
| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
Cdk4/cyclin D3 (IC50 = 9 nM); Cdk4/cyclin D1 (IC50 = 11 nM); Cdk6/cyclin D2 (IC50 = 16 nM); DYRK1A (IC50 = 2000 nM); MAPK (IC50 = 8000 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:PD 0332991 对其他蛋白激酶包括 EGFR、FGFR、PGFR、IR 几乎没有影响。 PD 0332991 是 Cdk4 的非 ATP 竞争性抑制剂。 PD 0332991 抑制 MDA-MB-435 乳腺癌细胞,IC50 为 66 nM,这是由于 Ser780 处的 Rb 磷酸化减少所致。 PD 0332991 抑制胸苷掺入 Rb 阳性人乳腺癌、结肠癌、肺癌以及人白血病的 DNA,IC50 值范围为 0.04-0.17 μM。 PD 0332991 在 Rb 阴性细胞中没有显示出活性。 PD 0332991 导致 MDA-MB-453 乳腺癌细胞和 Colo-205 癌细胞中 G1 期细胞积聚。 PD 0332991 还在 5T33MM 骨髓瘤细胞(免疫活性模型)中显示出活性,并使细胞对硼替佐米的杀伤敏感。 PD 0332991 抑制 luminal ER 阳性以及 HER2 扩增的乳腺癌细胞系,包括 MDA-MB-175、ZR-75-30、CAMA-1、MDA-MB-134、HCC-202 和 UACC-893。 PD 0332991 增强这些细胞系中他莫昔芬和曲妥珠单抗的活性。 PD 0332991 增强 MCF7 他莫昔芬耐药细胞中他莫昔芬的敏感性。最近的一项研究表明,PD 0332991 可以抑制恶性横纹肌瘤 (MRT) 细胞系,包括 MP-MRT-AN、KP-MRT-RY、G401、KP-MRT-NS,且 MRT 细胞系对 PD 0332991 的敏感性呈反比。与p16的表达相关。激酶测定:在 DMSO 中制备 PD0332991 的储备溶液。 CDK 测定在 96 孔过滤板中进行。所有CDK-细胞周期蛋白激酶复合物均通过杆状病毒感染在昆虫细胞中表达并纯化。检测的底物是与 GST 融合的 pRb 片段(氨基酸 792-928)(GST·RB-Cterm)。每孔总体积为 0.1 mL,含有终浓度 20 mM Tris-HCl、pH 7.4、50 mM NaCl、1 mM 二硫苏糖醇、10 mM MgCl2、25 μM ATP(对于 CDK4-细胞周期蛋白 D1、CDK6-细胞周期蛋白 D2、和 CDK6-细胞周期蛋白 D3)或 12 μM ATP(对于 CDK2-细胞周期蛋白 E、CDK2-细胞周期蛋白 A 和 CDC2-细胞周期蛋白 B),含 0.25 μCi [γ-32P]ATP、20 ng 酶、1 μg GST·RB -Cterm 和 PD 0332991 (0.001-0.1μM)。除 [γ-32P]ATP 外的所有组分均添加至孔中,并将板置于板混合器上 2 分钟。通过添加 [γ-32P]ATP 开始反应,并将板在 25 °C 下孵育 15 分钟。通过添加 0.1 mL 20% 三氯乙酸终止反应,并将板在 4 °C 下保持至少 1 小时,以使底物沉淀。然后用 0.2 mL 10% 三氯乙酸洗涤孔 5 次,并用 β 板计数器测定放射性掺入。细胞测定:细胞(肿瘤细胞系包括 MDA-MB-435、ZR-75-1、T-47D、MCF-7、H1299、Colo-205、MDA-MB-468、H2009、CRRF-CEM 和 K562)以每孔 2 × 104 的密度接种到 96 孔板中并孵育过夜。将 PD 0332991 (0.01-1 μM) 添加到孔中,并在 37 °C 下再孵育 24 小时。将[14C]胸苷(0.1μCi)添加到每个孔中,并允许放射性标记的掺入持续72小时。用β板计数器测定掺入的放射性。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
PD 0332991 表明 150 mg/kg 的 MDA-MB-435 异种移植物中肿瘤完全停滞。 PD 0332991 还通过消除肿瘤组织中的磷酸化 Rb 和增殖标记物 Ki-67 以及在 E2F 转录控制下下调基因,在多个人类肿瘤异种移植物中显示出广谱抗肿瘤活性。
三联疗法在体内抑制肿瘤生长方面显示出卓越的疗效[2] 研究人员接下来测试了我们的假设,即tucatinib、palbociclib和氟维司群的组合在体内具有疗效。对于体内实验,我们将分析重点放在含有图卡替尼的三重组合和双重组合上(图卡替尼加氟维司群或图卡替尼加帕博西利),并将其活性与赋形剂和单剂图卡替尼作比较。我们选择不在动物实验中测试单药帕博昔单抗、富司琼或帕博昔布和富司琼的组合的活性,因为已发表的临床研究表明,HER2抑制对于治疗HER2+乳腺癌症患者至关重要;在联合治疗方案中添加HER2抑制剂可改善OS(41,42)。因此,只有含tucatinib的组合对HR+/HER2+疾病患者具有临床相关性。 与赋形剂相比,tucatinib没有减少MDA-MB-361肿瘤的生长(图2A)。然而,图卡替尼与氟维司群或帕博西利的联合用药显著降低了肿瘤生长,三种联合用药对肿瘤生长的抑制作用最强。tucatinib组和赋形剂组在EOT时的平均肿瘤体积(VEOT)没有差异,而tucatinib+帕博西利、tucatinip+氟维司群和三联用药组的VEOT明显较小(图2B和C)。与两种双联合治疗相比,三种联合治疗的VEOT显著降低(图2B和C)。溶媒和tucatinib的平均TGR没有差异;然而,双重组合和三重组合都显著降低了TGR(图2D)。TGR在三重组合中最低,约为车辆的5.6倍(图2D)。Ki67的IHC染色显示,所有含帕博西利的组合都显著降低了增殖率。然而,在三重组合中观察到增殖细胞的百分比最低,其中Ki67明显低于最佳的双重组合(图2E和F)。 BT474肿瘤产生了类似的结果,其中三重组合诱导了肿瘤生长的最显著减少(图2G)。与赋形剂治疗相比,图卡替尼单独或与氟维司群或帕博西利联合使用也能减少肿瘤生长,尽管程度低于三联治疗。与单独使用tucatinib、tucatinib+fulvestrant或tucatinip+palbociclib组相比,三联用药的平均VEOT显著降低(图2H和I)。与实验开始时相比,三重联合治疗是唯一一种肿瘤大小缩小的治疗方法。三重组合诱导的TGR为阴性,远低于单药tucatinib或tucatinib+fulvestrant治疗组的TGR(图2J)。最后,Ki67分析显示,所有含帕博西利的组合都显著降低了增殖率,其中帕博西利布联合图卡替尼或三联治疗组的Ki67最低(图2K和L)。总结了动物实验的完整统计分析(补充图S4A)。在任何治疗方案中,小鼠的体重都没有明显减轻,这表明三联疗法对哺乳动物的毒性较低(补充图S4B和S4C)。 |
| 酶活实验 |
在 DMSO 中制备 PD0332991 的储备溶液。 CDK 检测在 96 孔过滤板上进行。通过用杆状病毒感染昆虫细胞,所有 CDK-细胞周期蛋白激酶复合物都得到表达和纯化。 pRb 与 GST 融合(GST·RB-Cterm)的一部分(跨越氨基酸 792-928)用作测定的底物。每孔总体积为 0.1 mL,包含以下终浓度:20 mM Tris-HCl,pH 7.4,50 mM NaCl,1 mM 二硫苏糖醇,10 mM MgCl2,25 μM ATP(用于 CDK4-细胞周期蛋白 D1、CDK6-细胞周期蛋白D2 和 CDK6-细胞周期蛋白 D3),或 12 μM ATP(对于 CDK2-细胞周期蛋白 E、CDK2-细胞周期蛋白 A 和 CDC2-细胞周期蛋白 B)。该混合物还含有 0.25 μCi 的 [γ-32P]ATP、20 ng 酶、1 μg GST·RB-Cterm 和 PD 0332991 (0.001-0.1μM)。将除 [γ-32P]ATP 之外的所有成分添加到孔中后,将板放在板混合器上两分钟。添加 [γ-32P]ATP 以引发反应后,将板在 25°C 下孵育 15 分钟。将板在 4 °C 下保持至少一小时,使底物沉淀,然后添加 0.1 mL 20% 三氯乙酸终止反应。接下来,用0.2mL 10%三氯乙酸洗孔5次,并使用β板计数器测量放射性掺入。
|
| 细胞实验 |
经过 72 小时载体或药物治疗后,使用 Cell Titer Glo 测定评估细胞活力。在氟维司群治疗之前,细胞在不含雌激素的条件下生长,并添加雌二醇至终浓度 10-8 M。对于每个细胞系,palbociclib、氟维司群和 tucatinib 的 IC30 值为决定; IC30 浓度随后用于后续研究。
|
| 动物实验 |
NCG mice injected with MDA-MB-361 cells
50mg/kg o.g. Oral administration of PD 0332991 to mice bearing the Colo-205 human colon carcinoma produces marked tumor regression. Therapeutic doses of PD 0332991 cause elimination of phospho-Rb and the proliferative marker Ki-67 in tumor tissue and down-regulation of genes under the transcriptional control of E2F. The results indicate that inhibition of Cdk4/6 alone is sufficient to cause tumor regression and a net reduction in tumor burden in some tumors.[1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Palbociclib presents a linear pharmacokinetic profile and its peak plasma concentration was observed 6-12 hours after oral administration. The oral bioavailability is reported to be of 46% with a steady-state reached after 8 days and a median accumulation ratio of 2.4. The absorption of palbociclib is significantly reduced under fasting conditions and hence, food intake is recommended when this drug is administered. The main route of elimination of palbociclib is through feces after hepatic metabolism while renal clearance seems to play a minor role accounting only for 17.5% of the eliminated dose. The mean apparent distribution of palbociclib is 2583 L which suggests that palbociclib penetrates extensively into peripheral tissues. The mean apparent oral clearance of palbociclib is of 63.1 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Palbociclib is mainly hepatically transformed. the metabolism is mainly performed by the activities of the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme 3A and the sulfotransferase 2A1. The metabolism of palbociclib is represented mainly by reactions of oxidation and sulfonation followed by acylation and glucuronidation as minor reactions. After its metabolism, palbociclib forms mainly inactive glucuronide and sulfamic acid conjugates. The major circulating metabolite, accounting for 1.5% of the dose in excreta is is the glucuronide conjugate. Biological Half-Life The mean plasma elimination half-life of palbociclib is 29 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In the large clinical trials, adverse events were common and led to dose reductions in one-third of patients and discontinuation in 8%. Publications on the efficacy and safety of palbociclib rarely mentioned serum ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity. In a study of women with refractory, metastatic breast cancer, serum ALT elevations occurred in 6% [2% over 5 times ULN] receiving palbociclib and fulvestrant compared to 3% [none over 5 times ULN] on fulvestrant alone. Since its approval and more widescale use, there have been several reports of prominent ALT elevations arising after 2 or 3 cycles of palbociclib, that improved on discontinuation and recurred rapidly when restarted. Serum bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase levels were normal and symptoms were not mentioned. In addition, there have been rare reports of patients with refractory metastatic breast cancer who developed pseudocirrhosis within 2 to 3 months of starting palbociclib presenting with fatigue, jaundice and ascites with only modest elevations in serum aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase levels. Imaging revealed a severely nodular liver, but liver histology showed desmoplastic changes in areas of necrotic metastatic tumor without cirrhosis. The liver also had vascular changes suggestive of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome, changes possibly caused by the dramatic involution of the metastatic tumor tissue combined with vascular damage. Pseudocirrhosis has been reported with other highly successful antineoplastic therapies of cancer metastatic to the liver, but the frequency is rare. Likelihood score: C (probable rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury that may represent pseudocirrhosis from nodular transformation of the liver in response to necrosis of hepatic metastases). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of palbociclib during breastfeeding. Because palbociclib is 85% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, its half-life is about 29 hours and it might accumulate in the infant. It is also given in combination with letrozole or fulvestrant, which may increase the risk to the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during palbociclib therapy and for 3 weeks after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Binding of palbociclib to human plasma proteins in vitro accounts for approximately 85% of the administered dose. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Due to its mechanism of action, palbociclib inhibits cell growth and suppresses DNA replication in retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene (RB) proficient cancer cells. As expected, these RB cells present a significant increase in the proportion of cells in G1 state and the presence of palbociclib produces effective dephosphorylation of RB, reduce proliferation and induce senescence causing cell-cycle arrest. In vitro studies showed the potential for palbociclib to reduce cellular proliferation of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cell lines through the inhibition of the cell-cycle progression from G1 to S phase. In this study, it was demonstrated that the sensitivity of the cells significantly increased with the expression of _RB1_ and _CCND1_ and low expression of _CDKN2A_. As well, palbociclib, combined with antiestrogens, enhanced _in vivo_ antitumor activity in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer mouse models. In clinical trials, palbociclib, in combination with letrozole, was shown to significantly increase the progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with metastatic breast cancer without prior endocrine treatment. In the results, the PFS increased from 4.5 to 9.5 months with an overall response rate (ORR) of 24.6%. Breast cancers that express hormonal receptors (HR) and HER2 display resistance to targeted therapy. Tumor-promotional signaling from the HER2 and estrogen receptor (ER) pathways converges at the cyclin D1 and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) 4 and 6 complex, which drives cell-cycle progression and development of therapeutic resistance. Therefore, we hypothesized that co-targeting of ER, HER2, and CDK4/6 may result in improved tumoricidal activity and suppress drug-resistant subclones that arise on therapy. We tested the activity of the triple targeted combination therapy with tucatinib (HER2 small-molecule inhibitor), palbociclib (CKD4/6 inhibitor), and fulvestrant (selective ER degrader) in HR+/HER2+ human breast tumor cell lines and xenograft models. In addition, we evaluated whether triple targeted combination prevents growth of tucatinib or palbociclib-resistant subclones in vitro and in vivo. Triple targeted combination significantly reduced HR+/HER2+ tumor cell viability, clonogenic survival, and in vivo growth. Moreover, survival of HR+/HER2+ cells that were resistant to the third drug in the regimen was reduced by the other two drugs in combination. We propose that a targeted triple combination approach will be clinically effective in the treatment of otherwise drug-resistant tumors, inducing robust responses in patients.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C24H29N7O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
447.54
|
| 精确质量 |
447.238
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 64.41; H, 6.53; N, 21.91; O, 7.15
|
| CAS号 |
571190-30-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Palbociclib monohydrochloride;827022-32-2;Palbociclib hydrochloride;571189-11-2;Palbociclib-d8;1628752-83-9;Palbociclib isethionate;827022-33-3;Palbociclib dihydrochloride;Palbociclib orotate;2757498-64-7;Palbociclib-d4 hydrochloride
|
| PubChem CID |
5330286
|
| 外观&性状 |
Yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
711.5±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
200ºC
|
| 闪点 |
384.1±35.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.648
|
| LogP |
0.99
|
| tPSA |
105.04
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
775
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C1C(C(C([H])([H])[H])=O)=C(C([H])([H])[H])C2=C([H])N=C(N([H])C3C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])N=3)N3C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])([H])C3([H])[H])N=C2N1C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H]
|
| InChi Key |
AHJRHEGDXFFMBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H29N7O2/c1-15-19-14-27-24(28-20-8-7-18(13-26-20)30-11-9-25-10-12-30)29-22(19)31(17-5-3-4-6-17)23(33)21(15)16(2)32/h7-8,13-14,17,25H,3-6,9-12H2,1-2H3,(H,26,27,28,29)
|
| 化学名 |
6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-[(5-piperazin-1-ylpyridin-2-yl)amino]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one;hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
PD0332991; Palbociclib free base; UNII-G9ZF61LE7G; 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-((5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)amino)pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(8H)-one; PD-0332991; PD 0332991; Trade name: Ibrance.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2 mg/mL (4.47 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2 mg/mL (4.47 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.0mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 6.67 mg/mL (14.90 mM) in 0.5% CMC/saline water (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液; 需要超声波加热并加热至 42°C。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2344 mL | 11.1722 mL | 22.3444 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4469 mL | 2.2344 mL | 4.4689 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2234 mL | 1.1172 mL | 2.2344 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03936270 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Palbociclib 125mg Drug: Letrozole 2.5mg |
Ovarian Cancer | Latin American Cooperative Oncology Group |
January 27, 2020 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04288089 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Palbociclib (75, 100, 125 milligram [mg]) Drug: H3B-6545 (150, 300, 450 mg) |
Receptors, Estrogen Genes, Erbb-2 |
Eisai Inc. | April 1, 2020 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02738866 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Palbociclib Drug: Fulvestrant |
Metastatic Breast Cancer | Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins |
October 25, 2016 | Phase 2 |
| NCT01864746 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Palbociclib PD-0332991 Drug: Placebo |
Breast Cancer Her2-normal |
German Breast Group | November 2013 | Phase 3 |
| NCT03446157 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Cetuximab Drug: Palbociclib |
Colonic Cancer Colon Cancer |
UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center |
March 13, 2018 | Phase 2 |
Evaluation of IC50concentrations of the CDK inhibitors dinaciclib and palbociclib on proliferation, and their effects on CDK-Rb-E2F signaling in human HPASMCs from healthy donors and IPAH patients.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
|---|
Effects of the CDK inhibitors dinaciclib and palbociclib on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
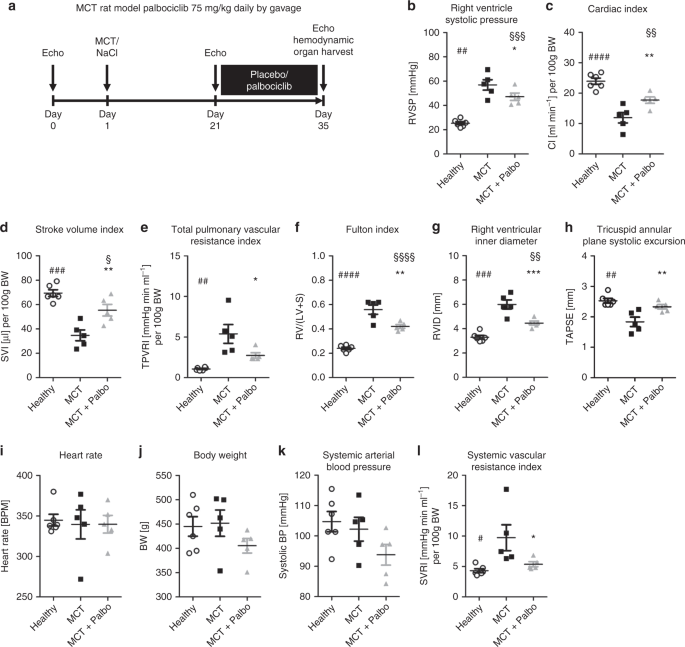 Effects of palbociclib on disease progression in the MCT rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
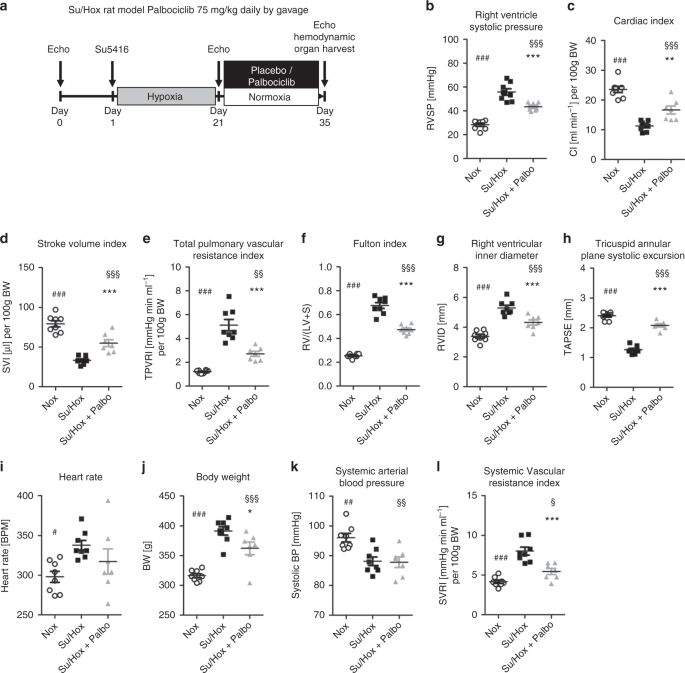 Effects of palbociclib on disease progression in the Su/Hox rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
|---|
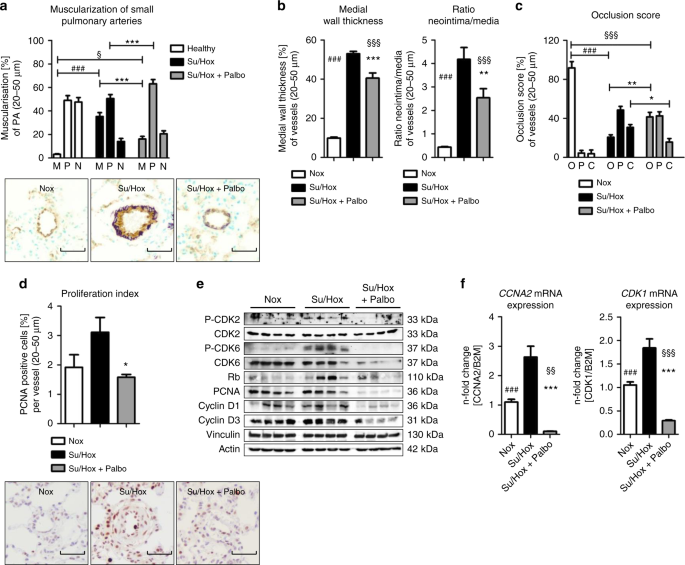 Ex vivo analyses of lung tissue for reversal of remodeling and in vivo drug efficacy in the Su/Hox model.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
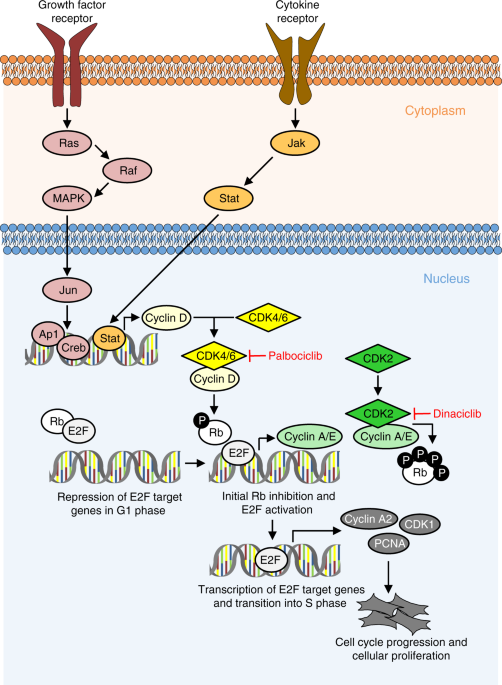 Proposed mechanism of action of palbociclib and dinaciclib in PAH. Multiple growth factors, cytokines, and mitogens induce the activation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), e.g., by increasing the expression of cyclin D1.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |