| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Natural product; secondary metabolite
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
破骨细胞是唯一可以吸收骨的细胞,它们是在M-CSF和RANKL存在下由单核细胞/巨噬细胞产生的,并在体内被免疫反应激活。松萝酸是地衣的次生代谢产物,具有独特的二苯并呋喃骨架。它已在化妆品、香水和传统药物中使用多年。它具有广泛的生物活性,包括抗炎、抗菌、抗癌、抗病毒等,但其抗破骨细胞的活性尚未见报道。在这项研究中,研究了松萝酸是否会影响RANKL介导的破骨细胞生成。Usnic酸通过降低破骨细胞生成的主要调节因子NFATc1的转录和翻译表达,显著抑制了RANKL介导的破骨细胞的形成和功能[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
松萝酸对LPS诱导的小鼠血清生化标志物的影响[1]
首次注射松萝酸8天后,通过ELISA从血清中测定骨吸收标志物TRAP-5b的浓度。LPS组血清TRAP-5b水平比对照组高约两倍,但LPS+松萝酸组血清TRAP-Pb水平比LPS组低约30%。 松萝酸抑制LPS诱导的小鼠骨丢失[1] 用LPS诱导的小鼠骨侵蚀模型评估松萝酸的抗吸收活性。从小鼠身上采集股骨,并通过微型计算机断层扫描(μCT)系统进行分析。μCT显示,LPS治疗降低了股骨干骺端区域小梁骨的骨量,而松萝酸治疗显著防止了LPS介导的小梁骨丢失(图6A)。松萝酸可显著预防LPS介导的骨密度(BMD)、骨体积/总体积(BV/TV)、骨表面积/总容积(BS/TV)和骨小梁分离(Tb.Sp)的变化。 松萝酸可预防脂多糖(LPS)诱导的小鼠骨侵蚀。综上所述,我们的研究结果表明,松萝酸可能是治疗骨质疏松症的潜在候选药物[1]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)测定血清TRAP[1]
从眶后神经丛采集血液,用LPS处理的骨质疏松症模型小鼠在18000g下离心5分钟。血清被分离并储存在-20°C下。使用抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶5b ELISA试剂盒测量血清TRAP-5b水平。根据制造商提供的方案进行分析。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定
使用细胞计数试剂盒-8(CCK-8)方法测定了Usnic acid对BMM存活率的影响。简而言之,将骨髓基质细胞以1×104个细胞/孔的密度接种在96孔板中,并用指定浓度的Usnic acid(0、0.3、1和3µM)培养3天。根据制造商的方案,使用CCK-8试剂盒评估细胞存活率。
骨坑形成试验 如前所述进行骨坑形成试验。BMM在骨测定板(24孔板)上以3×105个细胞/孔的密度分化,并在Usnic acid(0、1和3µM)存在下用10 ng/mL RANKL和30 ng/mL M-CSF刺激。4天后,用5%次氯酸钠去除细胞5分钟,然后在光学显微镜下观察再吸收面积(放大倍数,×50),之后用ImageJ软件测量。 |
| 动物实验 |
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-Induced Bone Erosion
All procedures involving mice were conducted in strict accordance with SCNU IACUC guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals (Permit No: SCNU IACUC-2016-08).
LPS-induced bone erosion was performed as described previously [28]. Five-week-old male ICR mice were divided into 3 groups of 6 mice. One day before injection of LPS (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and subsequently on every day for up to 8 days till the end of the experimental period, intraperitoneal injections of usnic acid (1 μg/g of body weight) or 10% Kolliphor ER in PBS (control) were administered. LPS (5 μg/μL in 0.1% BSA PBS) was injected intraperitoneally on days 1 and 4. All mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and their femora were scanned with High-resolution micro-CT (SKYSCAN 1272; Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) and imaged by DataViewer (SKYSCAN). The bone mineral density (BMD), bone volume/total volume (BV/TV), bone surface/total volume (BS/TV), and trabecular separation (Tb.Sp) were measured to assess the trabecular bone microstructure of the femur using the CTAn software provided with the SKYSCAN analysis tool.
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Adverse Effects
Skin Sensitizer - An agent that can induce an allergic reaction in the skin. mouse LD50 subcutaneous 75 mg/kg CRC Handbook of Antibiotic Compounds, Vols.1- , Berdy, J., Boca Raton, FL, CRC Press, 1980, 9(89), 1982 mouse LD50 intravenous 25 mg/kg Antibiotics., 1(611), 1967 rabbit LD oral >500 mg/kg Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research., 5(510), 1955 [PMID:13276269] Antidote and Emergency Treatment /SRP:/ Basic treatment: Establish a patent airway. Suction if necessary. Watch for signs of respiratory insufficiency and assist ventilations if needed. Administer oxygen by nonrebreather mask at 10 to 15 L/min. Monitor for pulmonary edema and treat if necessary ... . Monitor for shock and treat if necessary ... . Anticipate seizures and treat if necessary ... . For eye contamination, flush eyes immediately with water. Irrigate each eye continuously with normal saline during transport ... . Do not use emetics. For ingestion, rinse mouth and administer 5 ml/kg up to 200 ml of water for dilution if the patient can swallow, has a strong gag reflex, and does not drool ... . Cover skin burns with dry sterile dressings after decontamination ... . /Poison A and B/ /SRP:/ Advanced treatment: Consider orotracheal or nasotracheal intubation for airway control in the patient who is unconscious, has severe pulmonary edema, or is in respiratory arrest. Positive pressure ventilation techniques with a bag valve mask device may be beneficial. Monitor cardiac rhythm and treat arrhythmias as necessary ... . Start an IV with D5W /SRP: "To keep open", minimal flow rate/. Use lactated Ringer's if signs of hypovolemia are present. Watch for signs of fluid overload. Consider drug therapy for pulmonary edema ... . For hypotension with signs of hypovolemia, administer fluid cautiously. Watch for signs of fluid overload ... . Treat seizures with diazepam (Valium) ... . Use proparacaine hydrochloride to assist eye irrigation ... . /Poison A and B/ Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Dog iv 40 mg/kg PMID:12453567 LD50 Rabbit iv 30 mg/kg PMID:12453567 LD50 Rat iv 30 mg/kg PMID:12453567 LD50 Rabbit oral 500 mg/kg Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Dog iv 40 mg/kg LD50 Rabbit iv 30 mg/kg LD50 Rat iv 30 mg/kg LD50 Rabbit oral 500 mg/kg For more Non-Human Toxicity Values (Complete) data for USNIC ACID (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
7-Hydroxy-(S)-usnate is a member of benzofurans.
Usnic acid has been reported in Dimelaena oreina, Flavoparmelia haysomii, and other organisms with data available. See also: (-)-Usnic Acid (annotation moved to). Mechanism of Action The physiological effects of usnic acid /was investigated/ in two cultured species of the lichen alga Trebouxia. Exposing Trebouxia to the sodium salt of usnic acid resulted in the inhibition of growth and photosynthesis, an incr in membrane permeability and immobilization of zoospore. /Usnic acid, sodium salt/ The mechanism of action expressed by usnic acid remains speculative. (+)-Usnic acid has been shown to be an uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation in mouse-liver mitochondria at levels of 1 uM. The accumulation of usnic acid can be stimulated by the inhibition of photosynthesis, suggesting a possible role of glucose in regulating enzymes of phenol synthesis. Experiments show that usnic acid is an allelopathic agent, inhibiting moss spore germination and that its effectiveness is pH dependent. In vitro, usnic acid has a slight inhibitory action against leukotriene biosynthesis in bovine polymorphonuclear leukocytes by a specific enzyme interaction rather than acting as an antioxidant against the peroxidation process, or as a scavenger, or even as a source of free radicals. Osteoclasts are the only cells that can resorb bone and they are produced from monocytes/macrophages in the presence of M-CSF and RANKL and are activated in vivo by an immune response. Usnic acid is a secondary metabolite of lichen and has a unique dibenzofuran skeleton. It has been used for years in cosmetics, fragrances, and traditional medicines. It has a wide range of bioactivities, including anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, anti-cancer, anti-viral, and so on. However, the anti-osteoclastogenic activity of usnic acid has not been reported yet. In this study, we investigated whether usnic acid could affect RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis. Usnic acid significantly inhibited RANKL-mediated osteoclast formation and function by reducing the transcriptional and translational expression of NFATc1, a master regulator of osteoclastogenesis. In addition, it prevented lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced bone erosion in mice. Taken together, our results suggest that usnic acid might be a potential candidate for the treatment of osteoporosis.[1] Therapeutic Uses Recent studies in which the anti-inflammatory activity of (+)-usnic acid was compared to that of ibuprofen using the rat paw edema assay (acute effects) and the cotton pellet assay (chronic effects) showed (+)-usnic acid to be significantly effective in both assays at an oral dose of 100 mg/kg adn comparable to ibuprofen at the same dose. PMID:12453567 /EXPL THER: / Commercially obtained (+)-usnic acid was shown to inhibit cytopathic effects of Herpes simplex type 1 and polio type 1 viruses when administered on filter paper discs which were placed on virus-infected African green monkey kidney (BS-C-1) cells. PMID:12453567 /EXPL THER:/ Oral administration of usnic acid at 30 and 100 mg/kg resulted in significant analgesic effects as determined by the acetic acid-induced writhing- and tail pressure tests. Usnic acid administered orally at doses of 100 and 300 mg/kg exhibited significant antipyretic activity as evaluated through lipopolysaccharide-induced hyperthermia. PMID:12453567 /Usnic acid/ inhibits the growth of multi-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus, enterococci and mycobacteria. PMID:12061397 Usnic acid had anti-osteoclastogenesis activity by inhibiting the expression of NFATc1 via down-regulating RANKL-mediated ERK activation and it could significantly prevent LPS-induced bone loss in vivo. Therefore, usnic acid might be used as a new structural scaffold for the treatment of bone diseases, such as osteoporosis.[1] Therapeutic Uses Recent studies in which the anti-inflammatory activity of (+)-usnic acid was compared to that of ibuprofen using the rat paw edema assay (acute effects) and the cotton pellet assay (chronic effects) showed (+)-usnic acid to be significantly effective in both assays at an oral dose of 100 mg/kg adn comparable to ibuprofen at the same dose. /EXPL THER: / Commercially obtained (+)-usnic acid was shown to inhibit cytopathic effects of Herpes simplex type 1 and polio type 1 viruses when administered on filter paper discs which were placed on virus-infected African green monkey kidney (BS-C-1) cells. /EXPL THER:/ Oral administration of usnic acid at 30 and 100 mg/kg resulted in significant analgesic effects as determined by the acetic acid-induced writhing- and tail pressure tests. Usnic acid administered orally at doses of 100 and 300 mg/kg exhibited significant antipyretic activity as evaluated through lipopolysaccharide-induced hyperthermia. /Usnic acid/ inhibits the growth of multi-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus, enterococci and mycobacteria. For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for USNIC ACID (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 分子式 |
C18H16O7
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
344.31
|
| 精确质量 |
344.089
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 62.79; H, 4.68; O, 32.53
|
| CAS号 |
125-46-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
(+)-Usnic acid;7562-61-0
|
| PubChem CID |
5646
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid powder
|
| 熔点 |
204 °C
|
| LogP |
1.4
|
| tPSA |
118
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
708
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
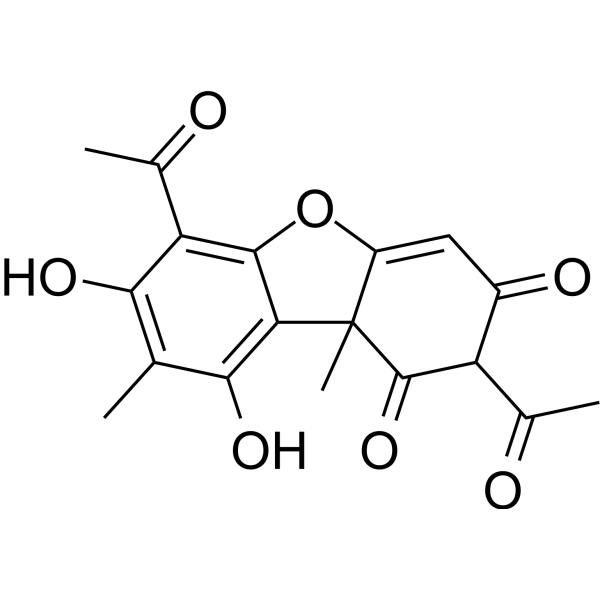
O=C(C1(C)C(OC2=C(C(C)=O)C(O)=C(C)C(O)=C12)=C3)C(C(C)=O)C3=O
|
| InChi Key |
CUCUKLJLRRAKFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H16O7/c1-6-14(22)12(8(3)20)16-13(15(6)23)18(4)10(25-16)5-9(21)11(7(2)19)17(18)24/h5,11,22-23H,1-4H3
|
| 化学名 |
2,6-diacetyl-7,9-dihydroxy-8,9b-dimethyldibenzofuran-1,3-dione
|
| 别名 |
NSC-8517; 125-46-2; Usno; 1,3(2H,9bH)-Dibenzofurandione, 2,6-diacetyl-7,9-dihydroxy-8,9b-dimethyl-; usnic-acid; L-Usnic acid; NSC 8517; NSC5890; NSC 8517; Usnic acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~3.33 mg/mL (~9.67 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9044 mL | 14.5218 mL | 29.0436 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5809 mL | 2.9044 mL | 5.8087 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2904 mL | 1.4522 mL | 2.9044 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。