| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
莫昔普利对血小板功能影响很小,并且没有抗炎作用[2]。当莫西普利水解时,会产生莫西普利拉,它能抑制兔肺和豚鼠血清中的 ACE,IC50 值分别为 2.6 nM 和 4.9 nM [2]。莫昔普利 (0.01 nM-0.1 mM) 的 IC50 值分别为 1.75 nM 和 2.1 nM,对大鼠血浆中的 ACE 和兔肺中的纯 ACE 表现出强大的功效 [3]。莫昔普利 (0-100 μM) 以剂量依赖性方式显着降低 24 小时内受损神经元的百分比 [4]。 moexipril(0-100 μM,24 小时)可显着降低 Fe2+/3+ 产生的神经毒性[4]。凋亡神经元的比例不受莫昔普利剂量的显着影响[4]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
莫昔普利不能渗透血脑屏障[1]。莫昔普利以 3 mg/kg、30 mg/kg 和 10 mg/kg 的剂量每天口服一次,连续五天,具有抗高血压作用和剂量依赖性作用[3]。莫昔普利(0.3 mg/kg,腹腔注射)可显着减少 NMRI 小鼠脑表面的梗塞面积[4]。在 Long-Evans 大鼠中,腹腔注射莫昔普利 (0.1 mg/kg) 可以显着减少皮质梗塞体积 [4]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Spontaneously hypertensive rats [3]
Doses: 30 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day; 5 days Experimental Results: The average blood pressure gradually diminished from 180 +/- 7 mmHg before treatment to the third 4 days of lows of 127 +/- 4 mmHg. Dose-dependently reduces arterial blood pressure and inhibits plasma and tissue ACE activity. Animal/Disease Models: Renal hypertension rats [3] Doses: 0.03-10 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day; 5 days Experimental Results: Caused a dose-dependent decrease in blood pressure, with a threshold dose of 0.3 mg/kg . The average blood pressure decreases by 3 mg/kg to approximately 70 mmHg. Animal/Disease Models: Perinephritis hypertensive dogs [3] Doses: 10 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day; 5 days Experimental Results: Due to the rapid onset of action and long duration of action, the average blood pressure dropped by 25 mmHg compared with the control before treatment , lasts 24 hrs (hrs (hours)). Animal/Disease Models: NMRI mouse (male, permanent focal ische |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Moexipril is incompletely absorbed, with bioavailability as moexiprilat of about 13% compared to intravenous (I.V.) moexipril (both measuring the metabolite moexiprilat), and is markedly affected by food, which reduces Cmax and AUC by about 70% and 40%, respectively, after the ingestion of a low-fat breakfast or by 80% and 50%, respectively, after the ingestion of a high-fat breakfast. Moexiprilat undergoes renal elimination. 183 L 441 mL/min Metabolism / Metabolites Rapidly converted to moexiprilat, the active metabolite. Conversion to the active metabolite is thought to require carboxyesterases and is likely to occur in organs or tissues, other than the gastrointestinal tract, in which carboxyesterases occur. The liver is thought to be one site of conversion, but not the primary site. Biological Half-Life Moexipril elimination half-life is approximately 1 hour. Moexiprilat elimination half-life is 2 to 9 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Moexipril, like other ACE inhibitors, is associated with a low rate of serum aminotransferase elevations ( Likelihood score: E* (unlikely but suspected rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because no information is available on the use of moexipril during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Moexiprilat is approxomately 50% protein bound. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Moexipril is a peptide.
Moexipril is a non-sulfhydryl containing precursor of the active angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor moexiprilat. It is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). It works by relaxing blood vessels, causing them to widen. Lowering high blood pressure helps prevent strokes, heart attacks and kidney problems. Moexipril is an Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of moexipril is as an Angiotensin-converting Enzyme Inhibitor. Moexipril is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor which is used in the therapy of hypertension. Moexipril is associated with a low rate of transient serum aminotransferase elevations, but has yet to be linked to instances of acute liver injury. Moexipril is a non-sulfhydryl angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor with antihypertensive activity. As a prodrug, moexipril is hydrolyzed into its active form moexiprilat, which competitively inhibits ACE, thereby blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. This prevents the actions of the potent vasoconstrictor angiotensin II and leads to vasodilation. It also prevents angiotensin II-induced aldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex, thereby promoting diuresis and natriuresis. See also: Hydrochlorothiazide; moexipril hydrochloride (annotation moved to). Drug Indication For the treatment of hypertension. Mechanism of Action Moexipril is a prodrug for moexiprilat, which inhibits ACE in humans and animals. The mechanism through which moexiprilat lowers blood pressure is believed to be primarily inhibition of ACE activity. ACE is a peptidyl dipeptidase that catalyzes the conversion of the inactive decapeptide angiotensin I to the vasoconstrictor substance angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a potent peripheral vasoconstrictor that also stimulates aldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex and provides negative feedback on renin secretion. ACE is identical to kininase II, an enzyme that degrades bradykinin, an endothelium-dependent vasodilator. Moexiprilat is about 1000 times as potent as moexipril in inhibiting ACE and kininase II. Inhibition of ACE results in decreased angiotensin II formation, leading to decreased vasoconstriction, increased plasma renin activity, and decreased aldosterone secretion. The latter results in diuresis and natriuresis and a small increase in serum potassium concentration (mean increases of about 0.25 mEq/L were seen when moexipril was used alone). Whether increased levels of bradykinin, a potent vasodepressor peptide, play a role in the therapeutic effects of moexipril remains to be elucidated. Although the principal mechanism of moexipril in blood pressure reduction is believed to be through the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, ACE inhibitors have some effect on blood pressure even in apparent low-renin hypertension. Pharmacodynamics Moexipril is a non-sulfhydryl containing precursor of the active angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor moexiprilat. It is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). It works by relaxing blood vessels, causing them to widen. Lowering high blood pressure helps prevent strokes, heart attacks and kidney problems. |
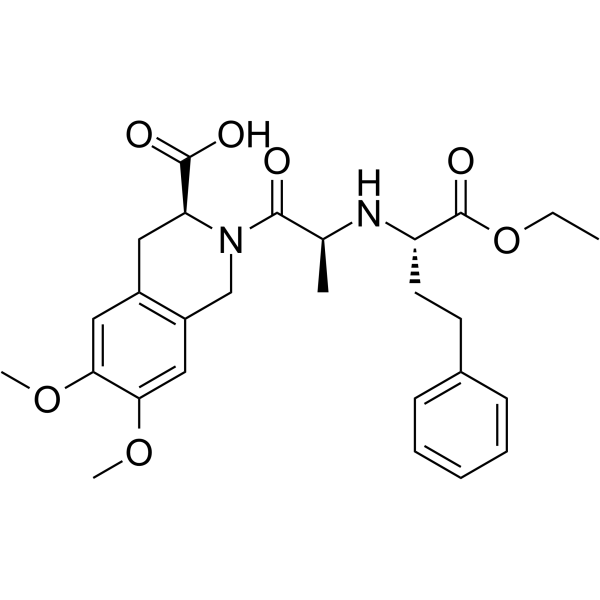
| 分子式 |
C27H34N2O7
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
498.56806
|
| 精确质量 |
498.236
|
| CAS号 |
103775-10-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Moexipril hydrochloride;82586-52-5;Moexipril-d5;1356929-49-1
|
| PubChem CID |
91270
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
709.3±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
382.8±32.9 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.565
|
| LogP |
4.05
|
| tPSA |
114.4
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
12
|
| 重原子数目 |
36
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
742
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
| SMILES |
CCOC([C@@H](N[C@H](C(N1CC2=CC(=C(C=C2C[C@H]1C(=O)O)OC)OC)=O)C)CCC1C=CC=CC=1)=O
|
| InChi Key |
UWWDHYUMIORJTA-HSQYWUDLSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C27H34N2O7/c1-5-36-27(33)21(12-11-18-9-7-6-8-10-18)28-17(2)25(30)29-16-20-15-24(35-4)23(34-3)14-19(20)13-22(29)26(31)32/h6-10,14-15,17,21-22,28H,5,11-13,16H2,1-4H3,(H,31,32)/t17-,21-,22-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(3S)-2-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino]propanoyl]-6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0057 mL | 10.0287 mL | 20.0574 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4011 mL | 2.0057 mL | 4.0115 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2006 mL | 1.0029 mL | 2.0057 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。