| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
厚朴酚对 RXRα 和 PPARγ 的 EC50 值分别为 10.4 μM 和 17.7 μM,使其成为双重凝固剂。 Magnolol (26.2 - 80 μM) 对 RXRαLBD 和 PPARγLBD 具有剂量依赖性结合行为,相应的 Kd 值为 45.7 μM 和 1.67 μM。 (1–20 μM) 对调制 RXRE 没有影响,但它会导致 PPRE 以分配方式发生变化 [1]。在存在胰岛素的情况下,厚朴酚 (1, 3, 10 μM) 会增强 3T3-L1 前脂肪细胞和 C3H10T1/2 多能干细胞的脂肪细胞分泌。 10 μM 的 magnolil 会增加脂肪细胞分泌标记基因 mRNA 的表达。在分泌型 3T3-L1 脂肪细胞中,厚朴醇 (1, 10 μM) 会增加基线和胰岛素刺激的脂肪细胞分泌 [2]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
厚朴酚(5-15 mg/kg,口服)可显着减轻小鼠葡萄糖发酵硫酸钠(DSS)诱导的热水钠形式的严重程度。在暴露于 DSS 的小鼠中,厚朴酚(10、15 mg/kg,无意)抑制髓过氧化物酶活性和底层组织的退行性改变。它还降低了 DSS 在底层组织中诱导的高水平促炎细胞因子 TNF-α、IL-1β 和 IL。 6. 厚朴醇(10 mg/kg,口服)也可以逆转和调节肾脏颜色通路异常[3]。
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
To investigate the relationship between magnolol and the clinical effects of Saiboku-To, urinary magnolol excretion was compared in responders and non-responders under long-term Saiboku-To treatment. The clinical outcome of the Saiboku-To treatment was evaluated in nine asthmatic patients at 52 weeks after the onset of the treatment, using individual fluctuation of asthmatic points obtained from the patients' diary cards. Three patients whose clinical conditions were improved by the treatment were termed responders and six others were termed non-responders. The difference in the amounts of the total magnolol excreted were not significant; however, free (or non-conjugated) amounts of magnolol excreted in the responders were 7 times those in the non-responders (P < 0.05). These results suggest that the magnolol might be responsible for the therapeutic effect of Saiboku-To, indicating practical bioavailability in the responders. Metabolism / Metabolites Magnolol has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[2-(2-hydroxy-5-prop-2-enylphenyl)-4-prop-2-enylphenoxy]oxane-2-carboxylic acid. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Interactions
Three neolignans, known as magnolol, honokiol and the new monoterpenylmagnolol, were isolated from the bark of Magnolia officinalis ... . The MeOH extract of this plant and magnolol exhibited remarkable inhibitory effects on mouse skin tumor promotion in an in vivo two stage carcinogenesis test... Magnolol has been reported to strongly inhibit the mutagenicity induced by indirect mutagens in the Ames test as well as the clastogenicity induced by benzo(a)pyrene (B(a)P) in the mice micronucleus test. Here, ... the inhibitory effect of magnolol on the DNA damage induced by 3-amino-1-methyl-5H-pyrido[4,3-b]indole (Trp-P-2) /was evaluated/ in various organs using the mice alkaline single cell gel electrophoresis (SCG) assay. Animals were treated with a single oral administration of magnolol (0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, and 100 mg/kg), followed by a single intraperitoneal injection of Trp-P-2 (10 mg/kg). The liver, lung, and kidney were removed at 3 hr after treatment and used in SCG assay. The results indicated that magnolol inhibited Trp-P-2-induced DNA damage in various organs. To elucidate the mechanism of this inhibitory effect against Trp-P-2, we investigated the inhibitory effect of magnolol on in vivo CYP1A2 activity using the zoxazolamine paralysis test. Magnolol significantly prolonged zoxazolamine paralysis time and showed an inhibitory effect on in vivo CYP1A2 activity. These results indicate that magnolol has an inhibitory effect on the DNA damage induced by Trp-P-2 in various organs in vivo. This inhibitory mechanism is considered due to in vivo CYP1A2 inhibition. ... The in vivo anti-clastogenic effect of magnolol against clastogenicity induced by B(a)P was evaluated using the micronucleus test in mice. Animals were treated with an oral administration of magnolol (1, 10, and 100 mg/kg) at -24, 0, 24, 48, 72, and 96 hr before a single intraperitoneal injection of B(a)P. Peripheral blood specimens were prepared 48 h after administration of B(a)P, and analyzed by the acridine orange (AO) technique. The results indicated that magnolol inhibited clastogenicity induced by B(a)P at various administration times. In order to elucidate the mechanism behind this effect, we measured the activity of the detoxifying enzymes [UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) and glutathione-S-transferase (GST)] and antioxidative enzymes [superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase] in the liver when treated with an oral administration of magnolol at various administration times. Its effect on clastogenicity created by exposure to oxidative DNA damage-inducing X-ray irradiation was also evaluated using the micronucleus test in mice. Results showed that magnolol increased the activity of both UGT and SOD enzymes, and also inhibited the clastogenicity induced by X-ray irradiation. Magnolol had an anti-clastogenic effect on B(a)P in the micronucleus test as well as an anti-mutagenic effect on indirect mutagens in the Ames test. The anti-clastogenic effect of magnolol was also suggested by the increases in UGT and SOD enzyme activity, and by the attenuation of oxidative damage induced by X-ray irradiation. ... Anti-mutagenic activity of magnolol against mutagenicity induced by direct mutagens [1-nitropyrene (1-NP), N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG) and N-ethyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (ENNG)] and indirect mutagens [2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline (IQ), 2-aminodipyrido[1,2-a:3',2'-d]imidazole (Glu-P-2), benzo(a)pyrene (B(a)P), 2-aminoanthracene (2-AA) and 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA)] were investigated using the bacterial mutagenicity test (Ames test). Results show that magnolol strongly inhibits mutagenicity induced by indirect mutagens, but does not affect direct mutagens. To elucidate the mechanism of this effect against indirect mutagens, effect of magnolol on CYP1A1- and CYP1A2-related enzyme activities of ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) and methoxyresorufin-O-demethylase (MROD) were investigated. Magnolol strongly and competitively suppressed these enzyme activities, suggesting it inhibited mutation induced by indirect mutagens through suppression of CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 activity. A23187-induced pleurisy in mice was used to investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of magnolol, a phenolic compound isolated from Chinese medicine Hou p'u (cortex of Magnolia officinalis). A23187-induced protein leakage was reduced by magnolol (10 mg/kg, ip), indomethacin (10 mg/kg, ip) and BW755C (30 mg/kg, ip). A23187-induced polymorphonuclear (PMN) leukocyte infiltration in the pleural cavity was suppressed by magnolol and BW755C, while enhanced by indomethacin. Like BW755C, magnolol reduced both prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and leukotriene B4 (LTB4) levels in the pleural fluid of A23187-induced pleurisy, while indomethacin reduced PGE2 but increased LTB4 formation. In the rat isolated peripheral neutrophil suspension, magnolol (3.7 uM) and BW755C (10 microM) also suppressed the A23187-induced thromboxane B2 (TXB2) and LTB4 formation. These results suggest that magnolol, like BW755C, might be a dual cyclo-oxygenase and lipoxygenase inhibitor. The inhibitory effect of magnolol on the A23187-induced pleurisy is proposed to be, at least partly, dependent on the reduction of the formation of eicosanoids mediators in the inflammatory site. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mouse oral 2200 mg/kg /from table/ |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Magnolol is a member of biphenyls.
Magnolol has been reported in Magnolia henryi, Magnolia officinalis, and other organisms with data available. See also: Magnolol; rhynchophylline (component of). Mechanism of Action The effects of honokiol and magnolol, two major bioactive constituents of the bark of Magnolia officinalis, on Ca(2+) and Na(+) influx induced by various stimulants were investigated in cultured rat cerebellar granule cells by single-cell fura-2 or SBFI microfluorimetry. Honokiol and magnolol blocked the glutamate- and KCl-evoked Ca(2+) influx with similar potency and efficacy, but did not affect KCl-evoked Na(+) influx. However, honokiol was more specific for blocking NMDA-induced Ca(2+) influx, whereas magnolol influenced with both NMDA- and non-NMDA activated Ca(2+) and Na(+) influx. Moreover, the anti-convulsant effects of these two compounds on NMDA-induced seizures were also evaluated. After honokiol or magnolol (1 and 5 mg/kg, ip) pretreatment, the seizure thresholds of NMRI mice were determined by tail-vein infusion of NMDA (10 mg/mL). Data showed that both honokiol and magnolol significantly increased the NMDA-induced seizure thresholds, and honokiol was more potent than magnolol. These results demonstrated that magnolol and honokiol have differential effects on NMDA and non-NMDA receptors, suggesting that the distinct therapeutic applications of these two compounds for neuroprotection should be considered. Magnolol inhibited phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-activated rat neutrophil aggregation in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 (concentration resulting in 50% inhibition) of 24.2 +/- 1.7 uM. Magnolol suppressed the enzyme activity of neutrophil cytosolic and rat brain protein kinase C (PKC) over the same range of concentrations at which it inhibited the aggregation. Magnolol did not affect PMA-induced cytosolic PKC-alpha and -delta membrane translocation or trypsin-treated rat-brain PKC activity, but attenuated [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate binding to neutrophil cytosolic PKC. These results suggest that the inhibition of PMA-induced rat neutrophil aggregation by magnolol is probably attributable, at least in part, to the direct suppression of PKC activity through blockade of the regulatory region of PKC. Magnolol, a substance purified from the bark of Magnolia officialis, inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in a variety of cancer cells. The aim of this study was to study the effects of magnolol on CGTH W-2 thyroid carcinoma cells. After 24 hr treatment with 80 u M magnolol in serum-containing medium, about 50% of the cells exhibited apoptotic features and 20% necrotic features. Cytochrome-c staining was diffused in the cytoplasm of the apoptotic cells, but restricted to the mitochondria in control cells. Western blot analyses showed an increase in levels of activated caspases (caspase-3 and -7) and of cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) by magnolol. Concomitantly, immunostaining for apoptosis inducing factor (AIF) showed a time-dependent translocation from the mitochondria to the nucleus. Inhibition of either PARP or caspase activity blocked magnolol-induced apoptosis, supporting the involvement of the caspases and PARP. In addition, magnolol activated phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) and inactivated Akt by decreasing levels of phosphorylated PTEN and phosphorylated Akt. These data suggest that magnolol promoted apoptosis probably by alleviating the inhibitory effect of Akt on caspase 9. Furthermore, inhibition of PARP activity, but not of caspase activity, completely prevented magnolol-induced necrosis, suggesting the notion that it might be caused by depletion of intracellular ATP levels due to PARP activation. These results show that magnolol initiates apoptosis via the cytochrome-c/caspase 3/PARP/AIF and PTEN/Akt/caspase 9/PARP pathways and necrosis via PARP activation. The mis-regulation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) signal pathway is involved in a variety of inflammatory diseases that leds to the production of inflammatory mediators. /These/ studies using human U937 promonocytes cells suggested that magnolol ... differentially down-regulated the pharmacologically induced expression of NF-kappaB-regulated inflammatory gene products MMP-9, IL-8, MCP-1, MIP-1alpha, TNF-alpha. Pre-treatment of magnolol blocked TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation in different cell types as evidenced by EMSA. Magnolol did not directly affect the binding of p65/p50 heterodimer to DNA. Immunoblot analysis demonstrated that magnolol inhibited the TNF-alpha-stimulated phosphorylation and degradation of the cytosolic NF-kappaB inhibitor IkappaBalpha and the effects were dose-dependent. Mechanistically, a non-radioactive IkappaB kinases (IKK) assay using immunoprecipitated IKKs protein demonstrated that magnolol inhibited both intrinsic and TNF-alpha-stimulated IKK activity, thus suggesting a critical role of magnolol in abrogating the phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaBalpha. The involvement of IKK was further verified in a HeLa cell NF-kappaB-dependent luciferase reporter system. In this system magnolol suppressed luciferase expression stimulated by TNF-alpha and by the transient transfection and expression of NIK (NF-kappaB-inducing kinase), wild type IKKbeta, constitutively active IKKalpha and IKKbeta, or the p65 subunit. Magnolol was also found to inhibit the nuclear translocation and phosphorylation of p65 subunit of NF-kappaB. In line with the observation that NF-kappaB activation may up-regulate anti-apoptotic genes, it was shown in U937 cells that magnolol enhanced TNF-alpha-induced apoptotic cell death. /The/ results suggest that magnolol or its derivatives may have potential anti-inflammatory actions through IKK inactivation. For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for MAGNOLOL (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
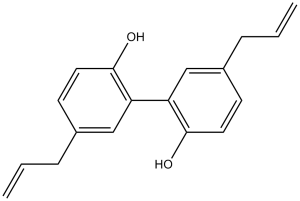
| 分子式 |
C18H18O2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
266.32
|
|
| 精确质量 |
266.13
|
|
| CAS号 |
528-43-8
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
72300
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
401.0±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
99 - 101ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
184.5±21.9 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.602
|
|
| LogP |
3.94
|
|
| tPSA |
40.46
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
293
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
VVOAZFWZEDHOOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H18O2/c1-3-5-13-7-9-17(19)15(11-13)16-12-14(6-4-2)8-10-18(16)20/h3-4,7-12,19-20H,1-2,5-6H2
|
|
| 化学名 |
5,5-diallyl-[1,1-biphenyl]-2,2-diol
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.39 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.39 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.39 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.7549 mL | 18.7744 mL | 37.5488 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7510 mL | 3.7549 mL | 7.5098 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3755 mL | 1.8774 mL | 3.7549 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。