| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
左炔诺孕酮(5-25 mg/mL;72 小时)具有浓度依赖性抑制子宫肌瘤细胞生长和增加细胞凋亡的能力 [1]。左炔诺孕酮(0.1-100 μM;4 小时)可减少黄体细胞中高浓度(100 μM)黄体酮的产生,而低剂量(0-10 μM)则无作用[2]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 Sprague-Dawley 大鼠中,左炔诺孕酮(0.005-0.15 mg/kg;每两天一次,持续三周)可减少骨转换,抑制骨吸收,并提高骨矿物质含量 [3]。当左炔诺孕酮(1 mg/kg;灌胃;每天一次,连续三天)与乙炔雌二醇联合使用时,黑线姬鼠可以成功避免怀孕[4]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
蛋白质印迹分析[1]
细胞类型:子宫肌瘤细胞 测试浓度: 5 mg/mL; 10毫克/毫升; 20 mg/mL 孵育时间: 实验结果: 高浓度(10 mg/mL 和 20 mg /mL)时抑制 Bcl-2 和生存素表达)。在高浓度(10 mg/mL 和 20 mg/mL)下显着增加 P38 磷酸化并增加 Caspase-3 表达。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Apodemus agrarius model[4]
Doses: 1 mg/kg Route of Administration: intragastric (po) administration (ig), one time/day for three days Experimental Results: Damaged the sperm ducts, decreased sperm production in combination with quinestrol. decreased population density in the field in combination with quinestrol. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Norgestrel is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, metabolised by the liver and excreted in the urine and faeces as glucuronide and sulphate conjugates. (14)C-Norgestrel was administered to seven human subjects and 43% of dose was excreted in the urine within 5 days; the biological half-life of the radioactivity was 24 hr. Enzymic hydrolysis released only 32% of the urinary radioactivity and a further 25% was excreted as sulphate conjugates. The metabolites excreted in the urine were much less polar than those following the administration of the related compounds, norethisterone or lynestrenol. The 3alphaOH,5beta and 3betaOH,5beta isomers of the tetrahydronorgestrel (13beta-ethyl-17alpha-ethynyl-5 beta-gonane-3alpha,17beta-diol) were isolated from urine and identified by mass spectrometry and thin-layer and gas-liquid chromatography. Plasma radioactivity decreased more rapidly than after the administration of norethisterone and lynestrenol. About 2% of the administered dose was converted to acidic compounds. There was no apparent difference in the rate of excretion of radioactivity or in the metabolites after either oral or intravenous administration of norgestrel. The binding of different synthetic steroids, used in hormonal contraception, to Sex Hormone Binding Globulin (SHBG) was studied by measuring their ability to displace tritiated testosterone from SHBG in a competitive protein binding system. Only 19-nortestosterone derivates had any significant ability to displace testosterone from SHBG, d-norgestrel (d-Ng) being the strongest displacer. Increasing the SHBG levels in women with previous constant plasma d-Ng levels increased these levels two- to sixfold. It is concluded that SHBG is the main carrier protein for d-Ng. The strong testosterone displacing activity of d-Ng might also explain androgenic side effects observed with d-Ng containig oral contraceptives. Metabolism / Metabolites (14)C-Norgestrel was administered to seven human subjects and 43% of dose was excreted in the urine within 5 days ... Enzymic hydrolysis released only 32% of the urinary radioactivity and a further 25% was excreted as sulphate conjugates. The metabolites excreted in the urine were much less polar than those following the administration of the related compounds, norethisterone or lynestrenol. The 3alphaOH,5beta and 3betaOH,5beta isomers of the tetrahydronorgestrel (13beta-ethyl-17alpha-ethynyl-5 beta-gonane-3alpha,17beta-diol) were isolated from urine and identified by mass spectrometry and thin-layer and gas-liquid chromatography. Plasma radioactivity decreased more rapidly than after the administration of norethisterone and lynestrenol. About 2% of the administered dose was converted to acidic compounds. There was no apparent difference in the rate of excretion of radioactivity or in the metabolites after either oral or intravenous administration of norgestrel. The comparative metabolism of dl-, d-, and l-norgestrel was investigated in African Green Monkeys (Cercopithecus aethiops). Total (14)C excretion in urine after a single oral dose of (14)C-dl-norgestrel (1 mg/kg) was significantly higher (51.4 +/- 5.0%) than that observed after administration of the d-enantiomer (37.5 +/- 5.4%) but not the l-enantiomer (44.2 +/- 8.9%). In all cases, the major part of the urinary radioactivity was present in a free fraction (48-62%), while an additional 13-27% was released by beta-glucuronidase preparations. No sulfate conjugates were detected. At least one major (16beta-hydroxylation) and one minor (16alpha-hydroxylation) metabolic pathway were stereoselective, i.e., they are operative with the I-but not the d-enantiomer. Three metabolites, 16beta-hydroxynorgestrel, 16alpha-hydroxynorgestrel, and 16-hydroxytetrahydronorgestrel (believed to be 16beta) were only detected in urine samples obtained from (14)C-dland -l-norgestrel-dosed animals. Following (14)C-d-norgestrel administration, 3alpha, 5beta-tetrahydronorgestrel was found to be the major urinary metabolite. These observations are compared with those reported earlier on the urinary metabolites of dl-norgestrel in women. The in vitro metabolism of stereo-isomers (d, l and the racemic mixture dl) of norgestrel by a microsomal fraction from rabbit liver was investigated. The metabolism of the biologically active l-norgestrel was more rapid than that of d-norgestrel (sic.) which is biologically inactive. This was mainly due to the more ready conversion of l-norgestrel to ring-A reduced metabolites. There was no difference between the two isomers in respect of the amount undergoing hydroxylation; about 40% of each isomer was converted to hydroxylated metabolites after 30 min incubation. However, there were differences between the isomers, l-norgestrel being converted mainly to the 16beta-hydroxysteroid and d-norgestrel to the 16alpha-hydroxysteroid. Similar amounts of both isomers were hydroxylated at C-6. The metabolism of the racemic mixture was intermediate between that of the d and l isomers. The rates of metabolism of synthetic gestagens derived from 19-nortestosterone by rabbit liver tissue in vitro were compared. Over a period of 1 hr norethisterone was metabolized as rapidly as 19-nortestosterone whereas d-norgestrel and lynestrenol were metabolized at a slightly lower rate. Less than 5% of l-norgestrel was metabolized. In all cases the reaction product was the tetrahydrosteroid. Lynestrenol was metabolised through norethisterone. Skeletal muscle, lung and small intestine also metabolized norethisterone and d-norgestrel but at a slower rate than liver tissue. Small amounts of norethisterone were metabolized by adipose tissue but heart and spleen were inactive. Lynestrenol and l-norgestrel were not metabolized by any of the extra-hepatic tissues studied. In vitro studies were conducted on the metabolism of 3 steroids used in OCs (oral contraceptives) by small pieces of human jejunal mucosa. This was done because the gastrointestinal mucosa of humans is known to metabolize a number of drugs. Almost 40% of the ethinyl estradiol, 9.8% of the levonorgestrel, and 7% of the mestranol were metabolized after incubation. All these metabolic responses were significantly different from those in the control groups. Results of the study show that the metabolism of the ethinyl estradiol was related to the weight of the tissue used. These results are consistent with the known marked 1st pass effect of ethinyl estradiol. Norgestrel, known to have little or no 1st pass effect, did not show a high rate of gut metabolism. Under the experimental conditions employed, no Phase 1 metabolism of either ethinyl estradiol or levonorgestrel was apparent. Hepatic. Route of Elimination: About 45% of levonorgestrel and its metabolites are excreted in the urine and about 32% are excreted in feces, mostly as glucuronide conjugates. Biological Half-Life (14)C-Norgestrel was administered to seven human subjects and 43% of dose was excreted in the urine within 5 days; the biological half-life of the radioactivity was 24 hr. ... |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Binds to the progesterone and estrogen receptors. Target cells include the female reproductive tract, the mammary gland, the hypothalamus, and the pituitary. Once bound to the receptor, progestins like levonorgestrel will slow the frequency of release of gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus and blunt the pre-ovulatory LH (luteinizing hormone) surge. Toxicity Data LD50 >5000 mg/kg (orally in rats) Interactions The metabolism of estrogens and progestagens may be increased by concomitant use of substances known to induce drug-metabolising enzymes, specifically cytochrome P450 enzymes, such as anticonvulsants (eg phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine), and anti-infectives (eg rifampicin, rifabutin, nevirapine, efavirenz). Ritonavir and nelfinavir, although known as strong inhibitors, by contrast exhibit inducing properties when used concomitantly with steroid hormones. Herbal preparations containing St John's Wort (Hypericum Perforatum) may induce the metabolism of estrogens and progestagens. Phenytoin and rifampin increase the serum concentrations of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG); this significantly decreases the serum concentration of free drug for some progestins, which is a special concern in patients using progestins for contraception. /Progestins/ Drug interaction data are not available for rifabutin, but because its structure is similar to that of rifampin, similar precautions with its use with progestins may be warranted. ... /Progestins/ Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat oral 5010 mg/kg LD50 Rat ip 11,200 mg/kg LD50 Mouse ip 7300 mg/kg LD50 Mouse oral 5010 mg/kg |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Contraceptives, Oral, Synthetic; Progestational Hormones, Synthetic Low-ogestrel (norgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets) is indicated for the prevention of pregnancy in women who elect to use this product as a method of contraception. /Included in US product label/ /Cyclo-Progynova is indicated as/ hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for estrogen deficiency symptoms in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women. /Cyclo-Progynova is indicated for/ prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at high risk of future fractures who are intolerant of, or contraindicated for, other medicinal products approved for the prevention of osteoporosis. Norgestrel ... /is/ indicated for the prevention of pregnancy. Progestin-only oral contraceptives are also called minipills and progestin-only oral pills (POPs). /Former/ Drug Warnings Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular side effects from oral contraceptive use. This risk increases with age and with heavy smoking (15 or more cigarettes per day) and is quite marked in women over 35 years of age. Women who use oral contraceptives should be strongly advised not to smoke. The use of oral contraceptives is associated with increased risks of several serious conditions including myocardial infarction, thromboembolism, stroke, hepatic neoplasia, and gallbladder disease, although the risk of serious morbidity or mortality is very small in healthy women without underlying risk factors. The risk of morbidity and mortality increases significantly in the presence of other underlying risk factors such as hypertension, hyperlipidemias, hypercholesterolemia, obesity and diabetes. Oral contraceptives should not be used in women who have the following conditions: thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders; a past history of deep vein thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders; cerebral vascular or coronary artery disease; Known or suspected carcinoma of the breast; carcinoma of the endometrium or other known or suspected estrogen-dependent neoplasia; undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding; cholestatic jaundice of pregnancy or jaundice with prior pill use; hepatic adenomas, carcinomas or benign liver tumors; known or suspected pregnancy The most frequent adverse effect of oral contraceptives is nausea. In addition, nausea has been reported in women using vaginal or transdermal estrogen-progestin contraceptives. The principal risk associated with currently recommended high-dose, postcoital estrogen-progestin combination regimens appears to be moderate to severe adverse GI effects including severe vomiting and nausea, which occur in 12-22 and 30-66%, respectively, of women receiving the short-course regimens and may limit compliance with, and effectiveness of, the regimens. In 2 prospective, randomized studies, nausea and vomiting were less common with a high-dose postcoital progestin-only regimen (0.75 mg levonorgestrel every 12 hours for 2 doses) than with a high-dose estrogen-progestin regimen (100 mcg ethinyl estradiol and 0.5 mg levonorgestrel every 12 hours for 2 doses). Other adverse GI effects include vomiting, abdominal cramps, abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation. Gingivitis and dry socket have also been reported. Changes in appetite and changes in weight also may occur. /Estrogen-Progestin Combination/ For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for NORGESTREL (52 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
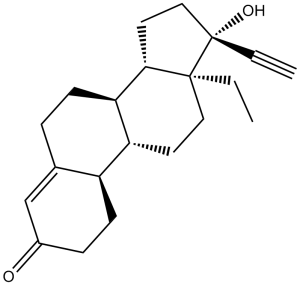
| 分子式 |
C21H28O2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
312.45
|
|
| 精确质量 |
312.208
|
|
| CAS号 |
797-63-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Dydrogesterone;152-62-5;Levonorgestrel-d8;Norgestrel-d6;2376035-98-0
|
|
| PubChem CID |
13109
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
459.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
206ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
195.4±21.3 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.571
|
|
| LogP |
3.92
|
|
| tPSA |
37.3
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
23
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
609
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
6
|
|
| SMILES |
CC[C@]12CC[C@H]3[C@H]([C@@H]1CC[C@]2(C#C)O)CCC4=CC(=O)CC[C@H]34
|
|
| InChi Key |
WWYNJERNGUHSAO-XUDSTZEESA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H28O2/c1-3-20-11-9-17-16-8-6-15(22)13-14(16)5-7-18(17)19(20)10-12-21(20,23)4-2/h2,13,16-19,23H,3,5-12H2,1H3/t16-,17+,18+,19-,20-,21-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
(8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17R)-13-ethyl-17-ethynyl-17-hydroxy-6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3(2H)-one
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.00 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2005 mL | 16.0026 mL | 32.0051 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6401 mL | 3.2005 mL | 6.4010 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3201 mL | 1.6003 mL | 3.2005 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Piroxicam and Levonorgestrel Co-treatment for Emergency Contraception
CTID: NCT03614494
Phase: Phase 2/Phase 3 Status: Completed
Date: 2024-05-06