| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
P2Y12 Receptor; CYP2B6 (IC50 = 18.2 nM); CYP2C19 (IC50 = 524 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
基因微阵列分析鉴定出79个基因在用或不用氯吡格雷处理细胞时差异表达(P<0.05,倍数变化>3)。基因本体分析显示,对应激的反应和细胞凋亡功能障碍是受影响的前10个细胞事件,当细胞用氯吡格雷处理时,内质网应激介导的凋亡途径的主要成分CHOP和TRIB3以浓度和时间依赖的方式上调。通路分析表明,在氯吡格雷处理的GES-1细胞中,多种MAPK激酶被磷酸化,但只有SB-203580(一种p38特异性MAPK抑制剂)减弱了细胞凋亡和CHOP过表达,这两者都是由氯吡格雷诱导的。结论:在氯吡格雷诱导的胃黏膜损伤中,内质网应激反应的增强与p38 MAPK的激活有关。[3]
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
与给予媒介物的糖尿病小鼠相比,在前三个月内给予氯吡格雷显着降低了纤连蛋白、胶原蛋白和血糖的表达。氯吡格雷可显着改善高血糖引起的肾纤维化[1]。与阿司匹林单药治疗相比,氯吡格雷和阿司匹林联合治疗(双联抗血小板治疗)已被证明具有显着优势。它还被证明可以降低 ACS 和亚急性支架血栓形成后的复发性缺血事件[2]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
氯吡格雷是一种强效的抗血栓药物,可抑制ADP诱导的血小板聚集。大型临床试验的结果表明,在有症状性动脉粥样硬化病史的患者中,氯吡格雷在预防血管缺血性事件(心肌梗死、中风、血管死亡)方面优于阿司匹林。氯吡格雷的抗聚集作用归因于ADP与血小板表面嘌呤能受体结合的不可逆抑制。氯吡格雷在体外没有活性,可以被认为是肝脏中形成的活性代谢产物的前体。最近描述了这种活性代谢物的化学结构及其生物活性。血小板上已经描述了几种嘌呤能受体;已发现钙通道P2X(1)和Gq偶联的七跨膜结构域受体P2Y1不会被氯吡格雷拮抗。另一种Gi(2)偶联受体(命名为P2Y12)最近被克隆并在CHO细胞中稳定表达。这些细胞对ADP的稳定类似物(33)P-2MeS-ADP表现出很强的亲和力,其结合特征在所有点上都与血小板上观察到的特征相对应。氯吡格雷的活性代谢产物强烈抑制了(33)P-2MeS-ADP与这些细胞的结合,其效力与该化合物在血小板上观察到的效力一致。在这些转染的CHO细胞中,与血小板一样,ADP和2MeS ADP诱导腺苷酸环化酶下调,这种作用被氯吡格雷的活性代谢产物抑制。这些结果表明,该受体对应于之前称为“P2t”的血小板受体,并表明氯吡格雷的活性代谢产物以共价方式与该受体结合,从而解释了它如何阻断ADP对血小板的聚集作用[4]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
以GES-1细胞为模型系统,通过人类基因表达微阵列和基因本体分析评估氯吡格雷对整个基因表达谱的影响,通过实时PCR和Western blot分析确定mRNA和蛋白质表达的变化,分别通过MTT法和流式细胞仪分析测量细胞存活率和凋亡率。[3]
|
| 动物实验 |
New Zealand white rabbits (1.9-2.7 kg) were treated orally with vehicle or clopidogrel (3 or 10 mg/kg) for three days. On the fourth day, the rabbits were anesthetized for blood collection and then euthanized. The brain was collected, and the middle cerebral arteries were isolated. We used light transmission aggregometry and pressure myography to elucidate the mechanisms of the off-target effects associated with clopidogrel treatment. We confirmed that inhibition of P2Y12 activation by clopidogrel inhibited ADP-induced platelet aggregation but had no impact on P2Y12-independent arachidonic acid- or collagen-induced platelet aggregation. Analysis of middle cerebral arteries from clopidogrel treated rabbits showed that clopidogrel did not affect P2Y4, P2Y6, and P2Y14 receptor-mediated contraction but attenuated the contractile response after P2Y2 receptor activation. Further analysis determined P2Y2-mediated constriction was endothelium-dependent. Vasoconstriction is a primary component of hemostasis, and impaired vasoconstriction can prolong bleeding. These results suggest clopidogrel inhibits the endothelial P2Y2 receptor in the middle cerebral artery, which provides a mechanistic explanation for the adverse cerebral bleeding associated with the drug.[5]
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
A 75mg oral dose of clopidogrel is 50% absorbed from the intestine. Clopidogrel can be taken with or without food. A meal decreases the AUC of the active metabolite by 57%. The active metabolite of clopidogrel reaches a maximum concentration after 30-60 minutes. Clopidogrel reached a Cmax of 2.04±2.0ng/mL in 1.40±1.07h. The AUC for a 300mg oral dose of clopidogrel was 45.1±16.2ng\*h/mL for poor metabolizers, 65.6±19.1ng\*h/mL for intermediate metabolizers, and 104.3±57.3ng\*h/mL for extensive metabolizers. The Cmax was 31.3±13ng/mL for poor metabolizers, 43.9±14ng/mL for intermediate metabolizers, and 60.8±34.3ng/mL for extensive metabolizers. An oral dose of radiolabelled clopidogrel is excreted 50% in the urine and 46% in the feces over 5 days. The remainder of clopidogrel is irreversibly bound to platelets for their lifetime, or approximately 8-11 days. The apparent volume of distribution of clopidogrel is 39,240±33,520L. The clearance of a 75mg oral dose was 18,960±15,890L/h and for a 300mg oral dose was 16,980±10,410L/h. Protein binding: Very high, for clopidogrel and its main circulating metabolite (98% and 94%, respectively). Binding is nonsaturable in vitro up to a concentration of 100 ug/mL. After single and repeated oral doses of 75 mg per day, clopidogrel is rapidly absorbed. Absorption is at least 50%, based on urinary excretion of clopidogrel metabolites. Time to peak effect: Steady state inhibition of platelet aggregation with repeated doses of 75 mg/day usually occurs between day 3 and day 7. Peak plasma concentration: Approximately 3 mg/L (carboxylic acid derivative) after repeated doses of 75 mg. Pharmacokinetics of the main circulating metabolite are linear (increased in proportion to dose) in a dose range of 50 to 150 mg. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CLOPIDOGREL (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites 85-90% of an oral dose undergoes first pass metabolism by carboxylesterase 1 in the liver to an inactive carboxylic acid metabolite. about 2% of clopidogrel is oxidized to 2-oxoclopidogrel. This conversion is 35.8% by CYP1A2, 19.4% by CYP2B6, and 44.9% by CYP2C19 though other studies suggest CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and CYP2C9 also contribute. 2-oxoclopidogrel is further metabolized to the active metabolite. This conversion is 32.9% by CYP2B6, 6.79% by CYP2C9, 20.6% by CYP2C19, and 39.8% by CYP3A4. CYP2C19 is involved in the formation of both the active metabolite and the 2-oxo-clopidogrel intermediate metabolite. Clopidogrel active metabolite pharmacokinetics and antiplatelet effects, as measured by ex vivo platelet aggregation assays, differ according to CYP2C19 genotype. Genetic variants of other CYP450 enzymes may also affect the formation of clopidogrel's active metabolite. Clopidogrel is extensively metabolized by two main metabolic pathways: one mediated by esterases and leading to hydrolysis into an inactive carboxylic acid derivative (85% of circulating metabolites) and one mediated by multiple cytochrome P450 enzymes. Cytochromes first oxidize clopidogrel to a 2-oxo-clopidogrel intermediate metabolite. Subsequent metabolism of the 2-oxo-clopidogrel intermediate metabolite results in formation of the active metabolite, a thiol derivative of clopidogrel. This metabolic pathway is mediated by CYP2C19, CYP3A, CYP2B6 and CYP1A2. The active thiol metabolite binds rapidly and irreversibly to platelet receptors, thus inhibiting platelet aggregation for the lifespan of the platelet. Biological Half-Life That half life of clopidogrel is approximately 6 hours following a 75mg oral dose while the half life of the active metabolite is approximately 30 minutes. After a single, oral dose of 75 mg, clopidogrel has a half-life of approximately 6 hours. The half-life of the active metabolite is about 30 minutes. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Clopidogrel is associated with serum enzyme elevations in 1% to 3% of patients during therapy. In several large clinical trials, elevations of serum ALT were no more frequent with clopidogrel as with placebo (or in comparator arms) and no instances of clinically apparent liver injury were reported. Since marketing and release, however, there have been more than a dozen published case reports of clinically apparent liver injury attributed to clopidogrel. The onset of symptoms was within 2 to 24 weeks (averaging 6 weeks) of starting, with fatigue and jaundice. Several patients had an accompanying fever but rash and eosinophilia were not common. The usual pattern of liver enzyme elevations was hepatocellular, but cases with mixed or cholestatic enzyme elevations have also been described (Case 1). Autoantibodies were rarely present. Most cases were self-limited with recovery within 1 to 2 months, but rare cases of acute liver failure or hepatic decompensation with death or need for liver transplantation have been described. Likelihood score: B (highly likely but rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No published information is available on the use of clopidogrel during breastfeeding. The manufacturer reports that no adverse effects have been observed in breastfed infants with maternal clopidogrel use during lactation in a small number of postmarketing cases. Since no published information is available on the use of clopidogrel during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. If it is used by a nursing mother, monitor the infant for bruising and bleeding. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◈ What is clopidogrel? Clopidogrel is an antiplatelet medication that helps prevent blood clots. It has been used to help prevent heart attacks and strokes. A brand name for clopidogrel is Plavix®.Sometimes when people find out they are pregnant, they think about changing how they take their medication, or stopping their medication altogether. However, it is important to talk with your healthcare providers before making any changes to how you take your medication. Your healthcare providers can talk with you about the benefits of treating your condition and the risks of untreated illness during pregnancy. ◈ I take clopidogrel. Can it make it harder for me to get pregnant? Studies have not been done in humans to see if clopidogrel can make it harder to get pregnant. In animal studies, clopidogrel did not affect fertility (ability to get pregnant). ◈ Does taking clopidogrel increase the chance of miscarriage? Miscarriage is common and can occur in any pregnancy for many different reasons. Studies have not been done in humans to see if clopidogrel increases the chance of miscarriage. In animal studies, there was no reported increase in miscarriages. ◈ Does taking clopidogrel increase the chance of birth defects? Every pregnancy starts out with a 3-5% chance of having a birth defect. This is called the background risk. Information on the use of clopidogrel in pregnancy is limited. In animal studies, clopidogrel did not increase the chance of birth defects. In 17 case reports of people taking clopidogrel during pregnancy, no birth defects were reported in 16 of the babies. A heart defect was reported in 1 baby. A single case report is not enough information to link an exposure to a birth defect. Also, in all of these reports, other medications were also taken during pregnancy. This makes it hard to know if clopidogrel, the combination of medications, or other factors are related to the reported heart defect. ◈ Does taking clopidogrel in pregnancy increase the chance of other pregnancy-related problems? Studies have not been done to see if clopidogrel increases the chance for pregnancy-related problems such as preterm delivery (birth before week 37) or low birth weight (weighing less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces [2500 grams] at birth).Taking clopidogrel during labor or delivery may increase the chance of bleeding and hemorrhaging (too much blood loss) in the person giving birth. There is also an increased chance of spinal hematoma (when blood collects in the spine) when people who take clopidogrel get an epidural (injection of medication into the space around your spinal nerves to provide pain relief (analgesia) or numbness in one area of the body). The product label and professional medical societies, including the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine and the American Academy of Pain Medicine, have recommended that anyone taking clopidogrel stop taking it 5-7 days before labor, delivery, or getting an epidural. ◈ Does taking clopidogrel in pregnancy affect future behavior or learning for the child? Studies have not been done to see if clopidogrel can cause behavior or learning issues for the child. ◈ Breastfeeding while taking clopidogrel: There are no published studies on the use of clopidogrel during breastfeeding. No side effects have been reported in a small number of infants exposed to clopidogrel through breast milk. If you suspect the baby has any symptoms (such as bruising or bleeding), contact the child’s healthcare provider.There is a theoretical concern (not proven) that if a baby is exposed to clopidogrel through breast milk, the baby’s platelets may not work correctly. This has not been reported in the reports on infants exposed to clopidogrel through breastmilk. ◈ If a male takes clopidogrel, could it affect fertility or increase the chance of birth defects? Studies have not been done in humans to see if clopidogrel could affect male fertility (ability to get partner pregnant) or increase the chance of birth defects above the background risk. In animal studies, there were no reported effects on fertility. In general, exposures that fathers or sperm donors have are unlikely to increase risks to a pregnancy. For more information, please see the MotherToBaby fact sheet Paternal Exposures at https://mothertobaby.org/fact-sheets/paternal-exposures-pregnancy/. Protein Binding Both the active and inactive metabolites of clopidogrel are 98% protein bound in plasma. Studies in cows show clopidogrel 71-85.5% bound to serum albumin. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Clopidogrel Reduces Fibronectin Accumulation and Improves Diabetes-Induced Renal Fibrosis. Int J Biol Sci. 2019 Jan.
[2]. An insight into the interaction between clopidogrel and proton pump inhibitors By Shah, Bhavik S.; Parmar, Sanjay A.; Mahajan, Shailaja; Mehta, Anita A. From Current Drug Metabolism (2012), 13(2),225-235. [3]. Increased endoplasmic reticulum stress response is involved in Clopidogrel-induced apoptosis of gastric epithelial cells. PLoS One. 2013 Sep 13;8(9):e74381. [4]. P2Y12, a new platelet ADP receptor, target of Clopidogrel.Semin Vasc Med. 2003 May;3(2):113-22. [5]. Clopidogrel treatment inhibits P2Y2-Mediated constriction in the rabbit middle cerebral artery [published online ahead of print, 2021 Oct 1]. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;174545. |
| 其他信息 |
Clopidogrel is a thienopyridine that is 4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine in which the hydrogen attached to the nitrogen is replaced by an o-chlorobenzyl group, the methylene hydrogen of which is replaced by a methoxycarbonyl group (the S enantiomer). A P2Y12 receptor antagonist, it is used to inhibit blood clots and prevent heart attacks. It has a role as a platelet aggregation inhibitor, an anticoagulant and a P2Y12 receptor antagonist. It is a thienopyridine, a member of monochlorobenzenes and a methyl ester. It is functionally related to a ticlopidine.
Clopidogrel is a prodrug of a platelet inhibitor used to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction and stroke. Clopidogrel is indicated to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction for patients with non-ST elevated acute coronary syndrome (ACS), patients with ST-elevated myocardial infarction, and in recent MI, stroke, or established peripheral arterial disease, It has been shown to be superior to [aspirin] in reducing cardiovascular outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease and provides additional benefit to patients with acute coronary syndromes already taking aspirin. Clopidogrel was granted FDA approval on 17 November 1997. Clopidogrel is a P2Y12 Platelet Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of clopidogrel is as a P2Y12 Receptor Antagonist, and Cytochrome P450 2C8 Inhibitor. The physiologic effect of clopidogrel is by means of Decreased Platelet Aggregation. Clopidogrel is an inhibitor of platelet aggregation that is used to decrease the risk of myocardial infarction and stroke in patients known to have atherosclerosis. Clopidogrel has been linked to rare instances of idiosyncratic, clinically apparent acute liver injury. Clopidogrel is a thienopyridine, with antiplatelet activity. Clopidogrel targets, irreversibly binds to and alters the platelet receptor for adenosine diphosphate (ADP), thereby blocking the binding of ADP to its receptor, inhibiting ADP-mediated activation of the glycoprotein complex GPIIb/IIIa, and inhibiting fibrinogen binding to platelets and platelet adhesion and aggregation. This results in increased bleeding time. A ticlopidine analog and platelet purinergic P2Y receptor antagonist that inhibits adenosine diphosphate-mediated PLATELET AGGREGATION. It is used to prevent THROMBOEMBOLISM in patients with ARTERIAL OCCLUSIVE DISEASES; MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; STROKE; or ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. See also: Clopidogrel Bisulfate (has salt form); Clopidogrel Besylate (is active moiety of); Clopidogrel Hydrochloride (has salt form) ... View More ... Drug Indication Clopidogrel is indicated to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction for patients with non-ST elevated acute coronary syndrome (ACS), patients with ST-elevated myocardial infarction, and in recent MI, stroke, or established peripheral arterial disease, FDA Label Clopidogrel is indicated in adults for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in: Patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. Secondary prevention of atherothrombotic eventsClopidogrel is indicated in: adult patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from seven days until less than six months) or established peripheral arterial disease; adult patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: non-ST-segment-elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA); ST-segment-elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (including patients undergoing a stent replacement) or medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic/fibrinolytic therapy. In patients with moderate to high-risk Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) or minor Ischemic Stroke (IS)Clopidogrel in combination with ASA is indicated in: Adult patients with moderate to high-risk TIA (ABCD2 score â¥4) or minor IS (NIHSS â¤3) within 24 hours of either the TIA or IS event. Prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events in atrial fibrillationIn adult patients with atrial fibrillation who have at least one risk factor for vascular events, are not suitable for treatment with vitamin-K antagonists and who have a low bleeding risk, clopidogrel is indicated in combination with ASA for the prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events, including stroke. Secondary prevention of atherothrombotic eventsClopidogrel is indicated in: Adult patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. Adult patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA). ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (including patients undergoing a stent placement) or medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic/fibrinolytic therapy. In patients with moderate to high-risk Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) or minor Ischemic Stroke (IS)Clopidogrel in combination with ASA is indicated in: Adult patients with moderate to high-risk TIA (ABCD2 score â¥4) or minor IS (NIHSS â¤3) within 24 hours of either the TIA or IS event. Prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events in atrial fibrillationIn adult patients with atrial fibrillation who have at least one risk factor for vascular events, are not suitable for treatment with Vitamin K antagonists (VKA) and who have a low bleeding risk, clopidogrel is indicated in combination with ASA for the prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events, including stroke. Secondary prevention of atherothrombotic eventsClopidogrel is indicated in: adult patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from seven days until less than six months) or established peripheral arterial disease; adult patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: non-ST-segment-elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA); ST-segment-elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. Prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events in atrial fibrillationIn adult patients with atrial fibrillation who have at least one risk factor for vascular events, are not suitable for treatment with vitamin-K antagonists and who have a low bleeding risk, clopidogrel is indicated in combination with ASA for the prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events, including stroke. For further information please refer to section 5. 1. Secondary prevention of atherothrombotic events Clopidogrel is indicated in: Adult patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. Adult patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA). ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. Prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events in atrial fibrillationIn adult patients with atrial fibrillation who have at least one risk factor for vascular events, are not suitable for treatment with Vitamin K antagonists (VKA) and who have a low bleeding risk, clopidogrel is indicated in combination with ASA for the prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events, including stroke. Clopidogrel is indicated in adults for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in: , , , Patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. , , , , , , Secondary prevention of atherothrombotic events, , Clopidogrel is indicated in:  , - Adult patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. , - Adult patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: ,   - Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA). ,    - ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. , , In patients with moderate to high-risk Transient Ischaemic Attack (TIA) or minor Ischaemic Stroke (IS), Clopidogrel in combination with ASA is indicated in: , - Adult patients with moderate to high-risk TIA (ABCD2 score â¥4) or minor IS (NIHSS â¤3) within 24 hours of either the TIA or IS event.  , , Prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events in atrial fibrillation, In adult patients with atrial fibrillation who have at least one risk factor for vascular events, are not suitable for treatment with Vitamin K antagonists (VKA) and who have a low bleeding risk, clopidogrel is indicated in combination with ASA for the prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events, including stroke. , , For further information please refer to section 5. 1. , , , , , , , Secondary prevention of atherothrombotic eventsClopidogrel is indicated in: Adult patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. Adult patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: - Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA). - ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. Prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events in atrial fibrillationIn adult patients with atrial fibrillation who have at least one risk factor for vascular events, are not suitable for treatment with Vitamin K antagonists (VKA) and who have a low bleeding risk, clopidogrel is indicated in combination with ASA for the prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events, including stroke. Prevention Secondary prevention of atherothrombotic events Clopidogrel is indicated in: Adult patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. Adult patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: - Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA). - ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. Prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events in atrial fibrillation: - In adult patients with atrial fibrillation who have at least one risk factor for vascular events, are not suitable for treatment with Vitamin K antagonists (VKA) and who have a low bleeding risk, clopidogrel is indicated in combination with ASA for the prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events, including stroke. Secondary prevention of atherothrombotic eventsClopidogrel is indicated in: Adult patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35days), ischaemic stroke (from 7days until less than 6months) or established peripheral arterial disease. Adult patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA). ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. Prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events in atrial fibrillationIn adult patients with atrial fibrillation who have at least one risk factor for vascular events, are not suitable for treatment with Vitamin K antagonists (VKA) and who have a low bleeding risk, clopidogrel is indicated in combination with ASA for the prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events, including stroke. Prevention of atherothrombotic events Clopidogrel is indicated in: Adult patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. Secondary prevention of atherothrombotic eventsClopidogrel is indicated in: Adult patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. Adult patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA). ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. Prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events in atrial fibrillationIn adult patients with atrial fibrillation who have at least one risk factor for vascular events, are not suitable for treatment with Vitamin K antagonists (VKA) and who have a low bleeding risk, clopidogrel is indicated in combination with ASA for the prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events, including stroke.  For further information please refer to section 5. 1. Clopidogrel is indicated in adults for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in: , , , , , Patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease, Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy, Patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome. , , , , Clopidogrel is indicated in: Adult patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. Adult patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA). ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. Prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events in atrial fibrillation In adult patients with atrial fibrillation who have at least one risk factor for vascular events, are not suitable for treatment with Vitamin K antagonists (VKA) and who have a low bleeding risk, clopidogrel is indicated in combination with ASA for the prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events, including stroke. Clopidogrel is indicated in adults for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in: Patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. Prevention of atherothrombotic eventsClopidogrel is indicated in: adult patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease; adult patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA); ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. Prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events in atrial fibrillationIn adult patients with atrial fibrillation who have at least one risk factor for vascular events, are not suitable for treatment with vitamin-K antagonists (VKA) and who have a low bleeding risk, clopidogrel is indicated in combination with ASA for the prevention of atherothrombotic and thromboembolic events, including stroke. Clopidogrel is indicated in adults for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in: Patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. For further information please refer to section 5. 1. Clopidogrel is indicated in adults for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in: Patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. Patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA). ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. For further information please refer to section 5. 1. Clopidogrel is indicated in adults for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in: patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. For further information please refer to section 5. 1. Clopidogrel is indicated in adults for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in: patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease; patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: - Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA); - ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. For further information please refer to section 5. 1. Clopidogrel is indicated in adults for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in: Patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. Patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: - Non ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non Q wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA). - ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. For further information please refer to section 5. 1. Clopidogrel is indicated in adults for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in: - Patients suffering from myocardial infarction (from a few days until less than 35 days), ischaemic stroke (from 7 days until less than 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease. - Patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome: Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), including patients undergoing a stent placement following percutaneous coronary intervention, in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA). ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction, in combination with ASA in medically treated patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy. Prevention of thromboembolic events Thromboembolic events Thromboembolic events Thromboembolic events Mechanism of Action Clopidogrel is activated via a 2 steps reaction to an active thiol-containing metabolite. This active form is a platelet inhibitor that irreversibly binds to P2Y12 ADP receptors on platelets. This binding prevents ADP binding to P2Y12 receptors, activation of the glycoprotein GPIIb/IIIa complex, and platelet aggregation. Clopidogrel must be metabolized by CYP450 enzymes to produce the active metabolite that inhibits platelet aggregation. The active metabolite of clopidogrel selectively inhibits the binding of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to its platelet P2Y12 receptor and the subsequent ADP-mediated activation of the glycoprotein GPIIb/IIIa complex, thereby inhibiting platelet aggregation. This action is irreversible. Consequently, platelets exposed to clopidogrel's active metabolite are affected for the remainder of their lifespan (about 7 to 10 days). Platelet aggregation induced by agonists other than ADP is also inhibited by blocking the amplification of platelet activation by released ADP. The P2Y12 receptor plays a crucial role in the regulation of platelet activation by several agonists, which is irreversibly antagonized by the active metabolite of clopidogrel, a widely used anti-thrombotic drug. In this study, we investigated whether reduction of platelet reactivity leads to reduced inflammatory responses using a rat model of erosive arthritis. We evaluated the effect of clopidogrel on inflammation in Lewis rats in a peptidoglycan polysaccharide (PG-PS)-induced arthritis model with four groups of rats: 1) untreated, 2) clopidogrel-treated, 3) PG-PS-induced, and 4) PG-PS-induced and clopidogrel-treated. There were significant differences between the PG-PS+clopidogrel group when compared to the PG-PS group including: increased joint diameter and clinical manifestations of inflammation, elevated plasma levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 beta, interferon (IFN) gamma, and IL-6), an elevated neutrophil blood count and an increased circulating platelet count. Plasma levels of IL-10 were significantly lower in the PG-PS+clopidogrel group compared to the PG-PS group. Plasma levels of platelet factor 4 (PF4) were elevated in both the PG-PS and the PG-PS+clopidogrel groups, however PF4 levels showed no difference upon clopidogrel treatment, suggesting that the pro- inflammatory effect of clopidogrel may be due to its action on cells other than platelets. Histology indicated an increase in leukocyte infiltration at the inflammatory area of the joint, increased pannus formation, blood vessel proliferation, subsynovial fibrosis and cartilage erosion upon treatment with clopidogrel in PG-PS-induced arthritis animals. In summary, animals treated with clopidogrel showed a pro-inflammatory effect in the PG-PS-induced arthritis animal model, which might not be mediated by platelets. |
| 分子式 |
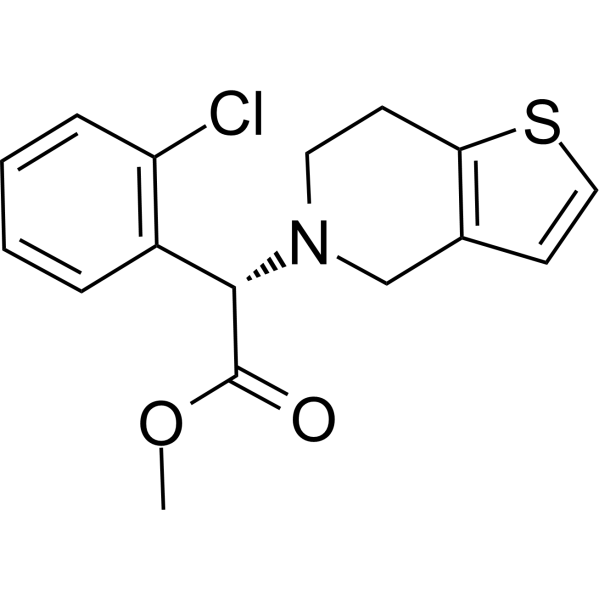
C16H16CLNO2S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
321.82
|
| 精确质量 |
321.059
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.72; H, 5.01; Cl, 11.02; N, 4.35; O, 9.94; S, 9.96
|
| CAS号 |
113665-84-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Clopidogrel thiolactone;1147350-75-1;Clopidogrel hydrogen sulfate;120202-66-6; 1217643-68-9; 90055-48-4 (racemic); 120202-66-6 (sulfate);120202-67-7 (HBr); 120202-65-5 (HCl); 744256-69-7 (besylate);
|
| PubChem CID |
60606
|
| 外观&性状 |
Colorless to light yellow ointment
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
423.7±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
210.0±28.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.617
|
| LogP |
4.23
|
| tPSA |
57.78
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
21
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
381
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
ClC1=C(C=CC=C1)[C@H](N2CCC3=C(C2)C=CS3)C(OC)=O
|
| InChi Key |
GKTWGGQPFAXNFI-HNNXBMFYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H16ClNO2S/c1-20-16(19)15(12-4-2-3-5-13(12)17)18-8-6-14-11(10-18)7-9-21-14/h2-5,7,9,15H,6,8,10H2,1H3/t15-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
methyl (2S)-2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(6,7-dihydro-4H-thieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5-yl)acetate
|
| 别名 |
clopidogrel; 113665-84-2; Zyllt; (S)-Clopidogrel; Thrombo; Plavix; (+)-Clopidogrel; (+)-(S)-Clopidogrel;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: 50 mg/mL (155.37 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.77 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.77 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (7.77 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1073 mL | 15.5366 mL | 31.0733 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6215 mL | 3.1073 mL | 6.2147 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3107 mL | 1.5537 mL | 3.1073 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。