| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following inhalation, salbutamol acts topically on bronchial smooth muscle and the drug is initially undetectable in the blood. After 2 to 3 hours low concentrations are seen, due presumably to the portion of the dose which is swallowed and absorbed in the gut. In particular, the systemic levels of salbutamol are low after inhalation of recommended doses. A trial conducted in 12 healthy male and female subjects using a higher dose (1,080 mcg of albuterol base) showed that mean peak plasma concentrations of approximately 3 ng/mL occurred after dosing when salbutamol was delivered using propellant HFA-134a. The mean time to peak concentrations (Tmax) was delayed after administration of VENTOLIN (salbutamol) HFA (Tmax = 0.42 hours) as compared with CFC-propelled salbutamol inhaler (Tmax = 0.17 hours). After oral administration, 58-78% of the dose is excreted in the urine in 24 hours, approximately 60% as metabolites. A small fraction is excreted in the feces. The volume of distribution recorded for intravenously administered salbutamol has been recorded as 156 +/- 38 L. The renal clearance of salbutamol has been documented as 272 +/- 38 ml/min after oral administration and 291 +/- 70 ml/min after intravenous administration. Furthermore, the renal clearance of the predominant sulfate conjugate metabolite was recorded as 98.5 +/- 23.5 ml/min following oral administration. Elimination: Renal, 69 to 90% (60% as the metabolite). Fecal, 4%. Extended-release tablets: Availability is approximately 80% of that for tablets after a single dose, regardless of whether or not taken with food, but is 100% of that for immediate-release tablets at steady-state. Food decreases the rate of absorption without affecting bioavailability. Rapidly and well absorbed following oral administration. Time to peak concentration: Syrup: within 2 hours. Tablets: 2 to 3 hours. It is not known whether albuterol is distributed into human breast milk Metabolism / Metabolites Salbutamol is not metabolized in the lung but is converted in the liver to the 4'-o-sulphate (salbutamol 4'-O-sulfate) ester, which has negligible pharmacologic activity. It may also be metabolized by oxidative deamination and/or conjugation with glucuronide. Salbutamol is ultimately excreted in the urine as free drug and as the metabolite. Metabolized through sulfate conjugation to its inactive 4'-O-sulfate ester by phenol sulphotransferase (PST). The (R)-enantiomer of albuterol is preferentially metabolized (ten fold) by PST compared to the (S)-enantiomer of albuterol. Hydrolyzed by esterases in tissue and blood to the active compound colterol. The drug is also conjugatively metabolized to salbutamol 4'-O-sulfate. Route of Elimination: Approximately 72% of the inhaled dose is excreted in the urine within 24 hours, 28% as unchanged drug and 44% as metabolite. Half Life: 1.6 hours Biological Half-Life The elimination half-life of inhaled or oral salbutamol has been recorded as being between 2.7 and 5 hours while the apparent terminal plasma half-life of albuterol has been documented as being approximately 4.6 hours. Elimination: 3.8 to 6 hours. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Salbutamol is a beta(2)-adrenergic agonist and thus it stimulates beta(2)-adrenergic receptors. Binding of albuterol to beta(2)-receptors in the lungs results in relaxation of bronchial smooth muscles. It is believed that salbutamol increases cAMP production by activating adenylate cyclase, and the actions of salbutamol are mediated by cAMP. Increased intracellular cyclic AMP increases the activity of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A, which inhibits the phosphorylation of myosin and lowers intracellular calcium concentrations. A lowered intracellular calcium concentration leads to a smooth muscle relaxation and bronchodilation. In addition to bronchodilation, salbutamol inhibits the release of bronchoconstricting agents from mast cells, inhibits microvascular leakage, and enhances mucociliary clearance. Toxicity Data LD50=1100 mg/kg (orally in mice) Interactions Following single-dose IV or oral administration of albuterol to healthy individuals who had received digoxin for 10 days, a 16-22% decrease in serum digoxin concentration was observed. Epinephrin, other orally inhaled sympathomimetic amines: May increase sympathomimetic effects and risk of toxicity. Avoid use together /with albuterol/. MAO inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants: Serious cardiovascular effects and risk of toxicity. Avoid use together /with albuterol/. Propanolol, other beta blockers: May antagonize effects of albuterol. Use together cautiously. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mouse oral > 2 g/kg |
| 参考文献 |
Clin Sci (Lond).1986 Feb;70(2):159-65.
|
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Bronchodilator; tocolytic Albuterol .... /is/ indicated for the symptomatic treatment of bronchial asthma and for treatment of reversible bronchospasm that may occur in association with bronchitis, pulmonary emphysema, and other obstructive airway diseases. /Included in US product labeling/ Albuterol is indicated a a temporary treatment option for hyperkalemia in acute situations in pediatric patients. /NOT included in US product labeling/ /ExpTher/ Orally inhaled albuterol has been used investigationally to prevent or alleviate episodes of muscle paralysis in the treatment of some patients with hyperkalemic familial periodic paralysis. Drug Warnings Tremor appears to be the most frequent reported adverse effect of albuterol, occurring in up to 20% of patients in clinical trials with various dosage forms of the drug. Other frequently reported adverse effects of albuterol include nervousness, nausea, tachycardia, palpitations, chest pain and dizziness. ... Albuterol also has been reported to cause maternal and fetal tachycardia and hyperglycemia (especially in patients with diabetes), as well as maternal hypotension, acute congestive heart failure, pulmonary edema, and death. Albuterol may delay preterm labor. Caution is recommended with use for bronchospasm in pregnant patients because of possible interference with uterine contractility. Pregnancy risk category: C /RISK CANNOT BE RULED OUT. Adequate, well controlled human studies are lacking, and animal studies have shown risk to the fetus or are lacking as well. There is a chance of fetal harm if the drug is given during pregnancy; but the potential benefits may outweigh the potential risk./ For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ALBUTEROL (22 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Salbutamol (INN) or albuterol (USAN), a moderately selective beta(2)-receptor agonist similar in structure to terbutaline, is widely used as a bronchodilator to manage asthma and other chronic obstructive airway diseases. The R-isomer, levalbuterol, is responsible for bronchodilation while the S-isomer increases bronchial reactivity. The R-enantiomer is available and sold in its pure form as levalbuterol and subsequently may produce fewer side-effects with only the R-enantiomer present - although this has not been formally demonstrated. After oral and parenteral administration, stimulation of the beta receptors in the body, both beta-1 and beta-2, occurs because (a) beta-2 selectivity is not absolute, and (b) higher concentrations of salbutamol occur in the regions of these receptors with these modes of administration. This results in the beta-1 effect of cardiac stimulation, though not so much as with isoprenaline, and beta-2 effects of peripheral vasodilatation and hypotension, skeletal muscle tremor, and uterine muscle relaxation. Metabolic effects such as hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia also may occur, although it is not known whether these effects are mediated by beta-1 or beta-2 receptors. The serum potassium levels have a tendency to fall. |
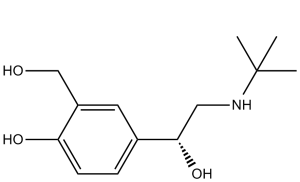
| 分子式 |
C13H21NO3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
239.31
|
| 精确质量 |
239.152
|
| CAS号 |
18559-94-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Salbutamol hemisulfate;51022-70-9;Salbutamol-d3;1219798-60-3;Salbutamol-d9;1173021-73-2;Salbutamol-d9 acetate;1781417-68-2
|
| PubChem CID |
2083
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
433.5±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
157-158ºC
|
| 闪点 |
159.5±17.9 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.566
|
| LogP |
0.01
|
| tPSA |
72.72
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
17
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
227
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
NDAUXUAQIAJITI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
NDAUXUAQIAJITI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| 化学名 |
4-[2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol
|
| 别名 |
Salbutamol Albuterol Proventil Sultanol Aerolin Albuterol Sulfate Proventil Salbutamol Sultanol Ventolin
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~417.87 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (10.45 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (10.45 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (10.45 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.1787 mL | 20.8934 mL | 41.7868 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8357 mL | 4.1787 mL | 8.3574 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4179 mL | 2.0893 mL | 4.1787 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。