| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Urinary excretion of administration p-toluenesulfonamide in rats was approx 80% with half of original compound being oxidized to p-sulfamoylbenzoic acid. More than 90% of /the p-sulfamoylbenzoic acid metabolite/ was excreted unchanged, but urine to feces ratios varied considerably among individual animals. After oral administration of (14)C-labeled compound to rats the label was rapidly eliminated largely in urine (66-89% of dose), with little in feces (2-8% of dose). (14)C in feces was 4-sulfamoylbenzoic acid, which probably originated in tissues. Metabolism / Metabolites /The purpose of this study was/ to study the in vivo and in vitro metabolism and the effect of para-toluene-sulfonamide (PTS) on cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP450). Total CYP450 and microsome protein content were determined after iv pretreatment of rats with PTS. CYP-specific substrates were incubated with rat liver microsomes. Specific CYP isoform activities were determined by using HPLC. CYP chemical inhibitors added to the incubation mixture were used to investigate the principal CYP isoforms involved in PTS metabolism. The effect of PTS on CYP isoforms was investigated by incubating PTS with specific substrates. The groups treated with 33 and 99 mg/kg per d PTS, respectively, had a total CYP content of 0.66+/-0.17 and 0.60+/-0.12 nmol/mg. The K(m) and V(max) were 92.2 umol/L and 0.0137 nmol/min per mg protein. CYP2C7, CYP2D1 and CYP3A2 might contribute to PTS metabolism in the rat liver. The inhibitory effects of sulfaphenazole and ketoconazole on PTS metabolism were shown to have a mixed mechanism, whereas PTS metabolism was inhibited noncompetitively by quinidine. PTS had little effect on the activities of the selected CYP isoforms. Generally speaking, it is relatively safe for PTS to be co-administered with other drugs. However, care should be taken when administering PTS with CYP inhibitors and the substrates of CYP2C, CYP2D and CYP3A. Aim of this study was to investigate liver metabolism of with regard to para toluene-sulfonamide (PTS), CYP isoforms, P-glycoprotein (P-gp), and drug interactions. Known substrates, inducers and inhibitors of CYP and inhibitor of P-gp were employed and metabolites were determined with HPLC. Male Wistar rats were pretreated with ip phenobarbital (PB), ketoconazole (Ket), or verapamil (Ver) for 3 days and in situ liver perfusion of PTS was conducted in a recirculation system. Rats were also pretreated with ip PTS (33 mg/kg/day or PTS 99 mg/kg/day) for 4 days before liver perfusions with dextromethorphan (Dex) and phenacetin (Phe) preparations were conducted. Microsome incubation was used to investigate PTS effect on five CYP isoforms and PTS-drug interactions probability with phyllotoxin and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in vitro. PTS at 60 min perfusates had areas of 61.4% and 133.6% of the blank control in PB group and Ket group, respectively. The result that PTS metabolism was enhanced by PB and inhibited by Ket treatments suggested liver CYP was attributed to PTS metabolism. PTS mg/kg/day pretreatment slowed down the metabolism of Dex and Phe while in vitro incubations did not show a PTS (0-160 umol/L) effect on CYP activities. PTS metabolite formation when co-incubated with phyllotoxin was 50.7% of the negative control. The potent inhibitory ability of phyllotoxin to PTS requires further clinical investigation regarding in concomitant administration. Fifteen adult rainbow trout were exposed to water solution of (14)C-tosylchloramide sodium (purity 93.7%, specific activity 1.2 ugCi/uM) at a concentration of 20 mg/L (twice the proposed treatment concentration) for a period of 1 hour and then transferred to fresh water. The temperature of the well water was 11 to 13 °C. ... tosylchloramide sodium was rapidly reduced to the primary metabolite para-toluenesulfonamide, but the levels were not quantified. ...50% of admin ortho- and para-toluenesulfonamides excreted in urine had been metabolized to ortho- and para-sulfamoylbenzoic acids, respectively. For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for p-Toluenesulfonamide (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Biological Half-Life Fingerlings and juvenile trout were exposed to 20 mg/L (twice the therapeutic concentration) of ring UL-14C-tosylchloramide sodium (purity 93.7%, specific activity 1.2 uCi/uM) for up to 1 hr and then transferred to fresh water for recovery to assess tissue accumulation and distribution of resulting residues. The temperature of the well water was 11.6 to 12.2 °C. The estimated half-life of para-toluenesulfonamide equivalents in fingerlings was 27.3 hours whereas determined by HPLC the half-life of para-toluenesulfonamide residues in whole-body homogenates was 36.3 hours. The estimated half-life of residues in juvenile fish was 32.6 hours, based on radiometric data, while determined by HPLC the half-life for para-toluenesulfonamide residues in whole body samples was 40.3 hours. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: p-Toluenesulfonamide is a solid. It is used in organic synthesis, in plasticizers and resins, and as a fungicide and mildewicide in paints and coatings. It has been used as experimental therapy. HUMAN STUDIES: It is known as a common contact allergen. ANIMAL STUDIES: No treatment-related effects were observed in a 90 day feeding study on dogs exposed to doses up to 3000 mg/kg feed of a mixture of p-toluenesulfonamide (68%) and ortho-toluenesulfonamide (32%), equivalent to 75 mg/kg bw/day. In a 90 day feeding study, rats were exposed to diets containing 0, 300, 1000 or 3000 mg/kg feed of mixture of p-toluenesulfonamide (68%) and ortho-toluenesulfonamide (32%), equivalent to approximately 15, 50 or 150 mg/kg bw/day. A slight reduction of weight gain and food consumption was present at 3000 mg/kg feed as the only treatment-related effects. Pregnant rats were treated by gavage on gestational days 6-15 with 0, 50, 250, or 500 mg/kg bw of a mixture of p-toluenesulfonamide (68%) and ortho-toluenesulfonamide (32%). At 250 and 500 mg/kg bw maternal weight gain was significantly reduced during the treatment period. At the same dose levels, postimplantation loss demonstrated a dose-related increase and fetal weight was reduced. No teratogenic effect was observed. p-Toluenesulfonamide was studied for mutagenic potential with Salmonella typhimurium/microsome test, basic-test in Drosophila melanogaster, and micronucleus test in mice. No test revealed mutagenic activity. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat oral 2400 mg/kg bw /Mixture of ortho-toluenesulfonamide (41%) and para-toluenesulfonamide (51%)/ LD50 Rat oral 2330 mg/kg bw LD50 Rat oral >2000 mg/kg LD50 Mouse oral 400 mg/kg LD50 Mouse ip 250 mg/kg |
| 其他信息 |
Toluene-4-sulfonamide is a sulfonamide that is benzenesulfonamide bearing a methyl group at position 4.
Para-toluenesulfonamide is a low-molecular-weight organic compound with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon intra-tumoral injection, para-toluenesulfonamide increases lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP) and the release of cathepsin B. Cytosolic cathepsin B released from lysosomes cleaves and activates proapoptotic B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) family member BH3 interacting-domain death agonist (Bid) and poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 (PARP-1), which may induce tumor cell death. Therapeutic Uses /CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Para-toluenesulfonamide is included in the database. /EXPL THER/ Severe malignant airway obstruction (SMAO) is a life-threatening form of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). /The purpose of this study was/ to determine the efficacy and safety of para-toluenesulfonamide (PTS) intratumoral injection in NSCLC-SMAO. Ninety patients with NSCLC-SAO received repeated courses of PTS intratumoral injection until tumor sizes had reduced by 50% or greater. Primary endpoint was objective alleviation rate, assessed by chest computed tomography (CT) and bronchoscopy, at day 7 and 30 following final dosing. Secondary endpoints included airway obstruction, spirometry, quality-of-life and survival time. In full-analysis set (N=88), using RECIST criteria, PTS treatment resulted in a significant objective alleviation rate [chest CT: 59.1% (95%CI: 48.1%-69.5%), bronchoscopy: 48.9% (95%CI: 38.1%-59.8%) at day 7; chest CT: 43.2% (95%CI: 32.7%-54.2%), bronchoscopy: 29.6% (95%CI: 20.3%-40.2%) at day 30]. There was a remarkable increase in FVC (mean difference: 0.35 liters, 95%CI: 0.16-0.53 liters), FEV1 (mean difference: 0.27 liters, 95%CI: 0.07-0.48 liters), Baseline Dyspnea Index (mean difference: 64.8%, 95%CI: 53.9-74.7%) and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Lung Cancer Subscale (mean difference: 6.9, 95%CI: 3.8-9.9) at day 7 post-treatment. We noted significantly reduced prevalence of atelectasis (by 42.9%) and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group physical performance scale (mean difference: 7.2, 95%CI: 3.9-10.5). Median survival time was 394 days in full-analysis set and 460 days in per-protocol set. Adverse events were reported in 64.0% of subjects. Seven severe adverse events (7.9%) were reported, of which three led to death (drug-related in one case). PTS intratumoral injection is effective and well tolerated for palliative therapy of NSCLC-SMAO. /EXPL THER/ /The purpose was/ to study the effect of percutaneous para-toluenesulfonamide (PTS) injection on transplanted hepatocarcinoma in nude mice. Sixty nude mice with subcutaneous transplanted hepatocarcinoma were randomized into 6 groups, namely PTS, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, PTS+chemotherapy, PTS+radiotherapy and control groups. PTS were injected into the tumor in the nude mouse models as indicated, and the tumor growth rate and survival time of the mice were recorded. All the treatments resulted in effective arrest of the tumor growth, but the effects of PTS+chemotherapy and PTS+radiotherapy were more obvious. No significant difference in the survival time of the mice were noted between the groups. PTS+chemotherapy and PTS+radiotherapy are safe and reliable, and produces better effects than either radiotherapy or chemotherapy alone. /EXPL THER/ Para-toluenesulfonamide (PTS) has been implicated with anticancer effects against a variety of tumors. In the present study, we investigated the inhibitory effects of PTS on tongue squamous cell carcinoma (Tca-8113) and explored the lysosomal and mitochondrial changes after PTS treatment in vitro. High-performance liquid chromatography showed that PTS selectively accumulated in Tca-8113 cells with a relatively low concentration in normal fibroblasts. Next, the effects of PTS on cell viability, invasion, and cell death were determined. PTS significantly inhibited Tca-8113 cells' viability and invasive ability with increased cancer cell death. Flow cytometric analysis and the lactate dehydrogenase release assay showed that PTS induced cancer cell death by activating apoptosis and necrosis simultaneously. Morphological changes, such as cellular shrinkage, nuclear condensation as well as formation of apoptotic body and secondary lysosomes, were observed, indicating that PTS might induce cell death through disturbing lysosomal stability. Lysosomal integrity assay and western blot showed that PTS increased lysosomal membrane permeabilization associated with activation of lysosomal cathepsin B. Finally, PTS was shown to inhibit ATP biosynthesis and induce the release of mitochondrial cytochrome c. Therefore, our findings provide a novel insight into the use of PTS in cancer therapy. /EXPL THER/ Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is difficult to eradicate due to its resilient nature. Portal vein is often involved in tumors of large size, which exclude the patient from surgical resection and local ablative therapy, such as percutaneous ethanol injection (PEI) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) because they were considered neither effective nor safe. Currently, there is almost no effective treatment for HCC of such condition. As a unique antitumor agent in form of lipophilic fluid for local injection, para-toluenesulfonamide (PTS) produces mild side effects while necrotizing the tumor tissues quickly and efficiently. Being largely different from both PEI and RFA therapies, PTS can disseminate itself in tumors more easily than other caustic agents, such as alcohol. So PTS may offer additional benefit to HCCs with vascular involvement. We herein describe a 70-year-old HCC patient who was treated with the combination of PTS injection and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization, resulting in a significantly improved clinical prognosis. |
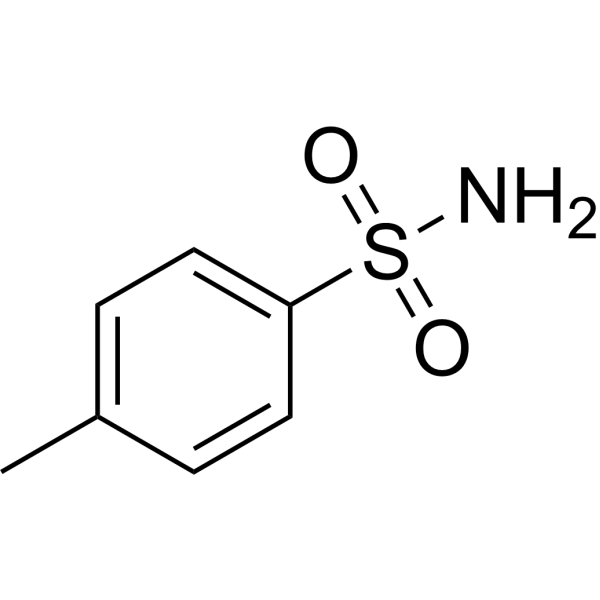
| 分子式 |
C7H9NO2S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
171.22
|
| 精确质量 |
171.035
|
| CAS号 |
70-55-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
4-Tolyl-sulfonamide-d4;1219795-34-2
|
| PubChem CID |
6269
|
| 外观&性状 |
Monoclinic plates (w+2)
White leaflets |
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
322.2±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
134-137 °C(lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
148.6±25.9 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.564
|
| LogP |
0.79
|
| tPSA |
68.54
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
11
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
209
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
S(C1C([H])=C([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])=C([H])C=1[H])(N([H])[H])(=O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
LMYRWZFENFIFIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C7H9NO2S/c1-6-2-4-7(5-3-6)11(8,9)10/h2-5H,1H3,(H2,8,9,10)
|
| 化学名 |
4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.8404 mL | 29.2022 mL | 58.4044 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.1681 mL | 5.8404 mL | 11.6809 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5840 mL | 2.9202 mL | 5.8404 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。