| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Troglitazone 是一种 PPARγ 激动剂;其对人和鼠 PPARγ 受体的 EC50 值分别为 550 nM 和 780 nM[1]。曲格列酮 (2-200 μM) 对胰腺癌细胞系(MIA Paca2 和 PANC-1 细胞)具有细胞毒性,IC50 分别为 49.9 ± 1.2 和 51.3 ± 5.3 μM。在 MIA Paca2 和 PANC-1 细胞中,曲格列酮 (50 μM) 会增加染色质浓缩,增加 caspase-3 活性,并降低 Bcl-2 表达 [2]。在人肺腺癌细胞中,曲格列酮(0、1、2 和 4 μM)使 TRAIL 介导的细胞凋亡变得敏感。自噬抑制可防止曲格列酮增强 TRAIL 诱导的细胞凋亡。此外,A549 细胞中 PPARγ 的激活会诱导曲格列酮的作用[3]。
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
MIA Paca2 异种移植模型对曲格列酮(200 mg/kg,口服)表现出生长抑制作用[2]。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Absorbed rapidly. Food increases the extent of absorption by 30% to 85%. Metabolism / Metabolites A sulfate conjugate metabolite (Metabolite 1) and a quinone metabolite (Metabolite 3) have been detected in the plasma of healthy males. A glucuronide conjugate (Metabolite 2) has been detected in the urine and also in negligible amounts in the plasma. In healthy volunteers and in patients with type 2 diabetes, the steady-state concentration of Metabolite 1 is six to seven times that of troglitazone and Metabolite 3. In in vivo drug interaction studies, troglitazone has been shown to induce cytochrome P450 CYP3A4 at clinically relevant doses. Troglitazone has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-[[2-[[4-[(2,4-dioxo-1,3-thiazolidin-5-yl)methyl]phenoxy]methyl]-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-yl]oxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid. A sulfate conjugate metabolite (Metabolite 1) and a quinone metabolite (Metabolite 3) have been detected in the plasma of healthy males. A glucuronide conjugate (Metabolite 2) has been detected in the urine and also in negligible amounts in the plasma. In healthy volunteers and in patients with type 2 diabetes, the steady-state concentration of Metabolite 1 is six to seven times that of troglitazone and Metabolite 3. In in vivo drug interaction studies, troglitazone has been shown to induce cytochrome P450 CYP3A4 at clinically relevant doses. Half Life: 16-34 hours Biological Half-Life 16-34 hours |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Troglitazone is a thiazolidinedione antidiabetic agent that lowers blood glucose by improving target cell response to insulin. It has a unique mechanism of action that is dependent on the presence of insulin for activity. Troglitazone decreases hepatic glucose output and increases insulin dependent glucose disposal in skeletal muscle. Its mechanism of action is thought to involve binding to nuclear receptors (PPAR) that regulate the transcription of a number of insulin responsive genes critical for the control of glucose and lipid metabolism. Troglitazone is a ligand to both PPAR‘± and PPAR‘_, with a highter affinity for PPAR‘_. The drug also contains an ‘±-tocopheroyl moiety, potentially giving it vitamin E-like activity. Troglitazone has been shown to reduce inflammation, and is associated with a decrase in nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-‘_B) and a concomitant increase in its inhibitor (I‘_B). NF-‘_B is an important cellular transcription regulator for the immune response. Unlike sulfonylureas, troglitazone is not an insulin secretagogue. Hepatotoxicity Large prospective studies showed that significant elevations in serum aminotransferase levels (equal to or greater than 3 times the upper limit of the normal range [ULN]) occurred in 1.9% of patients with diabetes treated with troglitazone for 24 to 48 weeks, compared to only 0.6% in placebo recipients. These enzyme elevations were usually asymptomatic and often resolved despite continuation of therapy. Nevertheless, elevations >10 times ULN occurred in 0.5% of patients (but in no placebo recipient) and a proportion of these developed symptoms of liver injury and jaundice. Soon after the approval of troglitazone as therapy for type 2 diabetes in the United States, cases of severe acute liver injury began to be reported, and dramatic case reports as well as small case series documented that clinically significant injury was occurring in 1:1000 to 1:10,000 recipients. The latency to onset of injury was typically 1 to 6 months and the onset was marked by fatigue, weakness, dark urine and jaundice, and an acute hepatitis-like elevation in serum enzymes (hepatocellular pattern). Allergic phenomena (rash, fever, eosinophilia) were uncommon and serum autoantibodies were not usually present. Liver biopsies showed acute inflammatory changes and variable degrees of necrosis, ranging from rare spotty necrosis to bridging hepatic necrosis and submassive or massive necrosis. At least two dozen cases of acute liver failure and death or need for liver transplantation were reported to the FDA before troglitazone was withdrawn from use in 2000. Likelihood score: A (well recognized cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding > 99% (primarily to serum albumin) |
||
| 参考文献 | |||
| 其他信息 |
Troglitazone is a member of chromanes and a thiazolidinone. It has a role as a hypoglycemic agent, an antioxidant, a vasodilator agent, an anticonvulsant, an anticoagulant, a platelet aggregation inhibitor, an antineoplastic agent, an EC 6.2.1.3 (long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase) inhibitor and a ferroptosis inhibitor.
Troglitazone was withdrawn in 2000 due to risk of hepatotoxicity. It was superseded by [pioglitazone] and [rosiglitazone]. Troglitazone was the first thiazolidinedione approved for use in the United States and was licensed for use in type 2 diabetes in 1997, but withdrawn 3 years later because of the frequency of liver injury including acute liver failure associated with its use. Troglitazone is an orally-active thiazolidinedione with antidiabetic and hepatotoxic properties and potential antineoplastic activity. Troglitazone activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-gamma), a ligand-activated transcription factor, thereby inducing cell differentiation and inhibiting cell growth and angiogenesis. This agent also modulates the transcription of insulin-responsive genes, inhibits macrophage and monocyte activation, and stimulates adipocyte differentiation. (NCI04) Troglitazone was withdrawn in 2000 due to risk of hepatotoxicity. It was superseded by pioglitazone and rosiglitazone. A chroman and thiazolidinedione derivative that acts as a PEROXISOME PROLIFERATOR-ACTIVATED RECEPTORS (PPAR) agonist. It was formerly used in the treatment of TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS, but has been withdrawn due to hepatotoxicity. Drug Indication For the treatment of Type II diabetes mellitus. It is used alone or in combination with a sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin as an adjunct to diet and exercise. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Troglitazone is a thiazolidinedione antidiabetic agent that lowers blood glucose by improving target cell response to insulin. It has a unique mechanism of action that is dependent on the presence of insulin for activity. Troglitazone decreases hepatic glucose output and increases insulin dependent glucose disposal in skeletal muscle. Its mechanism of action is thought to involve binding to nuclear receptors (PPAR) that regulate the transcription of a number of insulin responsive genes critical for the control of glucose and lipid metabolism. Troglitazone is a ligand to both PPARα and PPARγ, with a highter affinity for PPARγ. The drug also contains an α-tocopheroyl moiety, potentially giving it vitamin E-like activity. Troglitazone has been shown to reduce inflammation, and is associated with a decrase in nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) and a concomitant increase in its inhibitor (IκB). Unlike sulfonylureas, troglitazone is not an insulin secretagogue. Pharmacodynamics Troglitazone is an oral antihyperglycemic agent which acts primarily by decreasing insulin resistance. Troglitazone is used in the management of type II diabetes (noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) also known as adult-onset diabetes). It improves sensitivity to insulin in muscle and adipose tissue and inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis. Troglitazone is not chemically or functionally related to either the sulfonylureas, the biguanides, or the g-glucosidase inhibitors. Troglitazone may be used concomitantly with a sulfonylurea or insulin to improve glycemic control. |
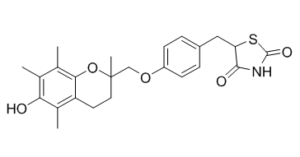
| 分子式 |
C24H27NO5S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
441.54
|
|
| 精确质量 |
441.16
|
|
| CAS号 |
97322-87-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Troglitazone-d4;2749370-85-0
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5591
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
657.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
184-186°C
|
|
| 闪点 |
351.2±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.608
|
|
| LogP |
4.99
|
|
| tPSA |
110.16
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
681
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
GXPHKUHSUJUWKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H27NO5S/c1-13-14(2)21-18(15(3)20(13)26)9-10-24(4,30-21)12-29-17-7-5-16(6-8-17)11-19-22(27)25-23(28)31-19/h5-8,19,26H,9-12H2,1-4H3,(H,25,27,28)
|
|
| 化学名 |
5-[[4-[(6-hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-3,4-dihydrochromen-2-yl)methoxy]phenyl]methyl]-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.66 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (22.65 mM) in 0.5% CMC-Na 0.5% Tween-80 (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2648 mL | 11.3240 mL | 22.6480 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4530 mL | 2.2648 mL | 4.5296 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2265 mL | 1.1324 mL | 2.2648 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|---|
|
|---|