| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
奎纳克林抑制兔醛氧化酶,IC50 值分别为 3.3 μM 和 10 μM[2]。电压钠通道被奎纳克林抑制 (IC50: 3.3 μM)[3]。奎纳克林(0–20 μM,24 小时)刺激和抑制 SGC-7901 细胞的发育 [7]。奎纳克林 (100 μM) 也是 PLA2 布拉格通道。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
甘油三酯可引起急性肾损伤,但奎纳克林(3-30 mg/kg,腹腔注射,每天一次,连续三天)可以预防这种损伤[5]。奎纳克林(腹腔注射,2.5~10 mg/kg,每日一次,连续三天)。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定 [7]
细胞类型: SGC-7901 细胞 测试浓度: 0、5、10、15、20 μM 孵育时间:24 h 实验结果:抑制细胞生长,IC50值为16.18 μM。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Acute kidney injury rat model [5]
Doses: 3-30 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection Experimental Results: Attenuated glycerol-induced structural and renal toxicity. Changes in kidney function. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Absorbed rapidly from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration. Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration. Also rapidly absorbed after intrapleural administration. Widely distributed; concentrates in the liver, spleen, lungs, and adrenal glands. Concentration in the liver may be 20,000 times that in the plasma. Also deposited in skin, fingernails, and hair. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentration are 1 to 5% of corresponding plasma level. Lowest concentrations are found in the brain, heart, skeletal muscles, and breast milk. Less than 11% eliminated in the urine daily; acidification of urine increases urinary excretion of quinacrine by up to 14%; excreted slowly, significant amounts being excreted in the urine for 2 months or more after discontinuation of quinacrine. Small amounts also excreted in bile, sweat, and saliva. Quinacrine crosses the placenta and concentrations of drugs in fetal tissue are similar to maternal concentrations. A small amount of quinacrine is excreted in breast milk. Metabolism / Metabolites Small amt of unchanged drug is eliminated (l-form; apparently d-form is metabolized completely) by man and other animals. Several metabolites have been found in small amt, but there is some disagreement as to their structure. Mepacrine yields 6-chloro-9-(4-ethylamino-1-methylbutyl amino)-2-methoxyacridine in rabbits Biological Half-Life 5 to 14 days |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Mepacrine has been reported to cause elevations in serum enzymes, but the frequency of such changes is unknown, arising after 1 to 6 weeks with a mixed pattern of enzyme elevations and resolving within 1 to 2 months of stopping. Most patients are asymptomatic and liver enzyme elevations can resolve with, and sometimes without dose modification. Clinically apparent liver injury from mepacrine has also been reported, but the clinical features of the injury have not been well defined. Because mepacrine causes a yellowing of the skin, jaundice is not a reliable finding and most reports of liver injury from mepacrine have not included bilirubin elevations. Nevertheless, several instances of acute liver failure and death have been attributed to mepacrine therapy, although the reports usually predated the availability of tests for hepatitis A, B and C and often lacked histological documentation. Mepacrine has also been implicated in cases of aplastic anemia and in hypersensitivity reactions with exfoliative dermatitis, suggestive of Stevens Johnson syndrome, conditions that can be associated with liver injury that may be severe. Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding 80-90% Interactions Convulsive seizures have occurred in patients receiving quinacrine and corticosteroids concomitantly. /Quinacrine hydrochloride/ Concurrent use /of primaquine/ with quinacrine may inhibit the metabolism of primaquine or may displace if from tissue-binding sites, thereby increasing serum concentrations and potential toxicity of primaquine. Aldehyde dehydrogenase may be inhibited by quinacrine, resulting in acummulation of acetaldehyde after alcohol ingestion and possibly "disulfram-like" reaction... Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mouse 1300 mg/kg |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Mesh Heading: Anticestodal agents, antimalarials, antinematodal agents, antineoplastic agents, enzyme inhibitors THERAP CAT: Anthelmintic (Cestodes); antimalarial. THERAP CAT (VET): Antiprotozoal, teniacide. MEDICATION (VET): Protozoacide, anthelmintic. /Used/...with varying results against flukes & poor results in coccidiosis of cattle; good results against moniezia expansa & m benedini in sheep, & trichomoniasis in chickens, ducks, & geese; effective against "ich" parasite in fish tank...in exptl histoplasmosis... /Quinacrine hydrochloride/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for QUINACRINE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Quinacrine should not be given to pregnant women because drug readily passes placenta and reaches fetus. Quinacrine crosses the placenta and reaches the fetal circulation. There is one case of possible renal agenesis and hydrocephalus in an infant, although normal pregnancies have been reported after quinacrine ingestion during the first 4 weeks of gestation. If possible, quinacrine treatment for giardiasis in asymptomatic pregnant women should be postponed until after delivery. Quinacrine may cause vomiting in children due to its bitter taste. The tablets may be crushed and mixed with jam, honey, or chocolate syrup or put in empty gelatin capsules to mask the taste. Children also tolerate quinacrine less well than do adults. Adverse effects of quinacrine in dosages used for the treatment of malaria include mild transient headache, dizziness, and GI disorders such as diarrhea, anorexia, nausea, abdominal cramps, and rarely, vomiting. Transient psychoses lasting 2 to 4 weeks have been reported in some patients receiving quinacrine. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for QUINACRINE (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Quinacrine has been used as an antimalarial drug and as an antibiotic. It is used to treat giardiasis, a protozoal infection of the intestinal tract, and certain types of lupus erythematosus, an inflammatory disease that affects the joints, tendons, and other connective tissues and organs. Quinacrine may be injected into the space surrounding the lungs to prevent reoccurrence of pneumothorax. The exact way in which quinacrine works is unknown. It appears to interfere with the parasite's metabolism. |
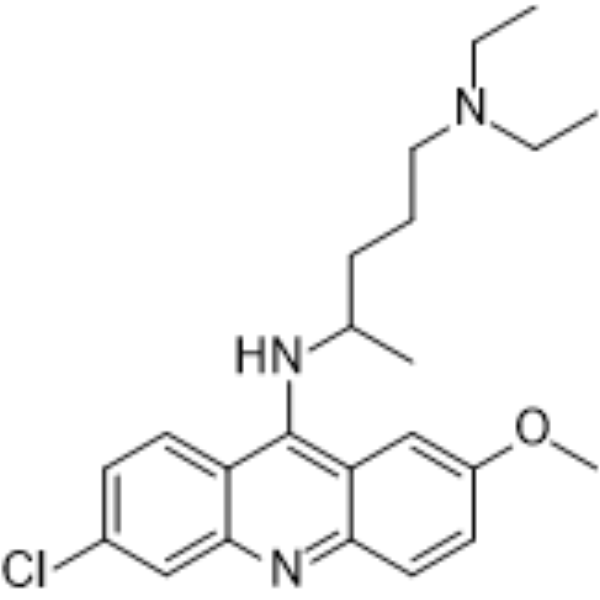
| 分子式 |
C23H30CLN30
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
399.21
|
| 精确质量 |
399.208
|
| CAS号 |
83-89-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Quinacrine dihydrochloride;69-05-6;l-Atabrine dihydrochloride;56100-42-6;d-Atabrine dihydrochloride;56100-41-5;Quinacrine hydrochloride hydrate;6151-30-0
|
| PubChem CID |
237
|
| 外观&性状 |
Bright yellow crystals
|
| 密度 |
1.156 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
557.1ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
247-250ºC
|
| 闪点 |
290.7ºC
|
| LogP |
6.045
|
| tPSA |
37.39
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
| 重原子数目 |
28
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
461
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CCN(CC)CCCC(C)N=C1C2=C(C=C(C=C2)Cl)NC3=C1C=C(C=C3)OC
|
| InChi Key |
GPKJTRJOBQGKQK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H30ClN3O/c1-5-27(6-2)13-7-8-16(3)25-23-19-11-9-17(24)14-22(19)26-21-12-10-18(28-4)15-20(21)23/h9-12,14-16H,5-8,13H2,1-4H3,(H,25,26)
|
| 化学名 |
4-N-(6-chloro-2-methoxyacridin-9-yl)-1-N,1-N-diethylpentane-1,4-diamine
|
| 别名 |
Haffkinine; Erion
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5049 mL | 12.5247 mL | 25.0495 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5010 mL | 2.5049 mL | 5.0099 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2505 mL | 1.2525 mL | 2.5049 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。