| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
用rel-反苯环丙明(SKF 385;静脉注射,0.1 至 3.0 mg/kg;杂种狗,5-10 kg)可升高血压。服用的剂量决定了药物升高血压的程度和持续时间。通常可以通过重复给药来获得动物对 rel-Tranylcypromine 的抑制反应[1]。
|
|---|---|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Interindividual variability in absorption. May be biphasic in some individuals. Peak plasma concentrations occur in one hour following oral administration with a secondary peak occurring within 2-3 hours. Biphasic absorption may represent different rates of absorption of the stereoisomers of the drug, though additional studies are required to confirm this. 1.1-5.7 L/kg THE MAO INHIBITORS ARE ABSORBED READILY WHEN GIVEN BY MOUTH. THESE DRUGS PRODUCE MAXIMAL INHIBITION OF MAO WITHIN 5-10 DAYS. ... ALTHOUGH THEIR BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY IS PROLONGED BECAUSE OF THE CHARACTERISTICS OF THEIR INTERACTION WITH THE ENZYME, THEIR CLINICAL EFFICACY APPEARS TO BE REDUCED WHEN THE DRUG IS GIVEN LESS FREQUENTLY THAN ONCE DAILY. /MAO INHIBITORS/ Metabolism / Metabolites Hepatic. Biological Half-Life 1.5-3.2 hours in patients with normal renal and hepatic function |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Tranylcypromine, like most monoamine oxidase inhibitors, can cause transient serum aminotransferase elevations in a proportion of patients. These elevations are usually mild, asymptomatic and self-limited and do not require dose modification. Tranylcypromine has also been associated with rare cases of acute, clinically apparent liver injury. The few cases described have resembled those caused by other MAO inhibitors. The time to clinical onset is typically 1 to 4 months and the usual pattern of serum enzyme elevations is hepatocellular (Case 1), although cholestatic injury has also been described. Immunoallergic features (rash, fever, eosinophilia) are uncommon as is autoantibody formation. Likelihood score: D (possible rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because little information is available on the use of tranylcypromine during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A woman with severe depression took tranylcypromine 100 to 120 mg daily, as well as pimozide, diazepam and alprazolam during pregnancy and postpartum. She breastfed her infant until about 2 weeks postpartum when the infant developed abdominal distension and feeding intolerance. The symptoms resolved on discontinuation of breastfeeding. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Nine subjects were treated with an average dose of 29 mg daily (range 10 to 40 mg daily) of oral tranylcypromine for an average of 16 days. Serum prolactin levels increased by 3 mcg/L.The clinical relevance of these findings in nursing mothers is not known. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. Interactions HEXOBARBITAL SLEEPING TIME IS PROLONGED BY PARNATE, INDICATING ITS ABILITY TO POTENTIATE OTHER DRUGS PRESUMABLY BY INTERFERING WITH THEIR DETOXIFICATION. /PARNATE/ MAO INHIBITORS ALSO ENHANCE EFFECTS OF EXOGENOUSLY ADMIN AMINES, SUCH AS 5-HT & NOREPINEPHRINE, AS WELL AS PRECURSORS, SUCH AS 3,4-HYDROXYPHENYLALANINE (DOPA) & 5-HYDROXYTRYPTOPHAN. /MAO INHIBITORS/ Meperidine should never be used for ... headaches /with the hypertensive episode/, and blood pressure should be evaluated immediately when a patient taking an MAO inhibitor reports a severe throbbing headache or a feeling of pressure in the head. /MAO INHIBITORS/ MAO INHIBITORS ... INTERFERE WITH DETOXICATION MECHANISMS FOR CERTAIN OTHER DRUGS. THEY PROLONG & INTENSIFY EFFECTS OF CENTRAL DEPRESSANT AGENTS, SUCH AS GENERAL ANESTHETICS, SEDATIVES, ANTIHISTAMINES, ALCOHOL, & POTENT ANALGESICS; OF ANTICHOLINERGIC AGENTS, PARTICULARLY THOSE USED IN THE TREATMENT OF PARKINSONISM; & OF ANTIDEPRESSANT AGENTS, ESP IMIPRAMINE & AMITRIPTYLINE. /MAO INHIBITORS/ For more Interactions (Complete) data for TRANYLCYPROMINE (37 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. TODA N, et al. The sympathomimetic effects of SKF-385 on blood pressure in dog. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1962;12:166-179.
|
| 其他信息 |
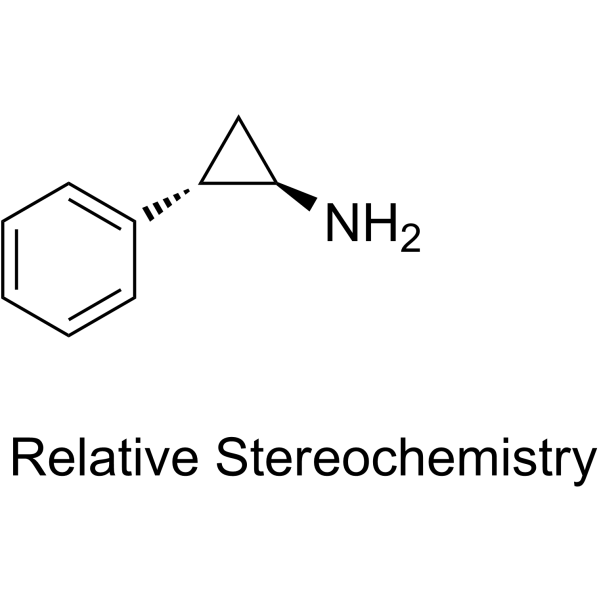
(1R,2S)-tranylcypromine is a 2-phenylcyclopropan-1-amine that is the (1R,2S)-enantiomer of tranylcypromine. It is a conjugate base of a (1R,2S)-tranylcypromine(1+). It is an enantiomer of a (1S,2R)-tranylcypromine.
A propylamine formed from the cyclization of the side chain of amphetamine. This monoamine oxidase inhibitor is effective in the treatment of major depression, dysthymic disorder, and atypical depression. It also is useful in panic and phobic disorders (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p311). Tranylcypromine is a racemate comprising equal amounts of (1R,2S)- and (1S,2R)-2-phenylcyclopropan-1-amine with the chiral centers both located on the cylopropane ring. An irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor that is used as an antidepressant (INN tranylcypromine). Tranylcypromine is a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of tranylcypromine is as a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor. Tranylcypromine is a nonhydrazine monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAO inhibitor) used in therapy of severe depression. Tranylcypromine therapy is associated with rare instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury. Tranylcypromine is an orally bioavailable, nonselective, irreversible, non-hydrazine inhibitor of both monoamine oxidase (MAO) and lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1/BHC110), with antidepressant and anxiolytic activities, and potential antineoplastic activities. Upon oral administration, tranylcypromine exerts its antidepressant and anxiolytic effects through the inhibition of MAO, an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine. This increases the concentrations and activity of these neurotransmitters. Tranylcypromine exerts its antineoplastic effect through the inhibition of LSD1. Inhibition of LSD1 prevents the transcription of LSD1 target genes. LSD1, a flavin-dependent monoamine oxidoreductase and a histone demethylase, is upregulated in a variety of cancers and plays a key role in tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. A propylamine formed from the cyclization of the side chain of amphetamine. This monoamine oxidase inhibitor is effective in the treatment of major depression, dysthymic disorder, and atypical depression. It also is useful in panic and phobic disorders. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p311) See also: Tranylcypromine Sulfate (has salt form). Drug Indication For the treatment of major depressive episode without melancholia. Mechanism of Action Tranylcypromine irreversibly and nonselectively inhibits monoamine oxidase (MAO). Within neurons, MAO appears to regulate the levels of monoamines released upon synaptic firing. Since depression is associated with low levels of monoamines, the inhibition of MAO serves to ease depressive symptoms, as this results in an increase in the concentrations of these amines within the CNS. RESULTS SUGGEST THAT D- & DL-TRANYLCYPROMINE HAVE DIRECT & INDIRECT ACTIONS ON TRYPTAMINERGIC NEUROTRANSMISSION. TRANYLCYPROMINE-HCL ADMIN IP (20 MG/KG) TO RATS: INCR IN HIPPOCAMPUS & DIENCEPHALON CONCN OF 2-PHENYLETHYLAMINE & TRYPTAMINE WERE MUCH HIGHER THAN THOSE OF M- & P-TYRAMINE. THESE MAY BE INVOLVED IN CNS NEURONAL FUNCTIONING, THEREFORE COMPONENT OF TRANYLCYPROMINE ACTIVITY. PLATELET MAO ACTIVITY MARKEDLY DECR (DL-TRANYLCYPROMINE SULFATE 10 & 20 MG ORAL): UPTAKE OF 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE, DOPAMINE & METARAMINOL ONLY SLIGHTLY DECR. MAO INHIBITOR ANTIDEPRESSANT ACTIVITY PROBABLY LESS RELATED TO CATECHOLAMINE UPTAKE INHIBITION THAN OXIDASE INHIBITION ...PRODUCE IRREVERSIBLE INACTIVATION OF MAO BY FORMING STABLE COMPLEXES WITH ENZYME. ... THERE IS EVIDENCE THAT SOME MAO INHIBITORS PREVENT RELEASE OF NOREPINEPHRINE FROM NERVE ENDINGS BY NERVE IMPULSES. /MAO INHIBITORS/ ... TRANYLCYPROMINE IS A POTENT BUT NOT SPECIFIC INHIBITOR OF CYP2C19. Therapeutic Uses Antidepressive Agents; Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors; Anti-Anxiety Agents DEG TO WHICH MAO IS INHIBITED IN PARTICULAR ORGAN OF BODY VARIES WITH PARTICULAR MAO INHIBITOR. SINCE MAO INHIBITION CANNOT BE EASILY MONITORED IN CLINICAL SITUATIONS (BECAUSE OF LONG LATENCY & DURATION OF ACTION), DRUGS ARE NEVER ADMIN PARENTERALLY. /MAO INHIBITORS/ MOST USEFUL EFFECT OF VARIOUS MAO INHIBITORS IS TO ELEVATE MOOD OF DEPRESSED PT. /MAO INHIBITORS/ MAO INHIBITORS ARE AMONG MOST EFFECTIVE REM SUPPRESSORS KNOWN. THIS EFFECT HAS BEEN USED THERAPEUTICALLY IN TREATMENT OF NARCOLEPSY. ... MAO INHIBITORS LOWER BLOOD PRESSURE & PROVIDE SYMPTOMATIC RELIEF IN ANGINA PECTORIS. /MAO INHIBITORS/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for TRANYLCYPROMINE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings MAJORITY OF SMALL NUMBER OF DEATHS...OCCURRED AFTER DOSES OF OVER 350 MG; PT HAVE SURVIVED AFTER INGESTION OF THIS AMT, HOWEVER. DEPENDENCE ON TRANYLCYPROMINE HAS BEEN REPORTED OCCASIONALLY. /SULFATE/ ...CONTRAINDICATED IN PT WITH CEREBROVASCULAR DEFECTS, CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS OR PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA... /SULFATE/ SWITCHING PT FROM ONE MAO INHIBITOR TO ANOTHER OR TO TRICYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANT REQUIRES REST PERIOD OF 10-14 DAYS. /MAO INHIBITORS/ ...TRANYLCYPROMINE CAN CAUSE REACTION IF ADMIN WHEN EFFECT OF PHENELZINE IS STILL PRESENT. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for TRANYLCYPROMINE (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Tranylcypromine belongs to a class of antidepressants called monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Tranylcypromine is a non-hydrazine monoamine oxidase inhibitor with a rapid onset of activity. MAO is an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative deamination of a number of amines, including serotonin, norepinephrine, epinephrine, and dopamine. Two isoforms of MAO, A and B, are found in the body. MAO-A is mainly found within cells located in the periphery and catalyzes the breakdown of serotonin, norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine and tyramine. MAO-B acts on phenylethylamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine and tyramine, is localized extracellularly and is found predominantly in the brain. While the mechanism of MAOIs is still unclear, it is thought that they act by increasing free serotonin and norepinephrine concentrations and/or by altering the concentrations of other amines in the CNS. It has been postulated that depression is caused by low levels of serotonin and/or norepinephrine and that increasing serotonergic and norepinephrinergic neurotransmission results in relief of depressive symptoms. MAO A inhibition is thought to be more relevant to antidepressant activity than MAO B inhibition. Selective MAO B inhibitors, such as selegiline, have no antidepressant effects. |
| 分子式 |
C9H11N
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
133.19
|
| 精确质量 |
133.089
|
| CAS号 |
155-09-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Tranylcypromine hemisulfate;13492-01-8;Tranylcypromine-d5 hydrochloride;107077-98-5
|
| PubChem CID |
19493
|
| 外观&性状 |
Liquid
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
218.3±29.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
79-80 °C at 1.50E+00 mm Hg
MP: 164-166 °C /Hydrochloride/ |
| 闪点 |
90.8±19.6 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.1±0.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.584
|
| LogP |
1.25
|
| tPSA |
26.02
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
1
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
10
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
116
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
C1C=CC(C2C[C@H]2N)=CC=1
|
| InChi Key |
AELCINSCMGFISI-DTWKUNHWSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C9H11N/c10-9-6-8(9)7-4-2-1-3-5-7/h1-5,8-9H,6,10H2/t8-,9+/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(1R,2S)-2-phenylcyclopropan-1-amine
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.5081 mL | 37.5404 mL | 75.0807 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.5016 mL | 7.5081 mL | 15.0161 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.7508 mL | 3.7540 mL | 7.5081 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。