affinity for the enzyme thymidine kinase (TK) encoded by HSV and VZV. This viral enzyme converts Vidarabine into Vidarabine monophosphate, a nucleotide analogue. The monophosphate is further converted into diphosphate by cellular guanylate kinase and into triphosphate by a number of cellular enzymes. In vitro, Vidarabine triphosphate stops the DNA replication of herpes virus by being incorporated into the DNA strand and preventing the formation of phosphodiester bridges between bases. This ultimately leads to destabilization of the viral DNA strands. |
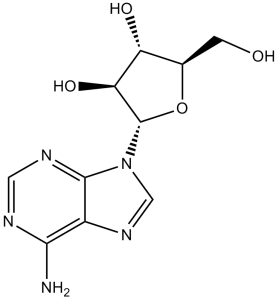
| 分子式 |
C10H13N5O4
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
267.24
|
|
| 精确质量 |
267.096
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 44.94; H, 4.90; N, 26.21; O, 23.95
|
|
| CAS号 |
5536-17-4
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
21704
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white crystalline powder
|
|
| 密度 |
2.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
676.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
260-265ºC (dec.)
|
|
| 闪点 |
362.8±34.3 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.907
|
|
| LogP |
-1.02
|
|
| tPSA |
139.54
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
19
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
335
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
|
| SMILES |
O[C@@H]([C@@H]1O)[C@@H](O[C@@H]1CO)N2C(N=CN=C3N)=C3N=C2
|
|
| InChi Key |
OIRDTQYFTABQOQ-UHTZMRCNSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C10H13N5O4/c11-8-5-9(13-2-12-8)15(3-14-5)10-7(18)6(17)4(1-16)19-10/h2-4,6-7,10,16-18H,1H2,(H2,11,12,13)/t4-,6-,7+,10-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
(2R,3S,4S,5R)-2-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.35 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.35 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.35 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.7420 mL | 18.7098 mL | 37.4195 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7484 mL | 3.7420 mL | 7.4839 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3742 mL | 1.8710 mL | 3.7420 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00000985 | Completed | Drug: Vidarabine Drug: Acyclovir |
Herpes Simplex | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) |
October 1990 | Phase 3 |
|