| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
VEGFR2 (IC50 = 40 nM); VEGFR3 (IC50 = 110 nM); EGFR/HER1 (IC50 = 500 nM)
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Vandetanib 抑制 VEGFR3 和 EGFR,IC50 分别为 110 nM 和 500 nM。 Vandetanib 对 MEK、CDK2、c-Kit、erbB2、FAK、PDK1、Akt 和 IGF-1R 几乎没有作用,IC50 高于 10 μM。相反,它对 PDGFRβ、Flt1、Tie-2 和 FGFR1 不敏感。 Vandetanib 对基底内皮细胞生长影响不大,但抑制 VEGF、EGF 和 bFGF 诱导的 HUVEC 增殖,IC50 值分别为 60 nM、170 nM 和 800 nM。 vandetanib 的 IC50 范围为 2.7 μM (A549) 至 13.5 μM (Calu-6) [1],可抑制肿瘤细胞的发育。与 Cat S 抑制剂 LHVS (IC50=0.001 μM) 相比并在小鼠 B 细胞系中进行测试 (IC50=1.5±0.4 μM),odanacatib 是一种温和的抗原呈递抑制剂。与 LHVS 相比,Odanacatib 的最低抑制剂量分别为 1-10 μM 和 0.01 μM,对小鼠脾细胞中 MHC II 不变链蛋白 Iip10 的加工具有较小的抑制作用 [2]。 Vandetanib 抑制肝癌细胞中 EGFR 和 HUVEC 中 VEGFR-2 的磷酸化以及细胞分裂 [4]。
|
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Vandetanib (15 mg/kg, po) 在 H1650 异种移植模型中比吉非替尼具有更强的抗肿瘤活性,并抑制肿瘤生长,IC50 为 3.5±1.2 μM [3]。在荷瘤小鼠中,凡德他尼(50或75 mg/kg)抑制肿瘤组织中VEGFR-2和EGFR的磷酸化,显着降低肿瘤血管密度,增强肿瘤细胞凋亡,抑制肿瘤生长,提高生存率,减少肝内转移的数量,并上调肿瘤组织中的 VEGF、TGF-α 和 EGF [4]。
|
|
| 酶活实验 |
在涂有聚(Glu、Ala、Tyr)6:3:1 无规共聚物底物的 96 孔板中,将凡德他尼与酶、10 mM MnCl2 和 2 μM ATP 一起孵育。下一步是通过依次孵育 2,2'-azino-bis(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)、辣根过氧化物酶连接的绵羊抗小鼠免疫球蛋白抗体和小鼠 IgG 抗磷酸酪氨酸 4G10 抗体来鉴定磷酸化酪氨酸。为了研究对与 FGFR1、c-kit、erbB2、IGF-1R、FAK、PDGFRβ、Tie-2 和 FGFR1 相关的酪氨酸激酶的选择性,对该方法进行了修改。所有酶测定(酪氨酸或丝氨酸-苏氨酸)均使用等于或略低于相应 Km (0.2–14 μM) 的适当 ATP 浓度。使用相关闪烁邻近分析 (SPA) 在 96 孔板中研究针对丝氨酸-苏氨酸激酶(CDK2、AKT 和 PDK1)的选择性。 CDK2 检测的条件如下:10 mM MnCl2、4.5 μM ATP、0.15 μCi [γ-33 P]ATP/反应、50 mM HEPES( pH 7.5)、1 mM DTT、0.1 mM 原钒酸钠、0.1 mM 氟化钠、10 mM 甘油磷酸钠、1 mg/mL BSA 组分 V 和视网膜母细胞瘤底物(视网膜母细胞瘤基因的一部分,792-928,以谷胱甘肽 S-转移酶表达系统;0.22 μM 初始浓度)。反应在室温下进行 60 分钟,然后使用 150 μL 溶液淬灭 2 小时,该溶液含有 0.8 mg/反应的 Protein A SPA-聚乙烯甲苯珠、3 μg 兔免疫球蛋白抗谷胱甘肽 S-转移酶抗体和EDTA(62 mM 最终浓度)。之后,将板密封,在1200 xg下离心五分钟,并使用微板闪烁计数器计数三十秒。
|
|
| 细胞实验 |
MTT 测定经过修改以测量生长抑制。简而言之,细胞以每孔 2000 个细胞的密度接种在 96 孔板中后,暴露于凡德他尼或吉非替尼 72 小时。每个测定进行三次。对于每种药物,50% 抑制浓度 (IC50) 使用平均值±标准差 (SD) 计算。
|
|
| 动物实验 |
|
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Slow- peak plasma concentrations reached at a median 6 hours. On multiple dosing, Vandetanib accumulates about 8 fold with steady state reached after around 3 months. About 69% was recovered following 21 days after a single dose of vandentanib. 44% was found in feces and 25% in urine. Vd of about 7450 L. Vandetanib binds to human serum albumin and a1-acid-glycoprotein with in vitro protein binding being approximately 90%. In ex vivo plasma samples from colorectal cancer patients at steady state exposure after 300 mg once daily, the mean percentage protein binding was 94%. Within a 21-day collection period after a single dose of (14)C-vandetanib, approximately 69% was recovered with 44% in feces and 25% in urine. Excretion of the dose was slow and further excretion beyond 21 days would be expected based on the plasma half-life. Vandetanib was not a substrate of hOCT2 expressed in HEK293 cells. Vandetanib inhibits the uptake of the selective OCT2 marker substrate 14C-creatinine by HEK-OCT2 cells, with a mean IC50 of 2.1 ug/mL. This is higher than vandetanib plasma concentrations (0.81 ug/mL) observed after multiple dosing at 300 mg. Inhibition of renal excretion of creatinine by vandetanib provides an explanation for increases in plasma creatinine seen in human subjects receiving vandetanib. Following oral administration of Caprelsa, absorption is slow with peak plasma concentrations typically achieved at a median of 6 hours, range 4-10 hours, after dosing. Vandetanib accumulates approximately 8-fold on multiple dosing with steady state achieved in approximately 3 months. Exposure to vandetanib is unaffected by food. The protein binding of (14)C-Vandetanib in plasma of mice, rats, rabbits dogs and human was moderate, from 83 to 90%. The tissue distribution of vandetanib and/or metabolites in pigmented and non pigmented male rats after single oral dosing was slow but extensive, and consistent with the distribution pattern of a lipophilic compound. Highest concentrations of vandetanib and/or its metabolites were seen in the majority of tissues at 6-8 hours after administration. The distribution of radioactivity to brain was evident. Retention of radioactivity was seen in pigmented tissues indicating melanin affinity. A significant distribution of radioactivity was seen in milk of lactating rats and further on in the plasma of suckling pups. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Vandetanib (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Unchanged vandentanib and metabolites vandetanib N-oxide and N-desmethyl vandetanib were detected in plasma, urine and feces. N-desmethyl-vandetanib is primarily produced by CYP3A4, and vandetanib-N-oxide is primarily produced by flavin–containing monooxygenase enzymes FMO1 and FMO3. The metabolism of vandetanib seemed to be similar in the toxicology species, rat and dog, as well as in mouse and human. The 2 major metabolites identified in excreta, were N-desmethyl-vandetanib and vandetanib-N-oxide. In mouse, a minor metabolite was also identified as O-desalkyl-vandetanib glucuronid. A glucuronide conjugate was also detected in human urine. Metabolism as well as biliary excretion appears to be most important for the elimination of vandetanib in preclinical species. CYP identification studies in vitro, suggest that CYP3A4 is involved in the formation of N-desmethyl-Vandetanib. vandetanib-N-oxide is formed via FMO1 and FMO3 (FMO=flavine mono-oxygenase). Both these enzymes are also found in kidney indicating that renal excretion might be contributed to the clearance of vandetanib. Following oral dosing of (14)C-vandetanib, unchanged vandetanib and metabolites vandetanib N-oxide and N-desmethyl vandetanib were detected in plasma, urine and feces. A glucuronide conjugate was seen as a minor metabolite in excreta only. N-desmethyl-vandetanib is primarily produced by CYP3A4 and vandetanib-N-oxide by flavin-containing monooxygenase enzymes FMO1 and FMO3. N-desmethyl-vandetanib and vandetanib-N-oxide circulate at concentrations of approximately 7-17% and 1.4-2.2%, respectively, of those of vandetanib. ... In plasma, concentrations of total radioactivity were higher than vandetanib concentrations at all time points, indicating the presence of circulating metabolites. Unchanged vandetanib and 2 anticipated metabolites (N-desmethylvandetanib and vandetanib N-oxide) were detected in plasma, urine, and feces. A further trace minor metabolite (glucuronide conjugate) was found in urine and feces. ... Unchanged vandetanib and N-desmethyl and N-oxide metabolites were detected in plasma, urine, and feces. Biological Half-Life Median half life of 19 days. ... Caprelsa at the 300 mg dose in medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) patients /is/ characterized by a ... median plasma half-life of 19 days. ... Vandetanib was absorbed and eliminated slowly with a half life of approximately 10 days after single oral doses. ... |
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In large clinical trials of vandetanib, abnormalities in routine liver tests were common with serum aminotransferase elevations, occurring in up to half of patients and rising above 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) 2% to 5% of patients. In prelicensure trials of vandetanib in thyroid cancer, there were no reports of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice or hepatic failure. Since approval and more wide scale use, there have been no published reports of hepatotoxicity due to vandetanib and the product label does not include discussion of hepatotoxicity. However, many of the kinase inhibitors used in cancer chemotherapy have been implicated in cases of clinically apparent liver injury which typically arises within the first 2 to 12 weeks of therapy, presenting with symptoms of fatigue, nausea and jaundice and a hepatocellular pattern of serum enzyme elevations without immunoallergic or autoimmune features. Several tyrosine kinase inhibitors (imatinib, nilotinib) have also been implicated in causing reactivation of hepatitis B. Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of vandetanib during breastfeeding. Because vandetanib is 90% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, its half-life is 19 days and it might accumulate in the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during vandetanib therapy and for 4 months after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Protein binding of about 90%. |
|
| 参考文献 |
|
|
| 其他信息 |
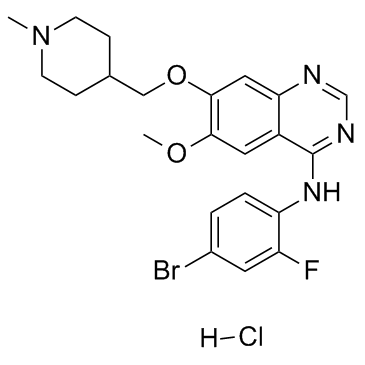
Vandetanib is a quinazoline that is 7-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]quinazoline bearing additional methoxy and 4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino substituents at positions 6 and 4 respectively. Used for the treatment of symptomatic or progressive medullary thyroid cancer in patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease. It has a role as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent. It is an aromatic ether, a secondary amine, a member of quinazolines, a member of piperidines, an organobromine compound and an organofluorine compound.
Vandetanib is an oral once-daily kinase inhibitor of tumour angiogenesis and tumour cell proliferation with the potential for use in a broad range of tumour types. On April 6 2011, vandetanib was approved by the FDA to treat nonresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer in adult patients. Vandetanib is a Kinase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of vandetanib is as a Protein Kinase Inhibitor. Vandetanib is a Kinase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of vandetanib is as a Protein Kinase Inhibitor, and P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor, and Organic Cation Transporter 2 Inhibitor. Vandetanib is a multi-kinase inhibitor that is used in the therapy of advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer. Vandetanib therapy is commonly associated with transient elevations in serum aminotransferase during therapy, but has not been linked to cases of clinically apparent acute liver injury with jaundice. Vandetanib is an orally bioavailable 4-anilinoquinazoline. Vandetanib selectively inhibits the tyrosine kinase activity of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2), thereby blocking VEGF-stimulated endothelial cell proliferation and migration and reducing tumor vessel permeability. This agent also blocks the tyrosine kinase activity of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a receptor tyrosine kinase that mediates tumor cell proliferation and migration and angiogenesis. Drug Indication Vandetanib is currently approved as an alternative to local therapies for both unresectable and disseminated disease. Because Vandetanib can prolong the Q-T interval, it is contraindicated for use in patients with serious cardiac complications such as congenital long QT syndrome and uncompensated heart failure. FDA Label Caprelsa is indicated for the treatment of aggressive and symptomatic medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) in patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease. Caprelsa is indicated in adults, children and adolescents aged 5 years and older. For patients in whom re-arranged-during-transfection(RET) mutation is not known or is negative, a possible lower benefit should be taken into account before individual treatment decision. Treatment of medullary thyroid carcinoma Mechanism of Action ZD-6474 is a potent and selective inhibitor of VEGFR (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor), EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) and RET (REarranged during Transfection) tyrosine kinases. VEGFR- and EGFR-dependent signalling are both clinically validated pathways in cancer, including non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). RET activity is important in some types of thyroid cancer, and early data with vandetanib in medullary thyroid cancer has led to orphan-drug designation by the regulatory authorities in the USA and EU. In vitro, vandetanib inhibited epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylation in tumor cells and endothelial cells and VEGF-stimulated tyrosine kinase phosphorylation in endothelial cells. In vitro studies have shown that vandetanib inhibits the tyrosine kinase activity of the EGFR and VEGFR families, RET, BRK, TIE2, and members of the EPH receptor and Src kinase families. These receptor tyrosine kinases are involved in both normal cellular function and pathologic processes such as oncogenesis, metastasis, tumor angiogenesis, and maintenance of the tumor microenvironment. In addition, the N-desmethyl metabolite of the drug, representing 7 to 17.1% of vandetanib exposure, has similar inhibitory activity to the parent compound for VEGF receptors (KDR and Flt-1) and EGFR. Oncogenic conversion of the RET /rearranged during transfection/ tyrosine kinase is a frequent feature of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC). Vandetanib is an ATP-competitive inhibitor of RET, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors kinases. In this study, vandetanib mechanism of action in TT and MZ-CRC-1 human MTC cell lines, carrying cysteine 634 to tryptophan (C634W) and methionine 918 to threonine (M918T) RET mutation respectively /were studied/. Vandetanib blunted MTC cell proliferation and RET, Shc and p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation. Single receptor knockdown by RNA interference showed that MTC cells depended on RET for proliferation. Adoptive expression of the vandetanib-resistant V804M RET mutant rescued proliferation of TT cells under vandetanib treatment, showing that RET is a key vandetanib target in these MTC cells. Upon RET inhibition, adoptive stimulation of EGFR partially rescued TT cell proliferation, MAPK signaling, and expression of cell-cycle-related genes. This suggests that simultaneous inhibition of RET and EGFR by vandetanib may overcome the risk of MTC cells to escape from RET blockade through compensatory over-activation of EGFR. Rearranged during transfection (RET) is widely expressed in neuroblastoma (NB) and partly contributes to high metastatic potential and survival of NB. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether vandetanib (a RET inhibitor) inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of NB cells in vitro. The effects of vandetanib on the proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle and on RET phosphorylation of SK-N-SH and SH-SY5Y cells were evaluated in vitro. The migration and invasion potential of vandetanib-treated NB cells were analyzed using Transwell cell migration and invasion assays, respectively. qPCR, western blotting and immunofluorescence were used to detect mRNA and protein levels in NB cells treated with vandetanib. Our data demonstrated that vandetanib inhibits the proliferation of SK-N-SH and SH-SY5Y cells and that this inhibition is mediated by the induction of G1 phase cell cycle arrest at lower concentrations and by apoptosis at higher concentrations. In the presence of vandetanib, the migration and invasion of two NB cell lines were markedly decreased compared with the control group (p<0.01). In addition, our data showed that the levels of C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) and matrix metalloproteinase 14 (MMP14) mRNA expression in NB cell lines treated with vandetanib were significantly lower than those in the cells that were treated with vehicle (p<0.01) and similar results were obtained for protein levels as determined by western blotting and immunofluorescence analysis. Vandetanib may inhibit the proliferation, migration and invasion of NB cells in vitro. The potential mechanisms for the inhibition of NB migration and invasion by vandetanib may partly be attributed to the ability of vandetanib to suppress the expression of CXCR4 and MMP14 in human NB cells. For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for Vandetanib (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 分子式 |
C22H25BRCLFN4O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
511.8
|
| 精确质量 |
510.083
|
| CAS号 |
524722-52-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Vandetanib;443913-73-3;Vandetanib trifluoroacetate;338992-53-3;Vandetanib-d6;1174683-49-8; 338992-00-0 (fumarate); 338992-00-0; 524722-52-9
|
| PubChem CID |
23133323
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| tPSA |
59.5
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
539
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
KVBQCJXMSFJOFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H24BrFN4O2.ClH/c1-28-7-5-14(6-8-28)12-30-21-11-19-16(10-20(21)29-2)22(26-13-25-19)27-18-4-3-15(23)9-17(18)24;/h3-4,9-11,13-14H,5-8,12H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26,27);1H
|
| 化学名 |
N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]quinazolin-4-amine;hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
Vandetanib hydrochloride; 524722-52-9; Vandetanib (hydrochloride); TCMDC-123476; N-(4-Bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-((1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy)quinazolin-4-amine hydrochloride; N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]quinazolin-4-amine;hydrochloride; Vandetanib HCl; N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]quinazolin-4-amine hydrochloride;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9539 mL | 9.7694 mL | 19.5389 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3908 mL | 1.9539 mL | 3.9078 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1954 mL | 0.9769 mL | 1.9539 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT01496313 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: 300mg vandetanib Drug: 150mg vandetanib |
Thyroid Cancer | Genzyme, a Sanofi Company/td> | August 28, 2012 | Phase 4 |
| NCT01582191 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Vandetanib Drug: Everolimus |
Advanced Malignant Neoplasm Metastatic Malignant Neoplasm |
M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | May 14, 2012 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00537095 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Vandetanib Other: Placebo |
Thyroid Neoplasms | Genzyme, a Sanofi Company | September 29, 2007 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04211337 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Selpercatinib Drug: Vandetanib |
Medullary Thyroid Cancer | Loxo Oncology, Inc. | February 11, 2020 | Phase 3 |
| NCT00410761 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: ZD6474 (Vandetanib) |
Thyroid Cancer | Genzyme, a Sanofi Company | November 30, 2006 | Phase 3 |