| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
ERK1 (IC50 = 5 nM); ERK2 (IC50 = 5 nM)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在生化测定中,Temuterkib 对 ERK1 和 ERK2 的 IC50 均为 5 nM,使其成为这两种酶的高度选择性抑制剂。 Temuterkib 可有效抑制含有 BRAF 和 RAS 突变的癌细胞系中的细胞磷酸化 RSK1。在抑制细胞增殖的无偏肿瘤细胞组敏感性分析中,具有 MAPK 通路改变(例如 BRAF、NRAS 或 KRAS 突变)的肿瘤细胞通常对 Temuterkib 敏感[1]。
LY3214996是一种高度选择性的ERK1和ERK2抑制剂,在生化分析中对这两种酶的IC50均为5 nM。它能有效抑制BRAF和RAS突变癌细胞系的细胞磷酸化rsk1。在抑制细胞增殖的无偏倚肿瘤细胞组敏感性分析中,具有MAPK通路改变(包括BRAF、NRAS或KRAS突变)的肿瘤细胞通常对LY3214996敏感。[1] |
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Temuterkib 抑制肿瘤异种移植模型中肿瘤中的磷酸化 p90RSK1 PD 生物标志物,PD 效应与化合物暴露和抗肿瘤活性相关。与已发表的其他 ERK 抑制剂相比,Temuterkib 在 BRAF 或 RAS 突变细胞系和异种移植模型中表现出相当或更好的抗肿瘤活性。在 BRAF 或 NRAS 突变黑色素瘤、BRAF 或 KRAS 突变结直肠癌、肺癌和胰腺癌异种移植物或 PDX 模型中,口服单药 Temuterkib 可显着抑制体内肿瘤生长,且耐受性良好。因此,可以对 Temuterkib 进行修改,用于治疗 MAPK 通路改变的癌症。 Temuterkib 在 PLX4032 耐药 A375 黑色素瘤异种移植模型中也表现出抗肿瘤活性,这表明它可能有助于治疗接受过无效 BRAF 疗法的黑色素瘤患者。更重要的是,Temuterkib 可以与研究中和已批准的药物结合用于临床前模型,特别是 KRAS 突变模型。 Temuterkib 和 CDK4/6 抑制剂 abemaciclib 联合使用时,耐受性良好,可在多种体内癌症模型中有效抑制肿瘤生长或使其缩小,包括 KRAS 突变结直肠癌和非小细胞肺癌[1] 。
LY3214996在BRAF-, KRAS-, NRAS-和mek -突变模型中作为单一药物[2] 显示出有效的体内抗肿瘤活性[2] 作为RAS/ERK通路改变的代表性例子,LY3214996和MEK抑制剂的体内疗效在几种结直肠癌(kras突变型HCT116、braf突变型col205和mek1突变型SW48)、黑色素瘤(nras突变型sk - mel30)、胰腺癌(kras突变型miapca -2)和非小细胞肺癌(kras突变型Calu6)模型的皮下异种移植模型中进行了评估。MEK抑制剂在小鼠中以预测的临床有效剂量给药。LY3214996治疗导致HCT116(31%)、col205(76%)、MiaPaCa-2(66%)和Calu-6(54%)异种移植肿瘤的显著肿瘤消退(图5A、B、E和F;补充表S3)。LY3214996治疗也导致SW48结直肠癌(%dT/C = 11)和SK-MEL-30黑色素瘤(%dT/C = 1)异种移植模型的显著生长抑制(图5C和D;补充表S3)。在HCT116研究中,所有单药治疗均具有良好的耐受性。S4和S5)。综上所述,我们的数据表明LY3214996对包括BRAF、MEK1、NRAS或KRAS突变在内的各种ERK通路改变的异种移植物模型具有强大的疗效(补充表S3)。值得注意的是,与MEK抑制剂相比,其疗效相似,这加强了pRSK1可能不需要持续抑制(bbb50 %)的观点,特别是在最反应性的肿瘤类型中。这些基因改变是LY3214996临床开发中患者选择和精准医疗的关键生物标志物。 LY3214996在A375黑色素瘤亲本模型中显示出持久的应答,在对vemurafenib耐药的A375模型或对vemurafenib固有耐药的结肠直肠癌PDX模型中显示出有效的抗肿瘤活性[2] 为了进一步测试LY3214996是否可以克服BRAF抑制剂耐药性,我们使用A375黑色素瘤细胞建立了对vemurafenib的体内获得性耐药模型。在亲代A375异种移植物模型中,LY3214996 (100 mpk qd)显示出明显的肿瘤消退,导致6只动物中的4只完全缓解和完全治愈,因为这些动物在21天治疗后115天无肿瘤(图6A)。我们使用相同的模型,通过长期给药vemurafenib (15 mpk b.i.d)来产生对vemurafenib的体内获得性耐药性模型。45天后首次出现获得性耐药(补充图S6)。来自这些耐药肿瘤的肿瘤片段被植入LY3214996疗效研究,如图6B所示。LY3214996在50 mpk b.i.d剂量下显示95%的肿瘤生长抑制(%dT/C = 5),而在vemurafenib存在下,对照物生长(15 mpk b.i.d;图6 b)。这些结果表明LY3214996可以克服BRAF v600e突变黑色素瘤对vemurafenib的获得性耐药。[2] LY3214996的有效性也在PDX模型中进行了测试,这些模型保持了原始肿瘤的形态相似性和分子特征。在BRAF v600e突变型结直肠癌PDX模型CTG-0652中,LY3214996治疗显示83%的肿瘤生长抑制(%dT/C = 17;图6 c)。总的来说,我们的数据表明LY3214996在BRAF抑制剂耐药的黑色素瘤和结直肠癌模型中具有单药活性。 LY3214996联合泛raf抑制剂LY3009120在HCT116结直肠癌异种移植模型中的疗效增强[2] 抑制ERK通路中的多个靶点已被用于增强黑色素瘤的治疗反应。利用这种模式,我们在kras突变型HCT116结直肠癌异种移植模型中探索了LY3214996与泛raf抑制剂LY3009120的联合应用。LY3214996单用、LY3009120单用、联合使用分别抑制52%、29%、94%的肿瘤生长,提示联合使用具有协同作用(P < 0.001;图6D和E)。根据研究中的体重测量,所有测试剂量均具有良好的耐受性。 |
||
| 酶活实验 |
生化试验与Ki测定[2]
使用LanthaScreen®TR-FRET检测试剂进行人ERK1和EKR2激酶的体外检测。通过加入ERK1或ERK2酶(终浓度分别为3.6 nM或1.7 nM),在激酶缓冲液(50 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 10µM ATP, 5 mM MgCl2, 200 nM GFP-ATF2 (19-96), 0.1 mM EGTA, 0.01% TritonTM X-100和1 mM DTT)中制备,并在384孔Proxi板上增加DMSO溶液(终浓度为4%,v/v)中的LY3214996浓度来模拟所有反应。反应在室温下孵育60分钟。然后,在TR-FRET稀释缓冲液中加入含有10 mM EDTA和2 nM Tb-(Terbium)-anti- patf2 (pThr71)抗体的停止缓冲液,停止反应。然后在室温下再孵育60分钟,在Envision平板阅读器上以340 nm的激发波长读取。通过将GFP受体发射信号(520 nm)除以Tb供体发射信号(495 nm),计算出TR-FRET比值。IC50值由浓度-响应曲线确定,该曲线用于计算Cheng和Prusoff描述的表观Ki。对于激酶选择性,LY3214996在KINOMEscan®平台的456个激酶靶点中以三种浓度(20、2和0.2µM)进行测试。对于每个靶点,使用LY3214996剂量浓度和测定得出的百分比对照数据计算三点IC50。 LY3214996 表现出效力(hERK1 IC50 5 nM、hERK2 IC50 5nM、pRSK IC50 0.43 µM)和溶解度的最佳平衡。 |
||
| 细胞实验 |
在抑制细胞增殖的无偏肿瘤细胞组敏感性分析中,具有 MAPK 通路改变(包括 BRAF、NRAS 或 KRAS 突变)的肿瘤细胞通常对LY3214996 敏感。
Western blotting [2] 细胞在10 cm培养皿中以LY3214996浓度处理指定时间点,并在RIPA裂解缓冲液(Millipore)中添加PMSF和Halt Phosphatase and Protease Inhibitor Cocktail,缓冲液中每种试剂的终浓度为5%。根据制造商的指导,通过BCA测定蛋白浓度,并使用一抗pCRAF、CRAF、pMEK1/2、MEK1/2、pERK1/2、ERK1/2、EGR1、c-MYC、DUSP4、pRSK1、SPRY4和β - actin进行SDS-PAGE和Western blotting。二抗采用Alexa Fluor 680山羊抗兔、山羊抗小鼠和驴抗兔(LI-COR)。使用LI-COR Odyssey经典红外成像系统在700和800 nm处读取印迹。使用Image Studio 3.1对图像进行处理和分析。 细胞增殖试验[2] 从ATCC中获得了60个人肺癌、结直肠癌、胰腺癌和皮肤癌细胞系。细胞保存在RPMI 1640或添加10%牛血清、丙酮酸钠、非必需氨基酸、l-谷氨酰胺和青霉素-链霉素(Invitrogen)的DMEM中。所有培养物均保存在37°C、5% CO2/95%空气、无支原体和致病性鼠病毒的加湿培养箱中。细胞从冷冻储备中恢复后用于< 7代的实验。细胞(3000个/孔)于96孔黑色板中,在含10%胎牛血清的RPMI 1640或DMEM中培养24小时。将10 mmol/L原液(0.001、0.003、0.01、0.03、0.1、0.3、1、3和10 μmol/L)用DMSO或LY3214996在含有0.1% DMSO和5% FBS或10% FBS(黑色素瘤细胞)的培养基中处理120小时。采用CellTiter-Glo荧光细胞活力法测定细胞活力。数据以绝对IC50 (Abs IC50)表示,并使用XLfit (IDBS)进行分析。 |
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
LY3214996 demonstrates good PK/PD correlation in tumors that correspond to potent tumor growth inhibition [2]
The kinetics of drug–target interactions can be quantified to predict in vivo PD and antitumor activity. A detailed PK/PD (pRSK1 inhibition) relationship of LY3214996 was generated in a KRAS-mutant HCT116 colorectal cancer xenograft model. After administration of a single dose of LY3214996 (6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, and 100 mpk) for dose–response study in nude mice bearing HCT116 xenografts, tumors were harvested at 4 hours after dosing, and pRSK1 was measured by sandwich ELISA (Fig. 4A).The PD effects correlated well with drug levels in the plasma (Fig. 4A). LY3214996 treatment showed dose-dependent increase in plasma drug exposure and inhibition of pRSK1 in tumors. LY3214996 was also evaluated at two different efficacious dose levels (50 and 100 mpk qd) for time-dependent plasma drug exposure and pRSK1 inhibition in the HCT116 colorectal cancer xenograft model. PD effects (pRSK1 inhibition) correlated well with PK (drug levels) in the plasma (Fig. 4B and C). After fitting to a four-parameter sigmoidal logistical model using XL fit, estimated TEC50 and TED50 (4 hours) values were 1,107 nmol/L and 16 mpk respectively. Our data suggest good PK and PD correlation of LY3214996 in a KRAS-mutant HCT116 colorectal cancer xenograft model. |
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
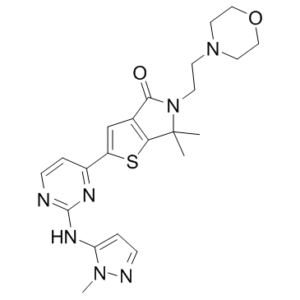
Temuterkib is an orally available inhibitor of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1 and 2, with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon oral administration, temuterkib inhibits both ERK 1 and 2, thereby preventing the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/ERK-mediated signal transduction pathways. This results in the inhibition of ERK-dependent tumor cell proliferation and survival. The MAPK/ERK pathway is often upregulated in a variety of tumor cell types and plays a key role in tumor cell proliferation, differentiation and survival.
The RAS/MAPK pathway is dysregulated in approximately 30% of human cancers, and the extracellular-signal-regulated kinases (ERK1 and ERK2) serves as key central nodes within this pathway. The feasibility and clinical impact of targeting the RAS/MAPK pathway has been demonstrated by the therapeutic success of BRAF and MEK inhibitors in BRAF V600E/K metastatic melanoma. However, resistance develops frequently through reactivation of the pathway. Therefore, simultaneous targeting of multiple effectors such as RAF, MEK and ERK in this pathway, offers a potential for enhanced efficacy while delaying and overcoming resistance. LY3214996 is a highly selective inhibitor of ERK1 and ERK2, with IC50 of 5 nM for both enzymes in biochemical assays. It potently inhibits cellular phospho-RSK1 in BRAF and RAS mutant cancer cell lines. In an unbiased tumor cell panel sensitivity profiling for inhibition of cell proliferation, tumor cells with MAPK pathway alterations including BRAF, NRAS or KRAS mutation are generally sensitivity to LY3214996. In tumor xenograft models, LY3214996 inhibits PD biomarker phospho-p90RSK1 in tumors and the PD effects are correlated with compound exposures and anti-tumor activities. LY3214996 shows either similar or superior anti-tumor activity as compared to other published ERK inhibitors in BRAF or RAS mutant cell lines and xenograft models. Oral administration of single-agent LY3214996 significantly inhibits tumor growth in vivo and is well tolerated in BRAF or NRAS mutant melanoma, BRAF or KRAS mutant colorectal, lung and pancreatic cancer xenografts or PDX models. Therefore, LY3214996 can be tailored for treatment of cancers with MAPK pathway alteration. In addition, LY3214996 has anti-tumor activity in a vemurafenib-resistant A375 melanoma xenograft model due to MAPK reactivation, may have potential for treatment of melanoma patients who have failed BRAF therapies. More importantly, LY3214996 can be combined with investigational and approved agents in preclinical models, particularly KRAS mutant models. Combination treatment of LY3214996 and CDK4/6 inhibitor abemaciclib was well tolerated and results in potent tumor growth inhibition or regression in multiple in vivo cancer models, including KRAS mutant colorectal and non-small cell lung cancers. Here, we first report the preclinical characterization of LY3214996, a novel small molecule ERK1/2 inhibitor currently in Phase I clinical trials in patients with advanced and metastatic cancers (NCT02857270).[1] The ERK pathway is critical in oncogenesis; aberrations in components of this pathway are common in approximately 30% of human cancers. ERK1/2 (ERK) regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival and is the terminal node of the pathway. BRAF- and MEK-targeted therapies are effective in BRAF V600E/K metastatic melanoma and lung cancers; however, responses are short-lived due to emergence of resistance. Reactivation of ERK signaling is central to the mechanisms of acquired resistance. Therefore, ERK inhibition provides an opportunity to overcome resistance and leads to improved efficacy. In addition, KRAS-mutant cancers remain an unmet medical need in which ERK inhibitors may provide treatment options alone or in combination with other agents. Here, we report identification and activity of LY3214996, a potent, selective, ATP-competitive ERK inhibitor. LY3214996 treatment inhibited the pharmacodynamic biomarker, phospho-p90RSK1, in cells and tumors, and correlated with LY3214996 exposures and antitumor activities. In in vitro cell proliferation assays, sensitivity to LY3214996 correlated with ERK pathway aberrations. LY3214996 showed dose-dependent tumor growth inhibition and regression in xenograft models harboring ERK pathway alterations. Importantly, more than 50% target inhibition for up to 8 to 16 hours was sufficient for significant tumor growth inhibition as single agent in BRAF- and KRAS-mutant models. LY3214996 also exhibited synergistic combination benefit with a pan-RAF inhibitor in a KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer xenograft model. Furthermore, LY3214996 demonstrated antitumor activity in BRAF-mutant models with acquired resistance in vitro and in vivo. Based on these preclinical data, LY3214996 has advanced to an ongoing phase I clinical trial (NCT02857270).[2] |
| 分子式 |
C22H27N7O2S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
453.56
|
|
| 精确质量 |
453.194
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 58.26; H, 6.00; N, 21.62; O, 7.05; S, 7.07
|
|
| CAS号 |
1951483-29-6
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1951483-29-6;2365171-00-0 (mesylate);
|
|
| PubChem CID |
121408882
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
711.5±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
384.1±35.7 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.723
|
|
| LogP |
1.36
|
|
| tPSA |
117Ų
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
677
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
S1C(C2C([H])=C([H])N=C(N([H])C3=C([H])C([H])=NN3C([H])([H])[H])N=2)=C([H])C2C(N(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N3C([H])([H])C([H])([H])OC([H])([H])C3([H])[H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C1=2)=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
JNPRPMBJODOFEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H27N7O2S/c1-22(2)19-15(20(30)29(22)9-8-28-10-12-31-13-11-28)14-17(32-19)16-4-6-23-21(25-16)26-18-5-7-24-27(18)3/h4-7,14H,8-13H2,1-3H3,(H,23,25,26)
|
|
| 化学名 |
6,6-dimethyl-2-[2-[(2-methylpyrazol-3-yl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl]-5-(2-morpholin-4-ylethyl)thieno[2,3-c]pyrrol-4-one
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2 mg/mL (4.41 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2 mg/mL (4.41 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.0mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2 mg/mL (4.41 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2048 mL | 11.0239 mL | 22.0478 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4410 mL | 2.2048 mL | 4.4096 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2205 mL | 1.1024 mL | 2.2048 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04005690 | Recruiting | Drug: Temuterkib Drug: Olaparib |
Stage II Pancreatic Cancer AJCC v8 Stage III Pancreatic Cancer AJCC v8 |
OHSU Knight Cancer Institute | August 1, 2019 | Early Phase 1 |
Ago1 promotes cell proliferation and migration though ERK1/2 not P38. aLevel of AGO1 protein was detected by western blotting assays.bLY3214996(ERK1/2) inhibitor significantly inhibited AGO1 cell growth compared to the normal group, while SB203580 (P38) did not significantly affect growth (*P Cell Death Dis.2018 Feb 27;9(3):324. |
|---|