| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Contaminant
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
近年来,渤海及其周边河流中的全氟和多氟烷基物质(PFAS)污染引起了相当大的关注。然而,关于PFAS在多种环境介质中的分布及其在悬浮颗粒和溶解相之间的分布,很少有研究进行。在这项研究中,在渤海收集了地表水、地表沉积物和空气样本,以调查39种目标PFAS的浓度和分布。此外,还收集了35个河口的河水样本,以估算PFAS向渤海的排放通量。结果表明,渤海水体和表层沉积物中的总离子化合物(∑i-PFASs)浓度分别为19.3至967 ng/L(平均125±152 ng/L)和0.70-4.13 ng/g dw(1.78±0.76 ng/g)。在河口,∑i-PFAS浓度范围为10.5至13500 ng/L(882±2410 ng/L)。在空气中,∑PFAS(∑i-PFAS+∑n-PFASs)的浓度范围为199至678 pg/m3(462±166 pg/m3)。全氟辛酸(PFOA)是海水、沉积物和河水中的主要化合物;在空气中,8:2氟调聚物醇占主导地位。小清河向渤海排放的∑i-PFAS通量最大,估计为12100 kg/y。一些替代品,即6:2氟调聚物磺酸(6:2 FTSA)、六氟环氧丙烷二聚酸(HFPO-DA)和氯化6:2多氟醚磺酸(Cl-6:2 PFESA),在一些采样点的浓度高于或相当于C8传统PFAS。海水中颗粒物的分布系数高于河水。使用高分辨率质谱法,在3个河水和3个海水样本中发现了29个非目标新兴PFAS。应进行进一步的研究,以澄清渤海地区这些新兴PFAS的来源和生态毒理学影响。[1]
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
2013年至2020年,在挪威的一个城市地区,对大量来自红狐和褐鼠的土壤、蚯蚓、鸟蛋和肝脏的陆地样本中的全氟和多氟烷基物质(PFAS)进行了分析。全氟辛烷磺酸和长链全氟氯化碳是所有样本中最主要的化合物,证明了它们的普遍分布。其他研究较少的化合物,如6:2 FTS,首先在蚯蚓中检测到。8:2 FTS在许多野禽卵、雀鹰卵和蚯蚓样本中发现,这些卵的浓度最高。在目前和以前的工业区检测到6:2 FTS和8:2 FTS的最高浓度。在该物种的许多样本中检测到FOSA,红狐肝和棕色大鼠肝中的浓度最高,分别为3.3和5.5纳克/克湿重。城市地区的PFAS浓度明显高于背景地区,表明其中一些物种可以作为城市环境中PFAS排放的标志。在已知或已经受到工业影响的地区,Fieldfare鸡蛋的全氟辛烷磺酸和全氟氯化碳浓度高得惊人。生物群落土壤累积因子和放大计算表明了几种PFAS的累积和放大潜力。蚯蚓和田鼠卵在鸟类野生动物和捕食者的饮食中的平均浓度高于加拿大和欧洲的阈值。对于蚯蚓,18%的样本超过了捕食者猎物中全氟辛烷磺酸的欧洲阈值(33纳克/克湿重),对于野鼠卵,35%的样本高于相同的阈值。所有土壤样本均未超过土壤生物全氟辛烷磺酸拟议PNEC 373纳克/克干重。[2] |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Emerging and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment, and air of the Bohai Sea and its surrounding rivers. Environ Pollut. 2020 Aug;263(Pt A):114391.
[2]. New insights from an eight-year study on per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in an urban terrestrial ecosystem. Environ Pollut . 2024 Apr 15:347:123735. |
| 其他信息 |
The contamination of surface waters in China with Per- and polyfluoroalkyl (PFASs) has been extensively studied in recent decades, however, almost all studies have been conducted in small areas and/or limited samples, which are not representative of the nationwide contamination of surface water environments with PFASs. In this study, attempt was made to provide a comprehensive report about PFASs pollution in Chinese surface water based on the PRISMA. By analyzing 111 papers published between 2006 and 2022, we provide a systematic review of the pollution of PFASs in surface water environments in China. The results show that 26 PFASs contaminants were detected at least once in China's surface water environment and were mainly concentrated in the eastern part of China. Most surface water environments in China had mean PFASs concentrations below 100 ng/L. The most polluted place was the Xiaoqing River, where sampling results in 2020 showed PFASs concentrations as high as 25,429 ng/L, followed by the Tangxun Lake, the Xi River, the Daling River, the Majia River, the Baiyangdian Lake, the Liuxi River, the Jiaolai River, the Tuo River and the Zhimai River. The Xiaoqing River also has the highest concentration of the novel pollutant, with concentrations of HFPO-TA and HFPO-DA as high as 1039 ng/L and 164 ng/L. Based on the source analysis, fluoropolymer manufacturing plants are the main source of PFASs pollutants in surface water. The results of the base risk analysis using risk quotients value (RQ) method show that the RQ values of the Xiaoqing River, the surface water near Bohai Bay, the Majia River and the Tuo River PFOA are 36.9, 7.7, 3.6 and 2.1 respectively, which are high risk areas and require enhanced control. This study provides information on surface waters contaminated by PFASs nationwide, and the results can be used as a reference for the development of pollution control and management strategies for PFASs in surface waters in China.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023 Jun 23:262:115178.
|
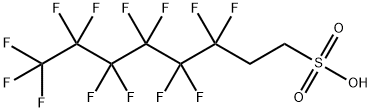
| 分子式 |
C8H5O3F13S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
428.1677
|
| 精确质量 |
427.97518
|
| CAS号 |
27619-97-2
|
| PubChem CID |
119688
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solids at room temperature
|
| LogP |
3.9
|
| tPSA |
62.8Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
16
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
0
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
585
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C(CS(=O)(=O)O)C(C(C(C(C(C(F)(F)F)(F)F)(F)F)(F)F)(F)F)(F)F
|
| InChi Key |
VIONGDJUYAYOPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C8H5F13O3S/c9-3(10,1-2-25(22,23)24)4(11,12)5(13,14)6(15,16)7(17,18)8(19,20)21/h1-2H2,(H,22,23,24)
|
| 化学名 |
3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,8-tridecafluorooctane-1-sulfonic acid
|
| 别名 |
1-Octanesulfonic acid, 3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,8-tridecafluoro-; 6:2 FTSA; 27619-97-2; 1h,1h,2h,2h-perfluorooctanesulfonic acid; 3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,8-tridecafluorooctane-1-sulfonic acid; 6:2 Fluorotelomer sulfonic acid; THPFOS; 6:2 FTS;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3355 mL | 11.6776 mL | 23.3552 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4671 mL | 2.3355 mL | 4.6710 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2336 mL | 1.1678 mL | 2.3355 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。