| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
沙奎那韦是一种蛋白酶抑制剂。蛋白酶是将蛋白质分子分解成更小的片段的酶。 HIV蛋白酶对于细胞内病毒复制和受感染细胞释放成熟病毒颗粒至关重要。沙奎那韦与病毒蛋白酶的活性位点结合并阻止病毒多蛋白的裂解,从而防止病毒成熟。沙奎那韦抑制 HIV-1 和 HIV-2 蛋白酶。研究还将沙奎那韦视为一种有前途的抗癌药物。
|
|---|---|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The absolute bioavailability of orally administered saquinavir is only ~4%, thought to be a consequence of incomplete absorption and extensive first-pass metabolism. It is co-administered with ritonavir, another protease inhibitor and a potent inhibitor of the enzymes responsible for saquinavir's first-pass metabolism, in order to dramatically boost its serum concentrations and, by extension, its therapeutic efficacy. Following administration of saquinavir 1000mg twice daily with ritonavir 100mg twice daily the AUC24h at steady-state was 39026 ng.h/mL. The primary means of elimination of saquinavir appears to be extensive hepatic metabolism followed by fecal excretion of both the parent drug and metabolic products. Following the administration of radiolabeled saquinavir (both orally and intravenously), approximately 81-88% of radioactivity is recovered in the feces within 5 days of dosing while only 1-3% is recovered in the urine. Mass balance studies indicate that only 13% of orally-administered plasma radioactivity is attributed to unchanged parent drug, with the remainder comprising metabolic products of saquinavir's hepatic metabolism. In contrast, intravenous administration resulted in approximately 66% of the circulating plasma radioactivity being attributed to unchanged parent drug, suggesting a high degree of first-pass metabolism with oral administration. The steady-state volume of distribution of saquinavir is approximately 700 L, suggesting extensive distribution into tissues. The systemic clearance of saquinavir is approximately 1.14 L/h/kg following intravenous administration. Following administration of saquinavir in a dosage of 1200 mg 3 times daily as liquid-filled capsules, mean steady-state AUC at 3 weeks was 7249 ngh/mL compared with an AUC of 866 ngh/mL reported following administration of saquinavir hard gelatin capsules in a dosage of 600 mg 3 times daily. While the AUC of saquinavir in adults receiving liquid-filled capsules was lower at week 61-69 compared with the AUC at week 3, the AUC at week 61-69 was greater than the AUC at the same time point in HIV-infected adults receiving saquinavir as hard gelatin capsules (600 mg 3 times daily). The relative oral bioavailability of saquinavir from liquid-filled (soft gelatin) capsules is estimated to average 331% (range: 207-530%) of that achieved with hard gelatin capsules of the drug when single 600-mg doses are administered. This would represent a calculated average oral bioavailability from the liquid-filled capsules of about 13% based on an average absolute bioavailability of 4% from the hard capsules; however, these are calculated estimates and not based on actual determination of absolute oral bioavailability from the liquid-filled capsules. Saquinavir and its metabolites are eliminated from the body primarily through the biliary system and feces (more than 95% of the drug), with minimal urinary excretion (less than 3% of administered drug). Oral bioavailability of the hard-gelatin capsule formulation of saquinavir (saquinavir mesylate, invirase) is only 4% due to limited absorption and extensive first-pass metabolism, with considerable interpatient variability. ... Absorption of saquinavir may be enhanced when the drug is taken with a high-calorie, high-fat meal. In addition, saquinavir demonstrates a greater than dose-proportional increase in exposure. For example, tripling the oral dose of saquinavir is associated with an eightfold increase in exposure. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for SAQUINAVIR (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Saquinavir is extensively metabolized in the liver following oral administration, and _in vitro_ studies have shown that >90% of its biotransformation is mediated by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme. Saquinavir is rapidly metabolized to a number of inactive mono- and di-hydroxylated compounds. Results of in vitro studies indicate that saquinavir is rapidly metabolized in the liver to several monohydroxylated and dihydroxylated inactive metabolites. Metabolism of saquinavir is mediated by cytochrome P450; the isoenzyme CYP3A4 is involved in more than 90% of this metabolism. Orally administered saquinavir appears to undergo substantial metabolism on first pass through the liver. Saquinavir is metabolized primarily by hepatic CYP3A4. The metabolites of saquinavir are not active against HIV-1. Saquinavir has known human metabolites that include (2S)-N-[(2S,3R)-4-[(3S,4aS,8aS)-3-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-7-hydroxy-decahydroisoquinolin-2-yl]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]-2-[(quinolin-2-yl)formamido]butanediamide, (2S)-N-[(2S,3R)-4-[(3S,4aS,8aS)-3-[(1-hydroxy-2-methylpropan-2-yl)carbamoyl]-decahydroisoquinolin-2-yl]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]-2-[(quinolin-2-yl)formamido]butanediamide, and (2S)-N-[(2S,3R)-4-[(3S,4aR,8aS)-3-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-6-hydroxy-decahydroisoquinolin-2-yl]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]-2-[(quinolin-2-yl)formamido]butanediamide. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Interactions
Concurrent use of saquinavir with terfenadine has resulted in an increase in the plasma concentrations of terfenadine; competition for the cytochrome p450 enzyme CYP3A by saquinavir may also inhibit the metabolism of astemizole, cisapride, ergot derivatives, midazolam, or triazolam, due to the potential for serious and/or life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias or prolonged sedation, concurrent use of any of these medications with saquinavir mesylate capsules or saquinavir soft gelatin capsules is not recommended. Concurrent administration of saquinavir mesylate capsules with these medications /calcium channel blocking agents, clindamycin, dapsone, or quinidine/ which are substrates of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme of the cytochrome p450 enzyme system, may result in elevated plasma concentrations of these medications; patients should be monitored for toxicities associated with these medications. Ethanol-intake decreases the bioavailability of SQV /saquinavir/ after oral administration alone or with RTV /ritonavir/. Concurrent administration of rifabutin or rifampin with saquinavir mesylate capsules has resulted in a decrease in the steady-state AUC and peak plasma concentration of saquinavir by approximately 80% and 40%, respectively; carbamazepine, dexamethasone, phenobarbital, phenytoin, or other medications that induce CYP3A4 may also reduce saquinavir plasma concentrations; use of alternative medications should be considered if patients are taking either formulation of saquinavir. For more Interactions (Complete) data for SAQUINAVIR (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Saquinavir, in combination with other antiretroviral agents, is indicated in the treatment of HIV infection or AIDS. Saquinavir soft gelatin capsule (Fortovase) is the preferred dosage form, according to the FDA. /Included in US product labeling/ Saquinavir was not detected in cord blood. Saquinavir soft-gel capsules are well tolerated during pregnancy and are not associated in this small study with birth abnormalities. Transmission of HIV infection from mother to child was successfully prevented in all cases. Low maternal exposures of saquinavir were noted. However, these did not appear to affect virologic efficacy of the combination. Samples from cord blood indicate minimal fetal exposure to saquinavir. Drug Warnings The principal adverse effects associated with saquinavir therapy involve the GI tract. In adults with HIV infection receiving saquinavir liquid-filled or hard gelatin capsules in conjunction with other antiretroviral agents (e.g., 2 dideoxynucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors), diarrhea occurred in 15.6-19.9%, abdominal discomfort in 8.6-13.3%, abdominal pain in 2.3-7.8%, nausea in 10.6-17.8%, dyspepsia in 8.4-8.9%, flatulence in 5.7-12.2%, vomiting in 2.9-4.4%, altered taste in 4.4%, and constipation in 3.3% of patients. Adverse GI effects reported in <2% of patients receiving saquinavir hard gelatin or liquid-filled capsules alone or in conjunction with other antiretroviral agents include anorexia, abdominal distention, buccal mucosa ulceration, oral canker sores, cheilitis, dry mouth, dysphagia, abdominal colic, esophageal ulceration, esophagitis, eructation, bloodstained or discolored feces, frequent bowel movements, fecal incontinence, gastralgia, gastritis, GI reflux, GI ulcer, GI inflammation, intestinal obstruction, gingivitis, glossitis, hemorrhoids, infectious diarrhea, melena, painful defecation, parotid disorder, pruritus ani, /SRP: heartburn/, stomach upset, pelvic pain, rectal hemorrhage, salivary gland disorder, stomatitis, unpleasant taste, toothache, and tooth disorder. Headache has occurred in 58.9% of adults with HIV infection receiving saquinavir liquid-filled capsules in conjunction with other antiretroviral agents. Depression has been reported in 2.7%, insomnia in 5.6%, and anxiety or libido disorder in 2.2% of patients receiving saquinavir liquid-filled capsules in conjunction with other antiretroviral therapy. Adverse nervous system effects that have been reported in less than 2% of patients receiving saquinavir hard gelatin or liquid-filled capsules alone or in conjunction with other antiretroviral agents include ataxia, cerebral hemorrhage, confusion, seizures, dizziness, dysarthria, dysesthesia, facial numbness, facial pain, numbness of the extremities, hyperesthesia, hyperreflexia, hyporeflexia, light-headed feeling, myelopolyradiculoneuritis, paresthesia, peripheral neuropathy, prickly sensation, paresis, poliomyelitis, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, spasms, tremor, and unconsciousness. Adverse psychologic effects reported in less than 2% of patients receiving the drug include agitation, amnesia, anxiety, behavior disturbances, excessive dreaming, euphoria, hallucination, irritability, lethargy, overdose effect, psychic disorder, psychosis, reduced intellectual ability, somnolence, and speech disorder. Serious adverse nervous system effects that have been reported rarely in clinical studies in patients receiving saquinavir alone or in conjunction with other antiretroviral agents which were considered to be at least possibly related to the study drugs include attempted suicide, episodes involving confusion, ataxia and weakness, and headache. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for SAQUINAVIR (23 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Saquinavir exerts its antiviral activity by inhibiting an enzyme critical for the HIV-1 viral lifecycle. Like other protease inhibitors, saquinavir has a propensity for participating in drug interactions - use caution when administering saquinavir to patients maintained on other pharmaceutical agents as pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic interactions are common. Saquinavir is known to increase the QTc-interval in otherwise healthy individuals, and should therefore be used with caution in patients maintained on other QTc-prolonging medications or for whom prolongation of the QTc-interval may be of particular consequence (e.g. patients with pre-existing heart disease). Careful and regular monitoring of patient bloodwork is recommended, as saquinavir has been associated with the development of metabolic complications (e.g. diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia) and worsening of pre-existing liver disease. |
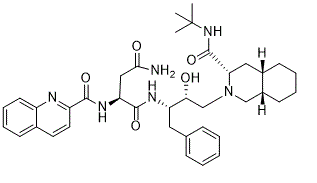
| 分子式 |
C38H50N6O5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
670.85
|
| 精确质量 |
670.384
|
| CAS号 |
127779-20-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Saquinavir mesylate;149845-06-7;Saquinavir-d9;1356355-11-7
|
| PubChem CID |
441243
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
1015ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
91.5ºC
|
| 闪点 |
567.7ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.646
|
| LogP |
6.4
|
| tPSA |
166.75
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
5
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
13
|
| 重原子数目 |
49
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1140
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
6
|
| SMILES |
CC(C)(C)NC(=O)[C@@H]1C[C@@H]2CCCC[C@@H]2CN1C[C@H]([C@H](CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(=O)N)NC(=O)C4=NC5=CC=CC=C5C=C4)O
|
| InChi Key |
QWAXKHKRTORLEM-UGJKXSETSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C38H50N6O5/c1-38(2,3)43-37(49)32-20-26-14-7-8-15-27(26)22-44(32)23-33(45)30(19-24-11-5-4-6-12-24)41-36(48)31(21-34(39)46)42-35(47)29-18-17-25-13-9-10-16-28(25)40-29/h4-6,9-13,16-18,26-27,30-33,45H,7-8,14-15,19-23H2,1-3H3,(H2,39,46)(H,41,48)(H,42,47)(H,43,49)/t26-,27+,30-,31-,32-,33+/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2S)-N-[(2S,3R)-4-[(3S,4aS,8aS)-3-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-3,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydro-1H-isoquinolin-2-yl]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]-2-(quinoline-2-carbonylamino)butanediamide
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~149.07 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.73 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.73 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.73 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.4906 mL | 7.4532 mL | 14.9065 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2981 mL | 1.4906 mL | 2.9813 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1491 mL | 0.7453 mL | 1.4906 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Drug Interactions of Amprenavir and Efavirenz, in Combination With a Second Protease Inhibitor, in HIV-Negative Volunteers
CTID: NCT00005762
Phase: N/A Status: Completed
Date: 2021-11-01