| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
... The objectives of the study were to 1) use the whole body fatty acid balance method to quantify whole-body concentrations of linoleate in humans, 2) estimate the distribution of linoleate between adipose and lean tissue, and 3) assess the effect of weight loss on linoleate stores and beta-oxidation in obese humans. Nine healthy obese men underwent supervised weight loss for 112 d (16 wk). Magnetic resonance imaging data and fatty acid profiles from fat biopsies were both used to determine linoleate stores in adipose and lean tissue and in the whole body. Linoleate beta-oxidation was calculated as intake - (accumulation + excretion). Mean weight loss was 13 kg and linoleate intake was 24 +/- 6 mmol/d over the study period. Whole-body loss of linoleate was 37 +/- 18 mmol/d, or 28% of the level before weight loss. Combining the intake and whole-body loss of linoleate resulted in linoleate beta-oxidation exceeding intake by 2.5-fold during the weight-loss period. All dietary linoleate is beta-oxidized and at least an equivalent amount of linoleate is lost from the body during moderate weight loss in obese men. The method studied permits the assessment of long-term changes in linoleate homeostasis in obese humans and may be useful in determining the risk of linoleate deficiency in other conditions. /Linoleate/ Human milk fatty acids vary with maternal dietary fat composition. Hydrogenated dietary oils with trans fatty acids may displace cis n-6 and n-3 unsaturated fatty acids or have adverse effects on their metabolism. The effects of milk trans, n-6, and n-3 fatty acids in breast-fed infants are unclear, although n-6 and n-3 fatty acids are important in infant growth and development. /The authors/ sought to determine the relations between trans and cis unsaturated fatty acids in milk and plasma phospholipids and triacylglycerols of breast-fed infants, and to identify the major maternal dietary sources of trans fatty acids. collected milk from 103 mothers with exclusively breast-fed 2-mo-old infants, blood from 62 infants, and 3-d dietary records from 21 mothers. Results: Mean (+/-SEM) percentages of trans fatty acids were as follows: milk, 7.1 +/- 0.32%; infants' triacylglycerols, 6.5 +/- 0.33%; and infants' phospholipids, 3.7 +/- 0.16%. Milk trans fatty acids, a-linolenic acid (18:3n-3), arachidonic acid (20:4n-6), docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3) (P < 0.001), and linoleic acid (18:2n-6) (P = 0.007) were each related to the same fatty acid in infant plasma phospholipids. Milk trans fatty acids were inversely related to milk 18:2n-6 and 18:3n-3, but not to milk or infant plasma 20:4n-6 or 22:6n-3. trans Fatty acids represented 7.7% of maternal total fat intake (2.5% of total energy); the major dietary sources were bakery products and breads (32%), snacks (14%), fast foods (11%), and margarines and shortenings (11%). There were comparable concentrations of trans fatty acids in the maternal diet, breast milk, and plasma triacylglycerols of breast-fed infants. Prepared foods were the major dietary source of trans fatty acids. Some /conjugated linoleic acid/ CLA appears to get incorporated into the phospholipids of cell membranes. /Conjugated linoleic acid/ Metabolism / Metabolites /OTHER TOXICITY INFORMATION/ The hepatotoxicity of orally administered secondary autoxidation products of linoleic acid in rats was investigated and compared to the effects following administration of a saline solution and linoleic acid as controls. The de novo synthesis of fatty acids was strongly reduced in the secondary products group. The level of nicotine adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) in the liver significantly decreased whereas that of nicotine adenine dinucleotide (NADH) did not. The activities of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphogluconate dehydrogenase apparently decreased. The activities of NAD + kinase and NAD + synthetase decreased and that of NAD + nucleosidase increased in the secondary products group. Therefore the depletion of nicotine adenine dinucleotide phosphate can be attributed to the inhibition of two metabolic systems (a nicotine adenine dinucleotide phosphate-supplemental system and a synthetic system of NADP and NAD), and resulted in the reduction of lipogenesis in the liver. /Autooxidation products/ ... Linoleic acid stimulated tumor growth because it is converted by hepatoma 7288CTC to the mitogen, 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (13-HODE). ... 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (13-HODE) synthesis is enhanced by cyclic AMP. Gamma-linolenic acid, a desaturated metabolite of linoleic acid, causes substantial stimulation of 13-HODE synthesis. A fall in gamma-linolenic acid synthesis with age may be related to the age-related fall in 13-HODE formation. /gamma-Linolenic acid/ Linoleic acid has known human metabolites that include Leukotoxin and Isoleukotoxin. |
|---|---|
| 其他信息 |
Linoleic acid is a colorless to straw colored liquid. A polyunsaturated fatty acid essential to human diet.
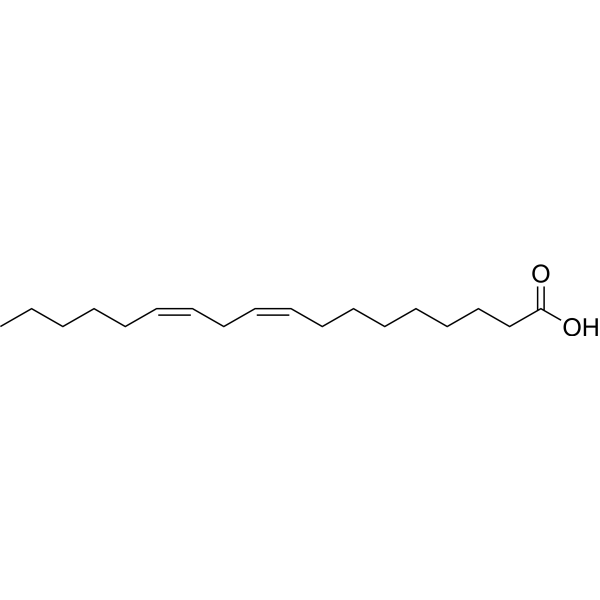
Linoleic acid is an octadecadienoic acid in which the two double bonds are at positions 9 and 12 and have Z (cis) stereochemistry. It has a role as a plant metabolite, a Daphnia galeata metabolite and an algal metabolite. It is an omega-6 fatty acid and an octadecadienoic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a linoleate. Linoleic Acid has been reported in Calodendrum capense, Camellia sinensis, and other organisms with data available. Linoleic Acid is a polyunsaturated essential fatty acid found mostly in plant oils. It is used in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins and cell membranes. Linoleic acid is a doubly unsaturated fatty acid, also known as an omega-6 fatty acid, occurring widely in plant glycosides. In this particular polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA), the first double bond is located between the sixth and seventh carbon atom from the methyl end of the fatty acid (n-6). Linoleic acid is an essential fatty acid in human nutrition because it cannot be synthesized by humans. It is used in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins (via arachidonic acid) and cell membranes. (From Stedman, 26th ed). A doubly unsaturated fatty acid, occurring widely in plant glycosides. It is an essential fatty acid in mammalian nutrition and is used in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins and cell membranes. (From Stedman, 26th ed) See also: Cod Liver Oil (part of); Krill oil (part of); Saw Palmetto (part of) ... View More ... Mechanism of Action /The objective of this work was/ to study the gene expression of the resistin and the effects of conjugated linoleic acid on its expression in white adipose tissue of obese rats fed with high fat diet during the formation of insulin resistance. Male Wistar rats were randomly separated in control group, high-fat group and high fat + conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) group (0.75 g, 1.50 g, 3.00 g per 100 g diet weight), using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) technique to measure the expression level of resistin and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma) mRNA expression. The serum insulin and glucose levels of obese rats were (11.11 +/- 2.73) mIU/L, (5.09 +/- 0.66) mmol/L, and supplement of CLA might decrease hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia, in CLA group (0.75 g, 1.50 g, 3.00 g per 100 g diet weight) the serum insulin levels were (6.99 +/- 1.77) mIU/L, (7.36 +/- 1.48) mIU/L, (7.85 +/- 1.60) mIU/L, and glucose levels were (4.28 +/- 0.72) mmol/L, (4.18 +/- 0.55) mmol/L, (4.06 +/- 0.63) mmol/L. The expression of resistin in adipose tissue of obese rat fed with high fat diet was increased as compared with those fed with basic diet. CLA might increase the expression of resistin and PPARgamma in adipose tissue of obese rat. The expression of resistin mRNA of obese rat fed with high fat diet was higher than those fed with basic diet, and CLA might improve the insulin resistance in obese rats and possibly upregulate the expression of resistin through activing PPARgamma. /Conjugated linoleic acid/ Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) is a mixture of positional (e.g. 7,9; 9,11; 10,12; 11,13) and geometric (cis or trans) isomers of octadecadienoic acid. This compound was first shown to prevent mammary carcinogenesis in murine models. Later investigations uncovered a number of additional health benefits, including decreasing atherosclerosis and inflammation while enhancing immune function. The mechanisms of action underlying these biological properties are not clearly understood. The aim of this review is to highlight recent advances in CLA research related to experimental inflammatory bowel disease. In addition, two possible mechanisms of action (i.e. endoplasmic and nuclear) were discussed in detail in the context of enteric inflammatory disorders. Conjugated linoleic acid was first implicated in down-regulating the generation of inducible eicosanoids (i.e. PGE(2) and LTB(4)) involved in early micro-inflammatory events (endoplasmic). More recently, CLA has been shown to modulate the expression of genes regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs; nuclear). In pigs, prolonged dietary CLA treatment stimulated the expression of PPAR-gamma in the muscle. Thus, evidence supporting both mechanistic theories of CLA acting through eicosanoid synthesis and PPAR activity is available. The further understanding of the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of action of CLA may yield novel nutritional therapies for enteric inflammation. /Conjugated linoleic acid/ /Conjugated linoleic acid/ CLA may modulate eicosanoid activity as well as the activity... of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. /Conjugated linoleic acid/ |
| 分子式 |
C18H32O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
280.4455
|
| 精确质量 |
280.24
|
| CAS号 |
60-33-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
7049-66-3;30175-49-6;67922-65-0
|
| PubChem CID |
5280450
|
| 外观&性状 |
Colorless oil
Colorless to straw-colored liquid |
| 密度 |
0.9±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
360.6±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
-5 °C
|
| 闪点 |
273.0±14.4 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.478
|
| LogP |
7.18
|
| tPSA |
37.3
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
14
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
267
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O([H])C(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])/C(/[H])=C(/[H])\C([H])([H])/C(/[H])=C(/[H])\C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])=O
|
| InChi Key |
OYHQOLUKZRVURQ-HZJYTTRNSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H32O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18(19)20/h6-7,9-10H,2-5,8,11-17H2,1H3,(H,19,20)/b7-6-,10-9-
|
| 化学名 |
(9Z,12Z)-octadeca-9,12-dienoic acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: (1). 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 (2). 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5657 mL | 17.8285 mL | 35.6570 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7131 mL | 3.5657 mL | 7.1314 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3566 mL | 1.7828 mL | 3.5657 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。