| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
human P2X3 (pIC50 = 8.0); rat P2X3 (pIC50 = 8.0); human P2X2/3 (pIC50 = 7.3)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在表达重组大鼠和人 P2X3 以及人 P2X2/3 通道的细胞系中,AF-353 (Ro-4) 在抑制 α,β-meATP 引起的细胞内钙通量方面表现出强大的效力 [1]。 AF-353 (Ro-4) 的 p50 为 7.3,同样能抑制人 P2X2/3 通道活性,但效力稍差 [1]。
采用放射配体结合、细胞内钙通量和全细胞电压钳电生理学方法测定AF-353对大鼠和人P2X3和人P2X2/3受体的拮抗效力(pIC(50))。 关键结果:这些受体的pIC(50)估计值在7.3至8.5之间,而300倍高的浓度对其他P2X通道或各种受体、酶和转运蛋白几乎没有影响。与A-317491和TNP-ATP相比,竞争结合和细胞内钙通量实验表明,AF-353以非竞争方式抑制ATP的激活。 结论和意义:有利的药代动力学特征与P2X3和P2X2/3受体的拮抗剂效力和选择性的结合表明,AF-353是动物模型中研究这些通道的优秀体内工具化合物,并证明了将分子鉴定和优化为潜在临床候选物的可行性,并最终成为治疗疼痛相关疾病的新型疗法[1]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
AF-353 (Ro-4)(10 mg/kg、20 mg/kg;静脉注射;持续 4-6 小时)可抑制正常和脊髓损伤 (SCI) 大鼠的嘌呤能反应 [2]。它还会缩短正常大鼠的收缩期间隔,但不会缩短 SCI 大鼠的收缩期 [2]。然而,SCI 大鼠中不排尿 (NVC) 的频率显着降低。 AF-353 (Ro-4) 不会损害氧气水平或心脏功能 [2]。
通过在T8-T9处完全横断诱导雌性大鼠脊髓损伤(SCI),并在4周后膀胱过度活动时进行实验。非横断大鼠用作对照(正常大鼠)。记录脊髓背角的神经活动,并通过耻骨上导管获取场电位,以响应膀胱内压力步骤。在对照条件下、用膀胱内ATP(1mm)刺激膀胱粘膜嘌呤能受体后以及静脉注射P2X3/P2X2/3拮抗剂AF-353(10mg/kg和20mg/kg)后记录场电位。在尿烷麻醉的大鼠膀胱内注入生理盐水进行膀胱测量。在基线记录后全身应用AF-353(10mg/kg);大鼠还接受了第二剂AF-353(20mg/kg)。评估排尿(VC)和非排尿(NVC)收缩频率的变化。 结果:SCI大鼠的场电位和NVC频率明显高于NL大鼠。在对照组而非SCI大鼠中,膀胱内ATP增加了场电位频率,而全身AF-353显著降低了两组的这一参数。AF-353也减少了对照组大鼠的收缩间期,但在SCI大鼠中没有;然而,SCI大鼠的NVC频率显著降低。 结论:膀胱传入神经上的P2X3/P2X2/3受体正向调节过度活动膀胱的感觉活动和NVCs[2]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
药理学选择性[1]
通过测量AF-353对表达重组P2X通道的细胞系中激动剂诱发的细胞内钙通量的拮抗效力,确定了AF-353对P2X3和P2X2/3通道的选择性优于其他同源P2X通道(见上文)。此外,在两个广泛的商业选择性小组中检查了AF-353,一个涵盖75个受体、通道、酶和转运蛋白,另一个涵盖100多种激酶(Ambit)。 放射性配体结合[1] 使用四环素非表达载体(Lachnit等人,2000)或表达hP2X3或hP2X2/3的1321N1人星形细胞瘤细胞,在来自表达大鼠P2X3(CHO-rP2X3)离子通道的中国仓鼠卵巢细胞(CHO)的膜中进行了放射性配体结合实验。在1X Versene中收获细胞,用Polytron在冰冷的50 mM Tris pH 7.4中用1X Complete™蛋白酶抑制剂混合物均质化。通过两步离心分离质膜。均质化膜在4°C下以1000×g离心15分钟。丢弃1000×g颗粒,将上清液在4°C下以43000×g离心30分钟。丢弃43000×g上清液,将沉淀物储存在-70°C下,直至进行分析。氚标记的AF-353(81.2 Ci·mmol−1)由罗氏放射化学部门合成;HPLC证实纯度>97%。在50mM Tris pH 7.4的平衡结合条件下测定P2X3和P2X2/3膜上的配体亲和力。[3H]-AF-353(同聚体离子通道为1.7–140 nM,异聚体离子信道为1.3–660 nM)与膜(200–350µg·mL-1)在不存在或存在10µM未标记的AF-353>类似物AF-010(用于定义非特异性结合)的情况下在22°C下孵育2–5小时,以确定其平衡解离亲和力常数(Kd)以及膜的受体表达水平(Bmax)。对于未标记分子,通过将未标记分子(连续稀释超过百万倍浓度范围)与[3H]AF-353(1-5nM)和CHO-rP2X3膜共孵育来确定解离亲和力常数(KB)。在所有情况下,通过在GF/B过滤器上用冰冷的50 mM Tris(pH 7.4)过滤来结束孵育。在使用Perkin-Elmer TopCount平板读数器定量过滤器捕获的放射性之前,将过滤器浸泡在MicroScint-20闪烁混合物中至少3小时。使用四参数双曲函数通过非线性回归分析竞争结合数据,以估计曲线最大值、曲线最小值、希尔斜率和IC50;使用Cheng-Prusoff方程根据观察到的IC50值计算KB估计值(Cheng和Prusoff,1973)。亲和力表示为在两到四个重复实验中确定的平均值和标准偏差。 [3H]AF-353和其他未标记的测试配体之间结合模式的竞争评估是基于Cheng-Prusoff关系的预期,该关系描述了两个配体以互斥的方式结合(Cheng和Prusoff,1973)。这种关系由方程内联图描述,其中[A*]表示放射性配体浓度,Kd表示A*的平衡解离常数,KB表示未标记的测试化合物的平衡解离常量,IC50是置换A*结合50%的测试化合物浓度。在上述条件下,通过在没有或存在竞争剂的情况下将CHO-rP2X3膜与[3H]-AF-353一起孵育,进行了放射性配体结合研究。对于这项分析,在5-8个不同的放射性配体浓度范围内([3H]-AF-353 0.1-60 nM),确定了每种未标记的测试化合物的IC50值。观察到的IC50值以IC50/KB与[a*]/Kd的比率绘制,用于所有测试浓度的放射性配体(a*)。根据Cheng-Prusoff方程,未标记配体和[3H]AF-353之间的竞争相互作用将绘制为斜率为1、Y轴截距为1的直线。 |
| 细胞实验 |
全细胞电压钳电生理学[1]
在这些实验中,我们采用了标准的千兆密封膜片钳技术来研究P2X2/3通道。膜片钳装置由以下部件组成:防振台、显微镜、显微操作器、膜片钳放大器、数字化仪、药物灌注系统和采集软件。 对于记录,浴溶液由(以mM计)155 NaCl、5 KCl、2 CaCl2、1 MgCl2、10 d-葡萄糖、10 HEPES组成,pH 7.4,含NaOH,310 mOsM,移液管细胞内溶液由(以mM计)130 CsF、10 NaCl、10 EGTA、1 MgCl2、10 HEPES组成,pH 7.2,含CsOH,290mOsM。用Sutter Instruments P-87移液管拉拔器拉拔标准壁硼硅酸盐玻璃电极(外径1.50 mm,内径0.87 mm,带细丝)。所用电极的平均电阻为3.5MOhm。为了激活P2X2/3异聚体通道,使用10µMα,β-meATP溶液(用NaOH调节pH值)。该值大约是实验条件下信道的EC50。以约30秒的规则间隔激活通道2秒。当来自通道的电流在至少三次激动剂应用中保持一致时(约90秒),加入测试化合物。监测化合物引起的堵塞,直至达到平衡,然后洗掉化合物以确定失速动力学。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Female SD (SD (Sprague-Dawley)) rats with SCI (250-300 g) [2]
Doses: 10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg Route of Administration: intravenous (iv) (iv)injection; intravenous (iv) (iv)injection; intravenous (iv) (iv)injection. 90 minutes apart, lasting 4 hrs (hrs (hours)) to 6 hrs (hrs (hours)) Experimental Results: Purinergic responses were Dramatically diminished in both normal and SCI rats. STIMULATION PROTOCOLS [2] Spinal cord field potentials were evaluated during intravesical pressure steps from 0 to 60 cmH2O. For stimulation of intravesical purinergic receptors each experiment was divided into three sections. First, bladders were infused with saline solution; second, bladders were filled with a saline solution containing 1 mm ATP; third, bladders were filled with 1 mm ATP during two (10 or 20 mg/kg) consecutive i.v. injections of AF-353 (i.e. 5-[5-iodo-4-methoxy-2-(1-methylethyl)phenoxy]-2,4-pyrimidinediamine hydrochloride, RO-4 hydrochloride). In each case, bladder pressure stimulation was maintained for 1 min followed by 3 min of recovery without pressure. This procedure was repeated twice. The total time of the experiment varied from 4 to 6 h and the interval between AF-353 applications was set at 90 min. SURGICAL PREPARATION FOR CYSTOMETRY [2] Control or SCI rats were anaesthetised with 1.0 g/kg urethane (s.c.). A suprapubic catheter was placed through the bladder dome and another catheter was inserted into the jugular vein for drug delivery. CYSTOMETRIC EVALUATION [2] The bladder catheter was connected to a syringe pump and saline solution was infused at 0.12 mL/min for 2 h, while the bladder contractions were measured with a pressure transducer (World Precision Instruments) connected to a data acquisition system. Bladder contractions were designated as voiding (VC) or non-voiding (NVC) contractions depending on whether saline was expelled during a bladder contraction. After baseline recordings, AF-353 was administered at a dose of 10 mg/kg, and 2 h later rats received a second application of 20 mg/kg. The frequency of the contractions was calculated during the last 60 min of each condition using the WINDAQ playback program Blood collection [1] Blood was collected at pre-determined time points, using lithium heparin as anticoagulant from the jugular vein. After centrifugation at 3000×g for 5 min, plasma was obtained and stored at −80°C until analysis. [1] Plasma protein binding [1] Heparinized rat plasma was obtained from Pel-Freez® Biologicals and stored at −80°C until use. Centrifree Micropartition Devices were used to separate unbound from protein-bound material. AF-353 was added to heparinized ultrafiltered plasma (n = 3) to yield a final concentration between 200 and 5000 ng·mL−1. One millilitre of the plasma solutions and 0.3 mL of the ultrafiltrate solution were added to the filtration device and centrifuged (fixed angle) for 20 min at 2000×g. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
To assess the utility of AF-353 as a tool to investigate antagonism of P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors in vivo, rats were dosed with 2 mg·kg−1 of AF-353 i.v. and orally as a suspension. The relevant pharmacokinetic parameters that were determined are shown in Table 3. AF-353 is orally bioavailable (F = 32.9%) with a Tmax of ∼30 min and plasma half-life of 1.63 h. CNS penetration was determined by measuring the brain to plasma ratio (B/P); AF-353 is highly CNS penetrant, with a B/P ratio of 6 (total brain extracted concentration/total plasma concentration). In addition; the in vitro protein binding was determined to be 98.2% in rat plasma. [1]
Favourable pharmacokinetic parameters were observed in rat, with good oral bioavailability (%F = 32.9), reasonable half-life (t(1/2) = 1.63 h) and plasma-free fraction (98.2% protein bound). |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Background and purpose: Purinoceptors containing the P2X3 subunit (P2X3 homotrimeric and P2X2/3 heterotrimeric) are members of the P2X family of ion channels gated by ATP and may participate in primary afferent sensitization in a variety of pain-related diseases. The current work describes the in vitro pharmacological characteristics of AF-353, a novel, orally bioavailable, highly potent and selective P2X3/P2X2/3 receptor antagonist.
Experimental approach: The antagonistic potencies (pIC(50)) of AF-353 for rat and human P2X3 and human P2X2/3 receptors were determined using methods of radioligand binding, intracellular calcium flux and whole cell voltage-clamp electrophysiology.
Key results: The pIC(50) estimates for these receptors ranged from 7.3 to 8.5, while concentrations 300-fold higher had little or no effect on other P2X channels or on an assortment of receptors, enzymes and transporter proteins. In contrast to A-317491 and TNP-ATP, competition binding and intracellular calcium flux experiments suggested that AF-353 inhibits activation by ATP in a non-competitive fashion. Favourable pharmacokinetic parameters were observed in rat, with good oral bioavailability (%F = 32.9), reasonable half-life (t(1/2) = 1.63 h) and plasma-free fraction (98.2% protein bound).
Conclusions and implications: The combination of a favourable pharmacokinetic profile with the antagonist potency and selectivity for P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors suggests that AF-353 is an excellent in vivo tool compound for study of these channels in animal models and demonstrates the feasibility of identifying and optimizing molecules into potential clinical candidates, and, ultimately, into a novel class of therapeutics for the treatment of pain-related disorders.[1]
We used in vivo electrophysiological and cystometric methods to evaluate the effect of the selective P2X3/P2X2/3 antagonist AF-353 on bladder sensory pathways in normal and SCI rats. The present results showed: (i) basal spinal neural activity was amplified in SCI rats compared with normal rats; (ii) in contrast to normal rats, spinal neural activity in SCI rats in response to noxious pressure was not augmented by activation of purinergic receptors with intravesical ATP; (iii) spinal neural activity in response to chemical (ATP) and noxious pressure stimulation was significantly reduced in normal and SCI rats by systemic application of the selective P2X3/P2X2/3 antagonist AF-353; and (iv) in agreement with the electrophysiological results, reflex bladder contractions were markedly decreased in both normal and SCI rats by AF-353. [2] |
| 分子式 |
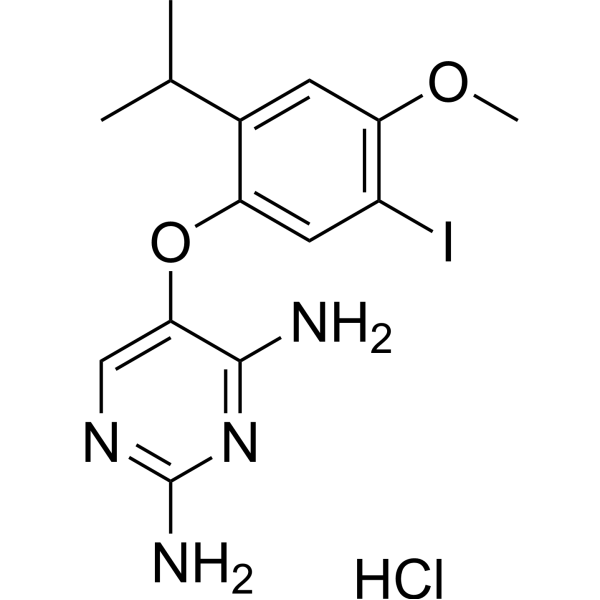
C14H18CLIN4O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
436.68
|
| CAS号 |
927887-18-1
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solids at room temperature
|
| SMILES |
C1(N)=NC=C(OC2=CC(I)=C(OC)C=C2C(C)C)C(N)=N1.[H]Cl
|
| 别名 |
Ro-4 hydrochloride; AF-353 hydrochloride; 927887-18-1; 5-(5-Iodo-2-isopropyl-4-methoxyphenoxy)pyrimidine-2,4-diamine hydrochloride; 5-(5-iodo-4-methoxy-2-propan-2-ylphenoxy)pyrimidine-2,4-diamine;hydrochloride; Ro 4 hydrochloride; AF-353 (hydrochloride); SCHEMBL2482416; QRBBKDZPXABQPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2900 mL | 11.4500 mL | 22.9001 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4580 mL | 2.2900 mL | 4.5800 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2290 mL | 1.1450 mL | 2.2900 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。