| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
ROS (reactive oxygen species)-induced agent
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
RIDR-PI-103是一种新型的活性氧(ROS)诱导的药物释放前药,具有与pan-PI3K抑制剂(PI-103)连接的自环化部分。在高ROS下,PI-103以受控方式释放以抑制PI3K。RIDR-PI-103治疗癌症的疗效和生物利用度尚待探索。在乳腺癌症细胞(MDA-MB-231、MDA-MB-361和MDA-MB-453)、非肿瘤性MCF10A和成纤维细胞上评估RIDR-PI-103的细胞活力。基质凝胶集落形成、细胞增殖和迁移试验检测了RIDR-PI-103和阿霉素治疗后乳腺癌的迁移特性。Western印迹测定了阿霉素±RIDR-PI-103对AKT活化和DNA损伤反应的影响。MDA-MB-453、MDA-MB-231和MDA-MB-361细胞对RIDR-PI-103敏感。阿霉素和RIDR-PI-103联合抑制癌症细胞的生长和增殖。阿霉素联合RIDR-PI-103抑制p-AktS473,上调p-CHK1/2和p-P53。[1]
研究者开发了一种新技术,称为RIDR(ROS-诱导药物释放),它是一种与PI3K抑制剂(PI-103)连接的自我循环试剂,在高度侵袭性乳腺癌中,包括三阴性乳腺癌症细胞系(TNBCs)和其他具有激活PIK3CA突变的ER+、HER2+乳腺癌症细胞系,在氧化应激下以可控方式排出PI-103。我们评估了RIDR-PI-103(5-100µM)或PI-103在正常成纤维细胞、T47D、MCF-7、MDA-MB-361、BT474、MDA-MD-453和MDA-MB-231乳腺癌症细胞系中的疗效。我们注意到,PI-103的IC50为3.34µM,而RIDR-PI-103在正常成纤维细胞中的IC50>100µM,这表明PI-103单独具有毒性,但RIDR-PI103在正常纤维细胞中没有毒性。我们的数据表明,30-40µM的RIDR-PI-103显著抑制T47D、MDA-MB-231、MDA-MB-361和MDA-MB-453细胞增殖,而较高浓度的药物对BT474和MCF-7乳腺癌症细胞系有效。我们的定量PCR数据显示,与这些癌症细胞系中的正常成纤维细胞相比,抗氧化剂过氧化氢酶mRNA水平在统计学上较低,这表明RIDR-PI-103的功效可能与过氧化氢酶表达相关。[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
RIDR-PI-103的药代动力学特性[1]
在这项小鼠的初步PK研究中,RIDR-PI-103(20mg/kg)经腹膜内给药,并在96小时内采集血液样本。选择20mg/kg的浓度是基于RIDR-PIL-103在40%丙二醇和60%注射盐水中的增溶能力。然后使用Phoenix®WinNonlin®v8.2使用隔室和非隔室分析(NCA)分析平均血浆浓度-时间曲线。如图7A、B所示,血浆浓度-时间曲线符合一室模型。表1列出了关键PK参数。如图所示,两种PK分析方法产生了相似的结果。RIDR-PI-103的最大血浆浓度(Cmax)为201.5 ng/mL(0.43µM),在达到1.44 h的最大浓度(Tmax)时达到。RIDR-PIL-103的消除半衰期为9.4 h(表2),与所采用的血液样本时间表一致(长达96 h,大约相当于10个半衰期),有助于完全表征消除曲线。基于这些研究,RIDR-PI-103具有较大的分布体积(Vd),为89 L/kg。 |
| 酶活实验 |
RIDR-PI-103是一种新型的活性氧(ROS)诱导的药物释放前药,具有与pan-PI3K抑制剂(PI-103)连接的自环化部分。在高ROS下,PI-103以受控方式释放以抑制PI3K。RIDR-PI-103治疗癌症的疗效和生物利用度尚待探索。对乳腺癌症细胞(MDA-MB-231、MDA-MB-361和MDA-MB-453)、非肿瘤性MCF10A和成纤维细胞评估RIDR-PI-103的细胞活力。基质凝胶集落形成、细胞增殖和迁移试验检测了RIDR-PI-103和阿霉素治疗后乳腺癌的迁移特性。Western印迹测定了阿霉素±RIDR-PI-103对AKT活化和DNA损伤反应的影响。使用C57BL/6J小鼠的药代动力学(PK)研究确定了RIDR-PI-103的全身暴露量(血浆浓度和曲线下总面积)和T1/2。MDA-MB-453、MDA-MB-231和MDA-MB-361细胞对RIDR-PI-103敏感。阿霉素和RIDR-PI-103联合抑制癌症细胞的生长和增殖。阿霉素联合RIDR-PI-103抑制p-AktS473,上调p-CHK1/2和p-P53。PK研究表明,初始剂量为20mg/kg,T1/2为10小时,在小鼠血浆中可实现约200 ng/mL(0.43µM)的RIDR-PI-103。(4) 前药RIDR-PI-103可能是一种潜在的治疗癌症患者的药物。[1]
磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(PI3K)是由PIK3C亚型基因编码的脂质激酶家族。PI3K将磷脂酰肌醇4,5-二磷酸(PIP2)磷酸化为磷脂酰肌醇3,4,5-三磷酸(PIP3),导致AKT磷酸化以及其他含有PH结构域的蛋白质。AKT磷酸化刺激蛋白质合成和癌症细胞生长。由于编码HER2、PTEN、PIK3CA或AKT1-3的基因异常导致新发和获得性治疗耐药性,在>60%的临床癌症患者中PI3K途径是高活性的。人们对开发靶向PI3K的药物产生了浓厚的兴趣。然而,由于PI3K在基本细胞过程中的生理作用,靶向PI3K活性的药物是有毒的。 阿霉素是一种临床相关的化学疗法,已知可诱导乳腺癌症细胞系中的活性氧(ROS)。我们目前正在评估福尔马林固定石蜡包埋的乳腺肿瘤中ROS的生物标志物水平,这些肿瘤在没有或有化疗的情况下治疗,包括8-羟基-2'-脱氧鸟苷(8-oxo-dG)和4-羟基-2-壬烯醛(4HNE)。我们的数据表明,阿霉素显著地使MDA-MB-453、MDA-MB-361和MDA-MB-231细胞对RIDR-PI-103敏感,联合药物治疗的IC50值明显低于单一药物。阿霉素和RIDR-PI-103在MDA-MB-361和MDA-MB-231细胞中显示出抑制癌症细胞增殖的协同作用。阿霉素在使这些细胞对生长抑制敏感方面比另一种化疗药物多西他赛更有效。因此,这种ROS激活的PI3K抑制剂前药和化疗的新组合为其继续开发和未来针对PI3K驱动肿瘤患者的临床试验提供了强有力的理由。 在其他实验中,我们发现最近FDA批准的CDK4/6抑制剂palbocilib使用细胞活力测定使ER+乳腺癌症细胞系(T47D和MDA-MB-361)对RIDR-PI103敏感。实验正在进行中,以确定这些新型药物组合的作用机制,这些药物组合有可能转化为临床治疗癌症患者。[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[1]
通过4,5-二甲基噻唑-2-基)-2,5-二苯基溴化四唑(MTT)法测定成纤维细胞、MCF10A、MDA-MB-231、MDA-MB-361和MDA-MB-453细胞的生长动力学。简而言之,将2×104个细胞/孔接种在96孔板上,一式三份。用RIDR-PI-103(0-110µM)和PI-103(0-5µM)处理72小时后,用50 mg/mL MTT溶液代替培养基,使用SPECTRAmax PLUS微孔板分光光度计板读数器在570 nm处记录吸光度,并表示为相对于载体(DMSO)对照的三份平均值以及平均值的标准误差(SEM)。在单独的实验中,在RIDR-PI-103(10-30µM)存在或不存在的情况下,使用阿霉素以一系列浓度处理MDA-MB-231、MDA-MB-361和MDA-MB-453细胞。MDA-MB-231细胞用500-5000 nM、MDA-MB-361用50-450 nM和MDA-MB-453用100-4000 nM阿霉素处理72小时。在RIDR-PI-103(10、15或30µM)存在或不存在的情况下,使用多西他赛以一系列浓度处理MDA-MB-231,MDA-MB-361,MDA-MB-453细胞。MDA-MB-231细胞用50-50000pM多西他赛处理。MDA-MB-361细胞用10-90nM的多西他赛处理。MDA-MB-453细胞接受50-10000pM的多西他赛。72小时后分析细胞增殖,并表示为相对于DMSO对照的三倍值的平均值。 细胞增殖试验[1] 将MDA-MB-231、MDA-MB-361和MDA-MB-453细胞以5×104个细胞/孔的密度接种在6孔板中,一式三份。每隔一天分别更换含有125 nM阿霉素或10µM RIDR-PI-103单独或两者组合的完整培养基,并在7-10天内用0.5%结晶紫甲醇溶液对细胞进行染色。使用Odyssey红外系统测量强度。这些值表示为从3个独立实验中获得的强度的平均值。 细胞迁移试验[1] 将MDA-MB-231、MDA-MB-361和MDA-MB-453细胞以5×104个细胞/孔的密度接种在6孔板中,并用载体(DMSO)、125 nM阿霉素和10µM RIDR-PI-103或两者的组合处理8小时。8小时后,计数细胞,将2×104个细胞/孔加入transwell的上室并孵育24-48小时。24-48 h后,用0.5%结晶紫对下腔室中的迁移细胞进行染色,并在相差显微镜下从三个区域捕获图像。使用ImageJ测量从三个独立实验中收集的三个区域的强度,并将其表示为对照的百分比,并用图形表示。 |
| 动物实验 |
Female C57BL/6J mice at 4 weeks were used with n = 3 per time point. Time points for blood collection were based on previous findings regarding the in vitro microsomal metabolic stability of RIDR-PI-103. RIDR-PI-103 was formulated using a mixture of 40% propylene glycol with 60% injectable saline in which RIDR-PI-103 was soluble in solution and not a suspension. The stability of RIDR-PI-103 in this formulation was ascertained by measuring drug content over 7 days. RIDR-PI-103 (dose = 20 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally in all mice at the start of the experiment. Blood collection was done via cardiac puncture under anesthesia at 0, 0.5, 4, 6, 24, 48, 72, 96 h post injection. Plasma was isolated from the blood samples by centrifugation and was stored at −80 °C until further analysis.
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
RIDR-PI-103 is a novel reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced drug release prodrug with a self-cyclizing moiety linked to a pan-PI3K inhibitor (PI-103). Under high ROS, PI-103 is released in a controlled manner to inhibit PI3K. The efficacy and bioavailability of RIDR-PI-103 in breast cancer remains unexplored. Cell viability of RIDR-PI-103 was assessed on breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-361 and MDA-MB-453), non-tumorigenic MCF10A and fibroblasts. Matrigel colony formation, cell proliferation and migration assays examined the migratory properties of breast cancers upon treatment with RIDR-PI-103 and doxorubicin. Western blots determined the effect of doxorubicin ± RIDR-PI-103 on AKT activation and DNA damage response. Pharmacokinetic (PK) studies using C57BL/6J mice determined systemic exposure (plasma concentrations and overall area under the curve) and T1/2 of RIDR-PI-103. MDA-MB-453, MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-361 cells were sensitive to RIDR-PI-103 vs. MCF10A and normal fibroblast. Combination of doxorubicin and RIDR-PI-103 suppressed cancer cell growth and proliferation. Doxorubicin with RIDR-PI-103 inhibited p-AktS473, upregulated p-CHK1/2 and p-P53. PK studies showed that ~200 ng/mL (0.43 µM) RIDR-PI-103 is achievable in mice plasma with an initial dose of 20 mg/kg and a 10 h T1/2. (4) The prodrug RIDR-PI-103 could be a potential therapeutic for treatment of breast cancer patients.[1]
The Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinases (PI3Ks) is a family of lipid kinases encoded by PIK3C isoform genes. PI3K phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3), leading to AKT phosphorylation along with other proteins containing a PH domain. Phosphorylation of AKT stimulates protein synthesis and cancer cell growth. PI3K pathway is hyper-activated in >60% of clinical breast cancer patients due to aberrations in the genes encoding HER2, PTEN, PIK3CA, or AKT1-3 leading to de novo and acquired treatment resistance. There has been intense interest in developing drugs that target PI3K. However, drugs targeting PI3K activity are toxic, due to the physiological roles of PI3Ks in basic cellular processes. We have developed a novel technology, called RIDR (ROS-Induced Drug Release) which is a self-cyclizing reagent linked to a PI3K inhibitor (PI-103) to eject PI-103 in a controlled manner under oxidative stress in highly aggressive breast cancers including triple negative breast cancer cell lines (TNBCs) and other ER+, HER2+ breast cancer cell lines with activating PIK3CA mutations. We evaluated the efficacy of RIDR-PI-103 (5-100 µM) or PI-103 (0-5 µM) in normal fibroblasts, T47D, MCF-7, MDA-MB-361, BT474, MDA-MB-453 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines. We noted that IC50 of PI-103 is 3.34 µM whereas IC50 of RIDR-PI-103 is >100 µM in normal fibroblasts, indicating the toxicity of the PI-103 alone but not the RIDR-PI-103 in normal fibroblasts. Our data indicated that ~30-40 µM RIDR-PI-103 significantly inhibited T47D, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-361 and MDA-MB-453 cell proliferation whereas higher concentrations of the drug were effective in BT474 and MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines. Our quantitative PCR data showed that the antioxidant catalase mRNA levels are statistically lower compared to normal fibroblasts in these cancer cell lines indicating that the efficacy of RIDR-PI-103 could be correlated to catalase expression. Doxorubicin is a clinically relevant chemotherapy known to induce reactive oxygen species (ROS) in breast cancer cell lines. We are currently assessing the levels of biomarkers for ROS in formalin-fixed paraffin embedded breast tumors treated without or with chemotherapy including 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dG) and 4-hydroxy-2-noneal (4HNE). Our data indicated that doxorubicin significantly sensitized MDA-MB-453, MDA-MB-361 and MDA-MB-231 cells to RIDR-PI-103 indicated by significant lower IC50 values of the combined drug treatment versus the single agent. Doxorubicin and RIDR-PI-103 showed a synergistic effect in MDA-MB-361 and MDA-MB-231 cells to inhibit cancer cell proliferation. Doxorubicin was more effective than docetaxel, another chemotherapeutic drug, in sensitizing these cells to growth inhibition. Thus, this novel combination of the ROS-activatable PI3K inhibitor prodrug and chemotherapy provides strong justification for its continued development and future clinical trials for patients stricken with PI3K driven tumors. In other experiments, we show that a recent FDA-approved CDK4/6 inhibitor, palbociclib, sensitized ER+ breast cancer cell lines (T47D and MDA-MB-361) to RIDR-PI103 using cell viability assays. Experiments are ongoing to determine the mechanism of action of these novel drug combinations that could be potentially translated to clinic for treatment of breast cancer patients.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C27H25N7O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
511.531904935837
|
| 精确质量 |
511.196
|
| CAS号 |
2581114-71-6
|
| PubChem CID |
163196423
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as Light yellow to yellow solid at room temperature
|
| LogP |
2.2
|
| tPSA |
155Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
38
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
801
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
MTALGWVUOBSKIC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C27H25N7O4/c28-15-22(35)31-20-14-17(29)6-7-21(20)37-18-4-1-3-16(13-18)25-32-23-19-5-2-8-30-27(19)38-24(23)26(33-25)34-9-11-36-12-10-34/h1-8,13-14H,9-12,15,28-29H2,(H,31,35)
|
| 化学名 |
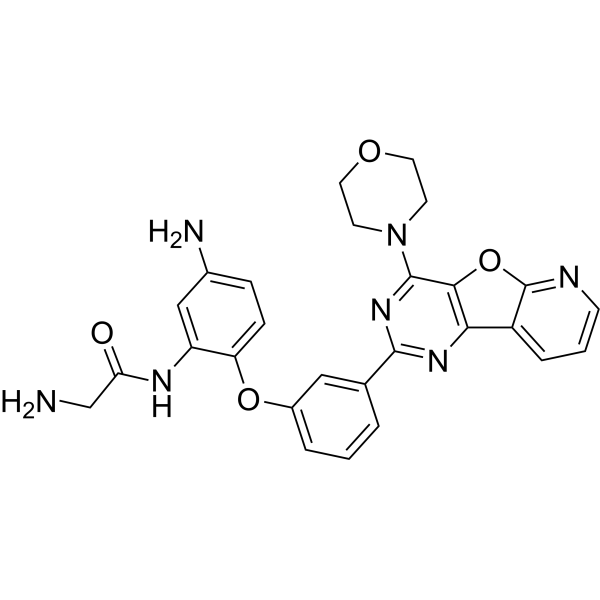
2-amino-N-[5-amino-2-[3-(6-morpholin-4-yl-8-oxa-3,5,10-triazatricyclo[7.4.0.02,7]trideca-1(9),2(7),3,5,10,12-hexaen-4-yl)phenoxy]phenyl]acetamide
|
| 别名 |
RIDR-PI-103; 2581114-71-6
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~195.49 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9549 mL | 9.7746 mL | 19.5492 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3910 mL | 1.9549 mL | 3.9098 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1955 mL | 0.9775 mL | 1.9549 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。