
| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
Cdk4/cyclin D3 (IC50 = 9 nM); Cdk4/cyclin D1 (IC50 = 11 nM); Cdk6/cyclin D2 (IC50 = 16 nM); DYRK1A (IC50 = 2000 nM); MAPK (IC50 = 8000 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:PD 0332991 对 CDK4/6 表现出绝对选择性,而对其他 CDK 几乎没有或没有活性。 PD 0332991 可有效降低 MDA-MB-435 乳腺癌细胞中 Ser780 和 Ser795 的 Rb 磷酸化,IC50 分别为 66 nM 和 63 nM。 PD 0332991 是一种有效的细胞生长抑制剂,通过阻止细胞进入 S 期来抑制 DNA 复制。 PD 0332991 抑制胸苷掺入 Rb 阳性人乳腺癌(例如 MDA-MB-435、MCF-7)、结肠癌(H1299)、肺癌(Colo-205)以及人白血病(CRRF-CEM)的 DNA和 K562),IC50 值范围为 0.04-0.17 μM。 PD 0332991显着增加了G1期MDA-MB-453的百分比。 PD 0332991 抑制循环 CD138+ 原代骨髓瘤细胞、未转化的原代 B 细胞、MM1.S 和 CAG HMCL 细胞系中 Rb 的磷酸化,IC50 分别为 <0.1 μM、0.05 μM 和 60-70 nM。 PD 0332991 治疗还诱导 CD138+ 原代骨髓瘤和未转化的原代 B 细胞的 G1 期停滞。 PD 0332991 诱导 MM1.S G1 期阻滞,IC50 约为 0.05 μM。 PD 0332991 优先抑制管腔雌激素受体阳性(包括 HER2 阳性)人乳腺癌细胞系的增殖。 PD 0332991 在大多数敏感品系中增加 pRb 和细胞周期蛋白 D1 的基因表达,并降低 CDKN2A (p16) 的基因表达。 PD 0332991 增强对 ER 阻断具有条件抗性的细胞系对他莫昔芬的敏感性。激酶测定:用于 IC50 测定和动力学评估的 CDK 测定在 96 孔滤板中进行。所有CDK-细胞周期蛋白激酶复合物均通过杆状病毒感染在昆虫细胞中表达并纯化。检测的底物是与 GST 融合的 pRb 片段(氨基酸 792-928)(GST•RB-Cterm)。总反应体积为 0.1 mL,含有最终浓度为 20 mM Tris-HCl、pH 7.4、50 mM NaCl、1 mM 二硫苏糖醇、10 mM MgCl2 25 μM ATP(对于 CDK4-细胞周期蛋白 D1、CDK6-细胞周期蛋白 D2 和 CDK6- cyclin D3) 含有 0.25 μCi 的 [γ-32P]ATP、20 ng 酶、1 μg GST•RB-Cterm 和适当稀释的抑制剂。除[γ-32P]ATP 之外的所有组分均添加至孔中,并置于平板混合器上 2 分钟。加入[γ-32P]ATP开始反应,25℃孵育15分钟。加入0.1 mL 20%三氯乙酸终止反应,并将板在4℃下保持至少1小时以使底物沉淀。然后用 0.2 mL 10% 三氯乙酸洗涤孔五次,并用 β 板计数器测定放射性掺入。细胞测定:将细胞(人乳腺癌细胞 MDA-MB-435)以每孔 5,000 至 10,000 个细胞一式两份接种在 24 孔板中。电镀后第二天,添加不同浓度的 PD 0332991。没有药物的对照孔也被接种。孵育结束时,将细胞用胰蛋白酶消化并置于 Isotone 溶液中,并立即使用 Coulter Z2 颗粒计数器进行计数。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
PD 0332991(150 mg/kg) 可快速消退 Colo-205 结肠癌异种移植物并延迟相应的肿瘤生长。 PD 0332991 (150 mg/kg) 可诱导 MDA-MB-435 乳腺癌完全肿瘤停滞和细胞死亡。 PD 0332991 (150 mg/kg) 还在携带 SF-295 胶质母细胞瘤异种移植物的小鼠以及 ZR-75-1 乳腺癌和 PC-3 前列腺肿瘤模型中诱导显着的肿瘤消退(完全抑制肿瘤生长)。 PD 0332991 (150 mg/kg) 在整个 24 小时内抑制 MDA-MB-435 乳腺癌中的 Rb Ser780 磷酸化。 PD 0332991 (150 mg/kg) 下调 Colo-205 癌异种移植物中四种 E2F 调节基因 CDC2、CCNE2、TK1 和 TOP2A 的表达。 PD 0332991 还可以快速抑制骨髓瘤肿瘤的生长。
对携带Colo-205人结肠癌的小鼠口服PD 0332991可产生明显的肿瘤消退。治疗剂量的PD 0332991导致肿瘤组织中磷酸化Rb和增殖标志物Ki-67的消除,并在E2F的转录控制下下调基因。结果表明,单独抑制Cdk4/6足以导致某些肿瘤的肿瘤消退和肿瘤负荷的净减少[1]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
CDK 测定在 96 孔滤板中进行,用于动力学分析和 IC50 计算。通过用杆状病毒感染昆虫细胞,所有 CDK-细胞周期蛋白激酶复合物都得到表达和纯化。与 GST 融合的 pRb 的一部分(氨基酸 792-928)用作测定的底物 (GST•RB-Cterm)。 20 mM Tris-HCl,pH 7.4,50 mM NaCl,1 mM 二硫苏糖醇,10 mM MgCl2,25 μM ATP(用于 CDK4-细胞周期蛋白 D1、CDK6-细胞周期蛋白 D2 和 CDK6-细胞周期蛋白 D3)、0.25 μCi [γ-32P ]ATP、20 ng 酶、1 μg GST•RB-Cterm 和适当稀释的抑制剂包含在 0.1 mL 的总反应体积中。将除 [γ-32P]ATP 之外的所有成分添加到孔中后,将它们放在平板混合器上两分钟。添加 [γ-32P]ATP 启动反应,然后在 25°C 下孵育 15 分钟。为了使底物沉淀,通过添加 0.1 mL 20% 三氯乙酸并将板在 4°C 下保持至少 1 小时来终止反应。用 0.2 mL 10% 三氯乙酸洗五次孔后,使用 β 板计数器测量放射性掺入。
|
| 细胞实验 |
在 24 孔板中,细胞一式两份接种,每孔 5,000-10,000 个细胞。电镀后第二天添加不同浓度的 PD 0332991。还接种无药物对照孔。孵育后,将胰蛋白酶处理的细胞添加到等酮溶液中,立即使用 Coulter Z2 颗粒计数器进行计数。
|
| 动物实验 |
Human colon carcinoma xenografts Colo-205
150 mg/kg o.p. injection every day Oral administration of PD 0332991 to mice bearing the Colo-205 human colon carcinoma produces marked tumor regression. Therapeutic doses of PD 0332991 cause elimination of phospho-Rb and the proliferative marker Ki-67 in tumor tissue and down-regulation of genes under the transcriptional control of E2F. The results indicate that inhibition of Cdk4/6 alone is sufficient to cause tumor regression and a net reduction in tumor burden in some tumors.[1] By specific inhibition of Cdk4/6, the orally active small-molecule PD 0332991 potently induces G(1) arrest in primary bone marrow myeloma cells ex vivo and prevents tumor growth in disseminated human myeloma xenografts. PD 0332991 inhibits Cdk4/6 proportional to the cycling status of the cells independent of cellular transformation and acts in concert with the physiologic Cdk4/6 inhibitor p18(INK4c). Inhibition of Cdk4/6 by PD 0332991 is not accompanied by induction of apoptosis. However, when used in combination with a second agent, such as dexamethasone, PD 0332991 markedly enhances the killing of myeloma cells by dexamethasone. PD 0332991, therefore, represents the first promising and specific inhibitor for therapeutic targeting of Cdk4/6 in multiple myeloma and possibly other B-cell cancers.[2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Palbociclib presents a linear pharmacokinetic profile and its peak plasma concentration was observed 6-12 hours after oral administration. The oral bioavailability is reported to be of 46% with a steady-state reached after 8 days and a median accumulation ratio of 2.4. The absorption of palbociclib is significantly reduced under fasting conditions and hence, food intake is recommended when this drug is administered. The main route of elimination of palbociclib is through feces after hepatic metabolism while renal clearance seems to play a minor role accounting only for 17.5% of the eliminated dose. The mean apparent distribution of palbociclib is 2583 L which suggests that palbociclib penetrates extensively into peripheral tissues. The mean apparent oral clearance of palbociclib is of 63.1 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Palbociclib is mainly hepatically transformed. the metabolism is mainly performed by the activities of the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme 3A and the sulfotransferase 2A1. The metabolism of palbociclib is represented mainly by reactions of oxidation and sulfonation followed by acylation and glucuronidation as minor reactions. After its metabolism, palbociclib forms mainly inactive glucuronide and sulfamic acid conjugates. The major circulating metabolite, accounting for 1.5% of the dose in excreta is is the glucuronide conjugate. Biological Half-Life The mean plasma elimination half-life of palbociclib is 29 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In the large clinical trials, adverse events were common and led to dose reductions in one-third of patients and discontinuation in 8%. Publications on the efficacy and safety of palbociclib rarely mentioned serum ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity. In a study of women with refractory, metastatic breast cancer, serum ALT elevations occurred in 6% [2% over 5 times ULN] receiving palbociclib and fulvestrant compared to 3% [none over 5 times ULN] on fulvestrant alone. Since its approval and more widescale use, there have been several reports of prominent ALT elevations arising after 2 or 3 cycles of palbociclib, that improved on discontinuation and recurred rapidly when restarted. Serum bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase levels were normal and symptoms were not mentioned. In addition, there have been rare reports of patients with refractory metastatic breast cancer who developed pseudocirrhosis within 2 to 3 months of starting palbociclib presenting with fatigue, jaundice and ascites with only modest elevations in serum aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase levels. Imaging revealed a severely nodular liver, but liver histology showed desmoplastic changes in areas of necrotic metastatic tumor without cirrhosis. The liver also had vascular changes suggestive of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome, changes possibly caused by the dramatic involution of the metastatic tumor tissue combined with vascular damage. Pseudocirrhosis has been reported with other highly successful antineoplastic therapies of cancer metastatic to the liver, but the frequency is rare. Likelihood score: C (probable rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury that may represent pseudocirrhosis from nodular transformation of the liver in response to necrosis of hepatic metastases). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of palbociclib during breastfeeding. Because palbociclib is 85% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, its half-life is about 29 hours and it might accumulate in the infant. It is also given in combination with letrozole or fulvestrant, which may increase the risk to the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during palbociclib therapy and for 3 weeks after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Binding of palbociclib to human plasma proteins in vitro accounts for approximately 85% of the administered dose. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Palbociclib Isethionate is the isethionate salt form of palbociclib, an orally available cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. Palbociclib selectively inhibits cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) and 6 (CDK6), thereby inhibiting retinoblastoma (Rb) protein phosphorylation early in the G1 phase leading to cell cycle arrest. This suppresses DNA replication and decreases tumor cell proliferation. CDK4 and 6 are serine/threonine kinases that are upregulated in many tumor cell types and play a key role in the regulation of cell cycle progression.
Palbociclib is a member of the class of pyridopyrimidines that is 2-{[5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]amino}pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one bearing additional methyl, acetyl and cyclopentyl substituents at positions 5, 6 and 8 respectively. It is used in combination with letrozole for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. It has a role as an EC 2.7.11.22 (cyclin-dependent kinase) inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent. It is a pyridopyrimidine, an aminopyridine, a secondary amino compound, a member of piperidines, an aromatic ketone, a member of cyclopentanes and a tertiary amino compound. Palbociclib is a piperazine pyridopyrimidine that acts in the cell cycle machinery. It is a second generation cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor selected from a group of pyridopyrimidine compounds due to its favorable physical and pharmaceutical properties. Palbociclib was developed by Pfizer Inc after the discovery that identified the cyclin-dependent kinases as key regulators of cell growth. It was originally FDA approved on March 2015 for the treatment of HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer and its indications were updated in April 2019 to include male patients based on findings from postmarketing reports and electronic health records demonstrating safety and clinical efficacy. Palbociclib is a Kinase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of palbociclib is as a Kinase Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 3A Inhibitor. Palbociclib is a unique cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor that is used in combination with aromatase inhibitors in the treatment of postmenopausal women with metastatic breast cancer. Palbociclib is associated with transient and usually mild elevations in serum aminotransferase during therapy and to an unusual form of liver injury called pseudocirrhosis caused by shrinkage of tumor metastases in the liver combined with desmoplastic changes and vascular damage, that can be severe, progressive and even fatal. Palbociclib is an orally available cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. Palbociclib selectively inhibits cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) and 6 (CDK6), thereby inhibiting retinoblastoma (Rb) protein phosphorylation early in the G1 phase leading to cell cycle arrest. This suppresses DNA replication and decreases tumor cell proliferation. CDK4 and 6 are serine/threonine kinases that are upregulated in many tumor cell types and play a key role in the regulation of cell cycle progression. See also: Palbociclib Isethionate (is active moiety of). Drug Indication Palbociclib is indicated in combination with [letrozole] as initial endocrine-based therapy for the treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 (HER2)-negative and hormone receptor(HR)-positive tumors in adult patients with advanced/metastatic breast cancer. It is as well approved in combination with [fulvestrant] in patients with disease progression with prior endocrine therapy. In the official labeling, the use of palbociclib should be accompanied with either an aromatase inhibition, no restricted to letrozole, as initial endocrine-based therapy in postmenopausal women or in man. The breast cancer starts as a group of cancer cells that grow into and destroy the nearby breast tissue. This growth can spread into other parts of the body which is called metastasis. According to the location of the cancer cells, it can be categorized in ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma. However, other types of breast cancer include inflammatory breast cancer, Paget disease of the breast, triple negative breast cancer non-Hodgkin lymphoma and soft tissue sarcoma. In males, breast cancer is usually treated as the cases of postmenopausal women and almost all the cases are ductal carcinoma. FDA Label Ibrance is indicated for the treatment of hormone receptor (HR) positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer : in combination with an aromatase inhibitor; in combination with fulvestrant in women who have received prior endocrine therapy. In pre- or perimenopausal women, the endocrine therapy should be combined with a luteinizing hormone releasing hormone (LHRH) agonist. Treatment of Ewing sarcoma Treatment of breast malignant neoplasms Mechanism of Action Palbociclib is a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor that acts by binding to the ATP pocket with an IC50 in the range of 9-15 nmol/L. It is important to consider that it presents low to absent activity against other kinases. The CDK4/6 kinase is involved, with coregulatory partner cyclin D, in the G1-S transition. Hence, inhibition of this step prevents cell cycle progression in cells in whose this pathway is functioning. This step includes the pathways of the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein and the E2F family of transcription factors. |
| 分子式 |
C26H35N7O6S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
573.66
|
| 精确质量 |
573.236
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 54.44; H, 6.15; N, 17.09; O, 16.73; S, 5.59
|
| CAS号 |
827022-33-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Palbociclib;571190-30-2;Palbociclib monohydrochloride;827022-32-2;Palbociclib dihydrochloride
|
| PubChem CID |
11478676
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
3.379
|
| tPSA |
188.02
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
40
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
892
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CC(C1=C(N2C3CCCC3)N=C(NC4=NC=C(N5CCNCC5)C=C4)N=C1)=C(C(C)=O)C2=O.OCCS(O)(=O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
LYYVFHRFIJKPOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H29N7O2.C2H6O4S/c1-15-19-14-27-24(28-20-8-7-18(13-26-20)30-11-9-25-10-12-30)29-22(19)31(17-5-3-4-6-17)23(33)21(15)16(2)32;3-1-2-7(4,5)6/h7-8,13-14,17,25H,3-6,9-12H2,1-2H3,(H,26,27,28,29);3H,1-2H2,(H,4,5,6)
|
| 化学名 |
6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-[(5-piperazin-1-ylpyridin-2-yl)amino]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one;2-hydroxyethanesulfonic acid
|
| 别名 |
PD0332991 isethionate salt; PD-0332991; Palbociclib Isethionate; 827022-33-3; PD0332991 Isethionate; PD 0332991 isethionate; UNII-W1NYL2IRDR; W1NYL2IRDR; Palbociclib Isethionate [USAN]; Palbociclib (isethionate); PD 0332991; Palbociclib isethionate salt; Trade name: Ibrance
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 1 mg/mL (1.74 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 10.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: Saline: 30 mg/mL (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加). *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7432 mL | 8.7160 mL | 17.4319 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3486 mL | 1.7432 mL | 3.4864 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1743 mL | 0.8716 mL | 1.7432 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04693468 | Recruiting | Drug: Palbociclib Isethionate Drug: Crizotinib |
Advanced Malignant Solid Neoplasm Metastatic Malignant Solid Neoplasm |
M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | December 1, 2020 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01602887 | Completed | Drug: PD-0332991 | Healthy | Pfizer | May 2012 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02041273 | Completed | Drug: palbociclib isethionate (phase 1 and 2 studies) Drug: palbociclib commercial free base capsule |
Healthy | Pfizer | January 2014 | Phase 1 |
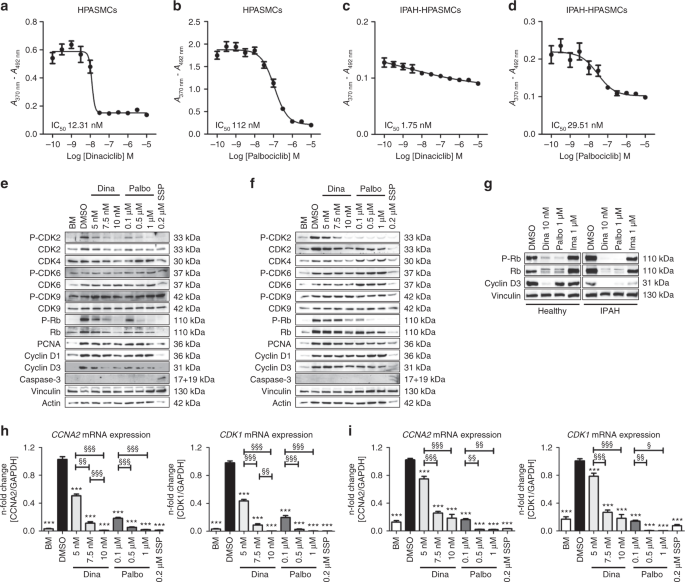 Evaluation of IC50concentrations of the CDK inhibitors dinaciclib and palbociclib on proliferation, and their effects on CDK-Rb-E2F signaling in human HPASMCs from healthy donors and IPAH patients.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
|---|
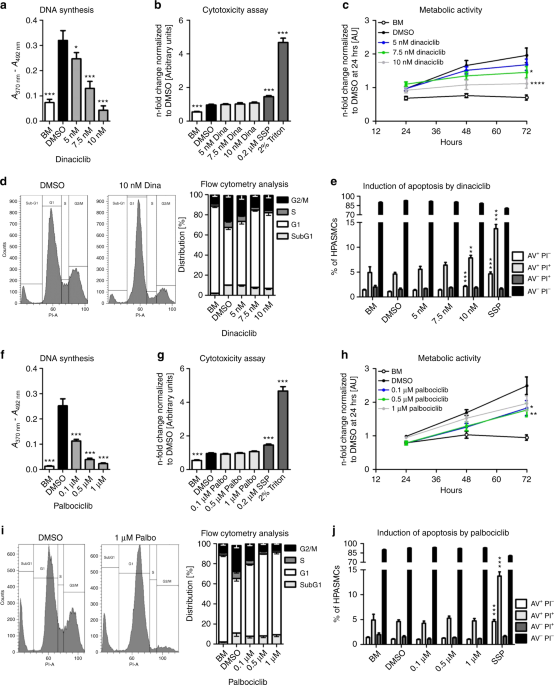 Effects of the CDK inhibitors dinaciclib and palbociclib on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
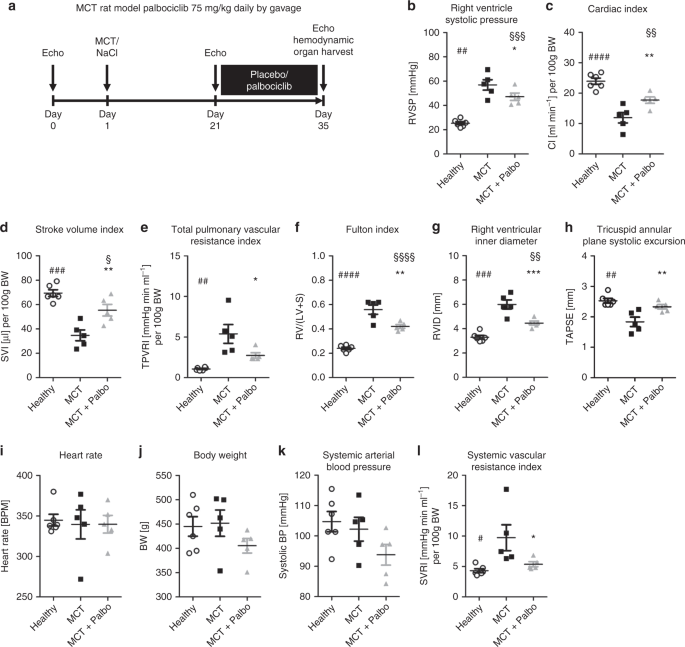 Effects of palbociclib on disease progression in the MCT rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
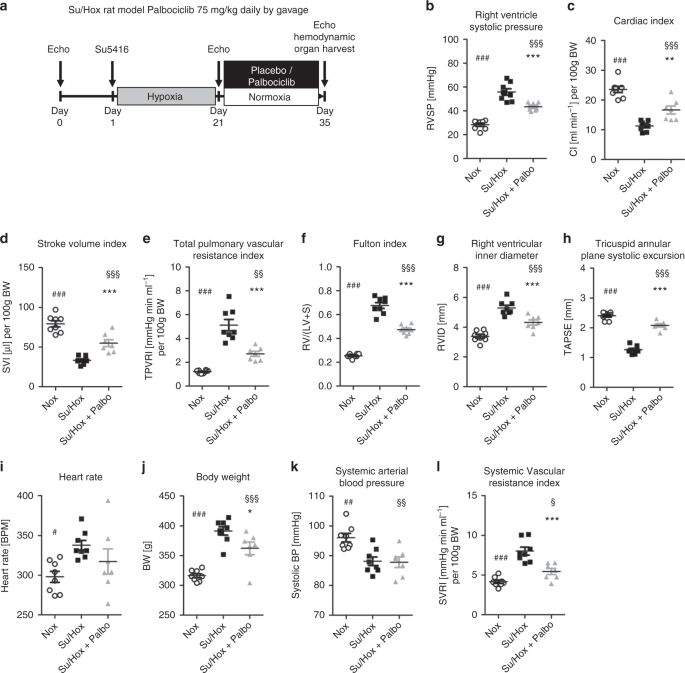 Effects of palbociclib on disease progression in the Su/Hox rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
|---|
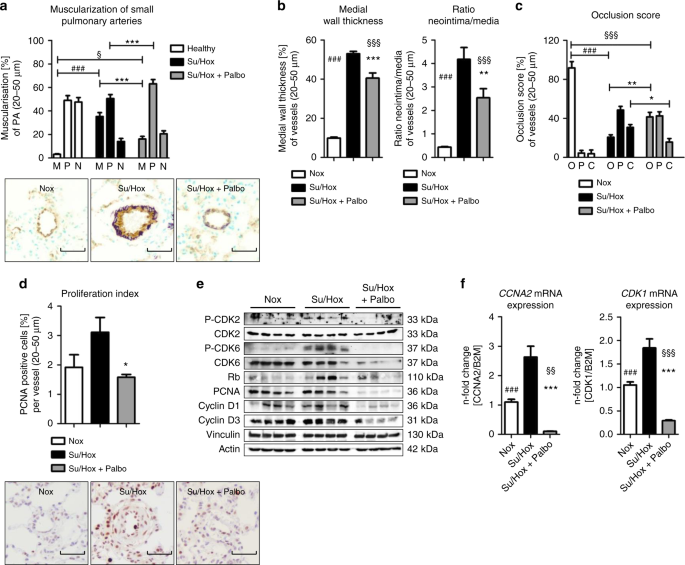 Ex vivo analyses of lung tissue for reversal of remodeling and in vivo drug efficacy in the Su/Hox model.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
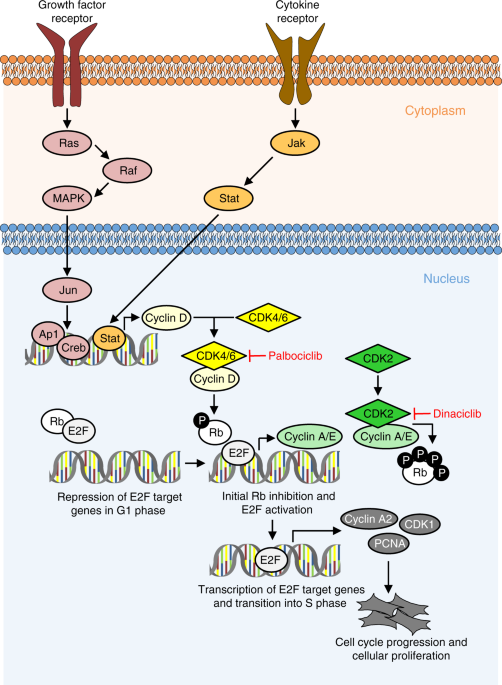 Proposed mechanism of action of palbociclib and dinaciclib in PAH. Multiple growth factors, cytokines, and mitogens induce the activation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), e.g., by increasing the expression of cyclin D1.Nat Commun.2019May 17;10(1):2204. |
|
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
|