| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
PDGFRβ (Ki = 8 nM); FGFR1 (Ki = 1.2 μM); Flt-1 (Ki = 2.1 μM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:TSU-68 是 ATP、Flk-1/KDR 反式磷酸化、FGFR1 反式磷酸化和 PDGFRβ 激酶自磷酸化的竞争性抑制剂。 TSU-68 (0.03-10 μM) 抑制 VEGF 刺激的 HUVEC 中 KDR 的酪氨酸磷酸化。 TSU-68 还以 0.03-0.1 μM 的最低浓度抑制过度表达 PDGFRβ 的 NIH-3T3 细胞中 PDGF 刺激的 PDGFRβ 酪氨酸磷酸化。 TSU-68 在 10 μM 或更高浓度时可抑制酸性 FGF 诱导的 FGFR1 底物 2 磷酸化。然而,TSU-68(最高 100 μM)对过度表达 EGFR 的 NIH-3T3 细胞中 EGF 刺激的 EGFR 酪氨酸磷酸化没有影响。 TSU-68 抑制 VEGF 驱动和 FGF 驱动的 HUVEC 有丝分裂,平均 IC50 分别为 0.34 μM 和 9.6 μM。在人骨髓性白血病 MO7E 细胞中,TSU-68 抑制干细胞因子 (SCF) 受体 c-kit 的酪氨酸自磷酸化,IC50 为 0.1-1 μM,以及 ERK1/2 磷酸化(c-下游的信号传导事件)套件激活。 TSU-68 还抑制 SCF 诱导的 MO7E 细胞增殖,IC50 为 0.29 μM,并诱导细胞凋亡。激酶测定:用于定量 Flk-1 和 FGFR1 转磷酸化活性的酪氨酸激酶测定在用肽底物聚-Glu 预涂(20 μg/孔,溶于 PBS;在 4 °C 下孵育过夜)的 96 孔微量滴定板中进行,提尔 (4:1)。多余的蛋白质结合位点用 PBS 中的 1-5% (w/v) BSA 封闭。然后将纯化的 GST-FGFR1(激酶结构域)或 GST-Flk-1(细胞质结构域)融合蛋白添加到含有 2 倍浓度激酶稀释缓冲液的微量滴定孔中,缓冲液由 100 mM HEPES、50 mM NaCl、40 μM NaVO4 和 0.02 组成。 % (w/v) BSA。 GST-Flk-1 和 GST-FGFR1 的最终酶浓度为 50 ng/mL。 SU6668 以最终所需浓度的 100 倍溶解在 DMSO 中,并在水中按 1:25 稀释。随后将 25 μL 稀释的 SU6668 添加到每个反应孔中。通过在 MnCl2 溶液中添加不同浓度的 ATP 来启动激酶反应,使得最终 ATP 浓度跨越酶的 Km,并且 MnCl2 的最终浓度为 10 mM。将板在室温下孵育 5-15 分钟,然后添加 EDTA 停止反应。然后用TBST洗涤板3次。将兔多克隆抗磷酸酪氨酸抗血清以 1:10000 稀释度添加到含有 0.5% (w/v) BSA、0.025% (w/v) 脱脂奶粉和 100 μM NaVO4 的 TBST 中,并在 37° 下孵育 1 小时C。然后用TBST洗涤板3次,随后添加与HRP缀合的山羊抗兔抗血清。将板在 37°C 下孵育 1 小时,然后用 TBST 洗涤 3 次。细胞测定:将细胞(HUVEC 和过表达 PDGFRβ 或 EGFR 的 NIH-3T3 细胞)接种(3 × 105 个细胞/35 mm 孔)于含有 10% (v/v) FBS 的 DMEM 中,生长至汇合,然后在 DMEM 中静止药物治疗前2小时含0.1%血清。 HUVEC(以 2 × 106 个细胞/10 cm 板接种)在内皮细胞生长培养基中生长至汇合,然后在药物治疗前在含有 0.5% FBS 的内皮细胞基础培养基中静默 24 小时。所有细胞系均与 SU6668 一起孵育 1 小时,然后配体刺激 (100 ng/mL) 10 分钟。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
TSU-68 (75-200 mg/kg) 可诱导无胸腺小鼠异种移植模型中多种肿瘤类型的肿瘤生长抑制,包括 A375、Colo205、H460、Calu-6、C6、SF763T 和 SKOV3TP5 细胞。 TSU-68 (75 mg/kg) 还抑制 C6 神经胶质瘤异种移植物的肿瘤血管生成。在 HT29 人类结肠癌肿瘤模型中,TSU-68 (200 mg/kg) 降低了肿瘤边缘和核心的平均血管通透性和平均血浆体积分数。 TSU-68 促进癌症周围的异常基质发育。在兔 VX2 肝肿瘤模型中,TSU-68 (200 mg/kg) 增强化疗输注的效果。
|
| 酶活实验 |
酪氨酸激酶测定在 96 孔微量滴定板中使用,该板已在 PBS 中预涂(20 μg/孔),并与肽底物聚-Glu,Tyr (4:1) 在 4 °C 下孵育过夜。这些测定的目的是量化 Flk-1 和 FGFR1 的转磷酸化活性。 PBS 中百分之一到百分之五 (w/v) 的 BSA 用于封闭多余的蛋白质结合位点。然后用纯化的 GST-FGFR1(激酶结构域)或 GST-Flk-1(细胞质结构域)融合蛋白填充微量滴定孔,该融合蛋白溶于 2 倍浓度的激酶稀释缓冲液中,该缓冲液含有 40 μM NaVO4、50 mM NaCl、100 mM HEPES 和 0.02% (w/v) BSA。对于 GST-Flk-1 和 GST-FGFR1,最终酶浓度为 50 ng/mL。 SU6668以100×最终所需浓度溶解在DMSO中后,用H2O稀释1:25。然后每个反应孔中填充 25 μL 稀释的 SU6668。将不同浓度的 ATP 添加到 MnCl2 溶液中以启动激酶反应。 MnCl2 的最终浓度为 10 mM,最终 ATP 浓度跨越酶的 Km。在添加 EDTA 终止反应之前,将板在室温下孵育 5 至 15 分钟。然后用TBST洗板3次。在含有 0.5% (w/v) BSA、0.025% (w/v) 脱脂奶粉和 100 μM NaVO4 的 TBST 中,将兔多克隆抗磷酸酪氨酸抗血清按 1:10,000 稀释并添加到孔中。孵化过程在 37°C 下持续一小时。接下来,在 3 次 TBST 洗涤后,将与 HRP 缀合的山羊抗兔抗血清添加到板中。将板在 37°C 下孵育一小时后,进行 3 次 TBST 洗涤。向每个孔中添加2,2后,测量磷酸酪氨酸的量。
|
| 细胞实验 |
在含有 10% (v/v) FBS 的 DMEM 中,接种细胞(HUVEC 和过表达 PDGFRβ 或 EGFR 的 NIH-3T3 细胞)(3 × 105 细胞/35 mm 孔),生长至汇合,然后在药物处理前在含有0.1%血清的DMEM中静默两小时。以 2 × 106 细胞/10 cm 板的密度接种后,HUVEC 在内皮细胞生长培养基中生长至汇合,随后在含有 0.5% FBS 的内皮细胞基础培养基中静默 24 小时药物治疗前。在用配体 (100 ng/mL) 刺激 10 分钟之前,所有细胞系均与 SU6668 一起孵育 1 小时。
|
| 动物实验 |
Mouse (Female, BALB/c, nu/nu) xenograft models of A375, Colo205, H460, Calu-6, C6, SF763T, and SKOV3TP5 tumor cells
75-200 mg/kg Via i.p. injection or oral gavage once daily. A s.c. tumor model of HT29 human colon carcinoma in athymic mice was used. DCE-MRI with a macromolecular contrast agent was used to measure transendothelial permeability and fractional plasma volume, accepted surrogate markers of tumor angiogenesis. CD31 immunohistochemical staining was used for assessing microvessels density and vessels area. Experiments were performed after 24 h, and 3, 7, and 14 days of treatment. Results: DCE-MRI clearly detected the early effect (after 24 h of treatment) of SU6668 on tumor vasculature as a 51% and 26% decrease in the average vessel permeability measured in the tumor rim and core (respectively). A substantial decrease was also observed in average fractional plasma volume in the rim (59%) and core (35%) of the tumor. Histological results confirmed magnetic resonance imaging findings. After 3, 7, and 14 days of treatment, postcontrast magnetic resonant images presented a thin strip of strongly enhanced tissue at the tumor periphery; histology examination showed that this hyperenhanced ring corresponded to strongly vascularized tissue adjacent but external to the tumor. Histology also revealed a strong decrease in the thickness of peripheral viable tissue, with a greatly reduced vessel count. SU6668 greatly inhibited tumor growth, with 60% inhibition at 14 days of treatment.[3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Metabolism / Metabolites
TSU-68 has known human metabolites that include TSU-68 metabolite 1, TSU-68 metabolite 2, and TSU-68 metabolite 3. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Orantinib has been used in trials studying the treatment of Lung Cancer, Breast Cancer, Kidney Cancer, Gastric Cancer, and Prostate Cancer, among others.
Orantinib is an orally bioavailable receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. SU6668 binds to and inhibits the autophosphorylation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2), platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), and fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR), thereby inhibiting angiogenesis and cell proliferation. SU6668 also inhibits the phosphorylation of the stem cell factor receptor tyrosine kinase c-kit, often expressed in acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Vascular endothelial growth factor, fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and their cognate receptor tyrosine kinases are strongly implicated in angiogenesis associated with solid tumors. Using rational drug design coupled with traditional screening technologies, we have discovered SU6668, a novel inhibitor of these receptors. Biochemical kinetic studies using isolated Flk-1, FGF receptor 1, and PDGF receptor beta kinases revealed that SU6668 has competitive inhibitory properties with respect to ATP. Cocrystallographic studies of SU6668 in the catalytic domain of FGF receptor 1 substantiated the adenine mimetic properties of its oxindole core. Molecular modeling of SU6668 in the ATP binding pockets of the FIk-1/KDR and PDGF receptor kinases provided insight to explain the relative potency and selectivity of SU6668 for these receptors. In cellular systems, SU6668 inhibited receptor tyrosine phosphorylation and mitogenesis after stimulation of cells by appropriate ligands. Oral or i.p. administration of SU6668 in athymic mice resulted in significant growth inhibition of a diverse panel of human tumor xenografts of glioma, melanoma, lung, colon, ovarian, and epidermoid origin. Furthermore, intravital multifluorescence videomicroscopy of C6 glioma xenografts in the dorsal skinfold chamber model revealed that SU6668 treatment suppressed tumor angiogenesis. Finally, SU6668 treatment induced striking regression of large established human tumor xenografts. Investigations of SU6668 activity in cancer patients are ongoing in Phase I clinical trials.[1] SU5416 and SU6668 are potent antiangiogenic small-molecule inhibitors of receptor tyrosine kinases, including those of the vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptor families. The stem cell factor (SCF) receptor, c-kit, is structurally related to these receptors and, although not expressed on mature peripheral blood cells, is expressed in leukemic blasts derived from 60% to 80% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients. The c-kit kinase inhibitory activity of SU5416 and SU6668 was evaluated in MO7E cells, a human myeloid leukemia cell line. Tyrosine autophosphorylation of the receptor, induced by SCF, was inhibited in these cells by SU5416 and SU6668 in a dose-dependent manner (inhibitory concentration of 50% [IC(50)] 0.1-1 microM). Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation, a signaling event downstream of c-kit activation, was also inhibited in a dose-dependent manner. Both compounds also inhibited SCF-induced proliferation of MO7E cells (IC(50) 0.1 microM for SU5416; 0.29 microM for SU6668). Furthermore, both SU5416 and SU6668 induced apoptosis in a dose- and time-dependent manner as measured by the increase in activated caspase-3 and the enhanced cleavage of its substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. These findings with MO7E cells were extended to leukemic blasts from c-kit(+) patients. In patient blasts, both SU5416 and SU6668 inhibited SCF-induced phosphorylation of c-kit and ERK1/2 and induced apoptosis. These studies indicate that SU5416 and SU6668 inhibit biologic functions of c-kit in addition to exhibiting antiangiogenic properties and suggest that the combination of these activities may provide a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of AML.[2] |
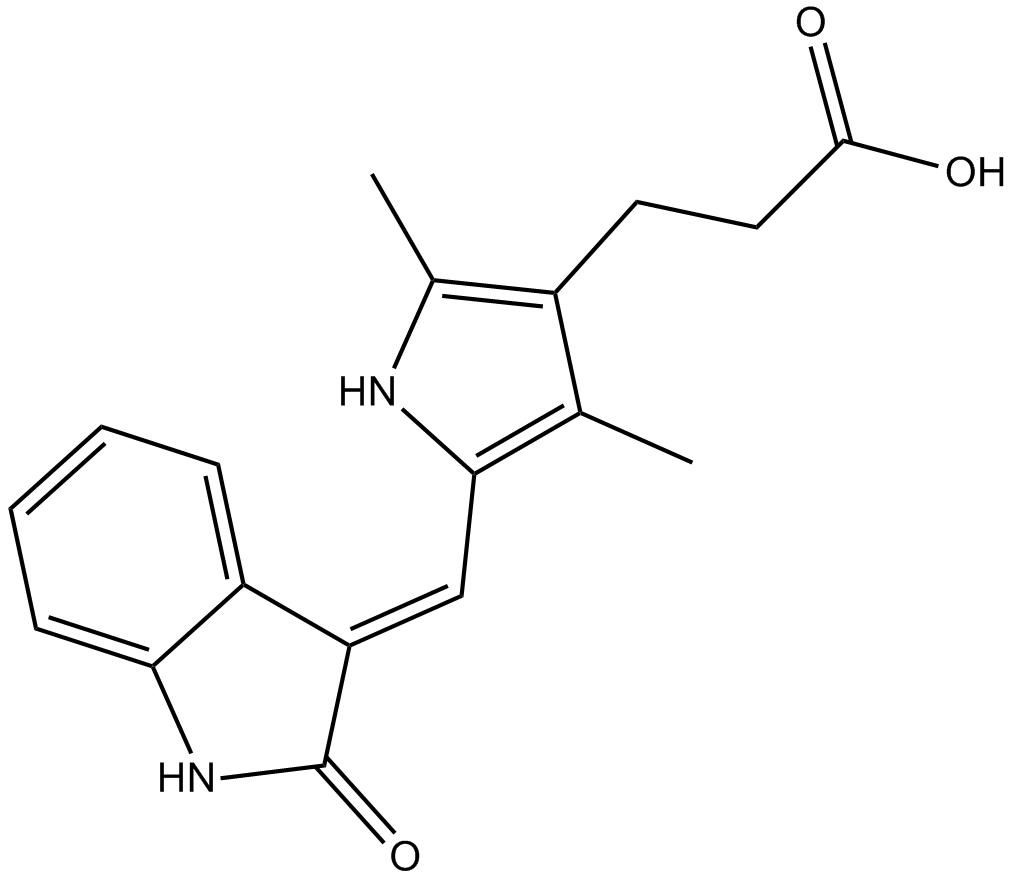
| 分子式 |
C18H18N2O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
310.35
|
| 精确质量 |
310.131
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 69.66; H, 5.85; N, 9.03; O, 15.47
|
| CAS号 |
252916-29-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
(Z)-Orantinib;210644-62-5
|
| PubChem CID |
5329099
|
| 外观&性状 |
Yellow to orange solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
590.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
310.9±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.675
|
| LogP |
2.49
|
| tPSA |
82.19
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
23
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
516
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CC1=C(/C=C2C3=CC=CC=C3NC/2=O)NC(C)=C1CCC(O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
NHFDRBXTEDBWCZ-ZROIWOOFSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H18N2O3/c1-10-12(7-8-17(21)22)11(2)19-16(10)9-14-13-5-3-4-6-15(13)20-18(14)23/h3-6,9,19H,7-8H2,1-2H3,(H,20,23)(H,21,22)/b14-9-
|
| 化学名 |
3-[2,4-dimethyl-5-[(Z)-(2-oxo-1H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]propanoic acid
|
| 别名 |
Orantinib; NSC 702827; NSC-702827; NSC702827; TSU68; TSU-68; SU-6668; SU 6668; SU6668; NSC702827; TSU 68
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 10 mg/mL (32.22 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 100.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 1% DMSO+30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80: 30 mg/mL 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2222 mL | 16.1108 mL | 32.2217 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6444 mL | 3.2222 mL | 6.4443 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3222 mL | 1.6111 mL | 3.2222 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00024206 | Completed | Other: pharmacological study Drug: orantinib |
Unspecified Adult Solid Tumor, Protocol Specific |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
July 2001 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00784290 | Completed | Drug: Orantinib (TSU-68) |
Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | September 2003 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT01465464 | Terminated | Drug: Orantinib (TSU-68) Drug: Placebo |
Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | December 2010 | Phase 3 |
Efficacy of SU6668 on s.c. A431 xenograft growth in athymic mice.Cancer Res.2000Aug 1;60(15):4152-60. |
Effect of SU6668 on tumor xenograft angiogenesis.Cancer Res.2000Aug 1;60(15):4152-60. |
Efficacy of SU6668 against established A431 s.c. xenografts in athymic mice. A, SU6668 regresses established tumors in athymic mice.Cancer Res.2000Aug 1;60(15):4152-60. |
A, HUVECs;B, NIH-3T3 cells overexpressing PDGFRβ;C, NIH-3T3 cells;D, NIH-3T3 cells overexpressing EGFR.Cancer Res.2000Aug 1;60(15):4152-60. |
Inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation stimulated by either VEGF or FGF.Cancer Res.2000Aug 1;60(15):4152-60. |
Crystal structure of SU6668 in FGFR1 (left panel) and homology model of SU6668 in PDGFR (right panel).Cancer Res.2000Aug 1;60(15):4152-60. |