| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
Histamine H1-receptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
众所周知,嗜酸性粒细胞在过敏性疾病的发展和维持中发挥着重要作用。然而,组胺H1受体拮抗剂对嗜酸性粒细胞功能,特别是趋化因子产生的影响尚不明确。因此,在本研究中,我们通过在体外和体内使用左西替利嗪,检测了组胺H1受体拮抗剂对嗜酸性粒细胞产生趋化因子的影响。在不同浓度的左西替利嗪存在下,用特异性抗原刺激从小鼠制备的嗜酸性粒细胞。24小时后,通过酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)测定培养上清液中受激活调节的正常T细胞表达和分泌(RANTES)和eotaxin水平。在花粉季节(2012年2月至2012年4月),日本雪松花粉症患者接受5 mg左西替利嗪治疗,每天一次,持续四周。还通过ELISA检测鼻腔分泌物中RANTES和eotaxin的水平。向嗜酸性粒细胞培养物中添加左西替利嗪导致细胞对抗原刺激产生RANTES和eotaxin的能力呈剂量依赖性降低,导致显著降低的最小浓度为0.05μM。尽管西替利嗪也对嗜酸性粒细胞产生RANTES和eotaxin具有抑制作用,但引起显著抑制的最小浓度为0.15μM,是左西替利津的三倍。口服左西替利嗪四周也降低了花粉症患者鼻腔分泌物中的RANTES和eotaxin水平,同时减轻了临床症状。左西替利嗪降低RANTES和eotaxin水平的能力可能至少部分解释了该药物治疗过敏性疾病(包括过敏性鼻炎)的临床疗效[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
左西替利嗪(0.4 mg/kg;口服;雄性 Sprague-Dawley 大鼠)治疗显示 Cmax、AUC0-t、AUC0-∞ 和 t1/2 分别为 0.34 μg/mL、3.26 μg h/mL 和 3.67 μg。 h/mL 在 Sprague-Dawley 大鼠中分别为 2.34 小时 [1]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
转录因子激活测定。根据制造商的建议,通过含有足够试剂和抗p65单克隆抗体的市售NF-κB ELISA检测试剂盒分析培养的嗜酸性粒细胞中的NF-κB活性。简言之,将嗜酸性粒细胞的核提取物(5.0 mg蛋白质)引入预涂有体积为20.0μl的含有NF-κB共有位点(5'-GGGGACTTTCC-3’)的寡核苷酸的96孔微孔板的每个孔中,然后在25°C下孵育1小时。洗涤三次后,将100μl抗p65单克隆抗体加入适当的孔中,并在25°C下再孵育一小时。然后加入体积为100μl的抗IgE辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)缀合物,并将平板在25°C下再孵育1小时。在加入四甲基联苯胺(TMB)溶液后测量450nm处的吸光度。AP-1活性也以类似的方式用市售的AP-1 ELISA测试试剂盒进行测量[2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
信使核糖核酸表达测定。用寡核苷酸(dT)包被的磁性微珠从培养的细胞中分离出Poly A+mRNA。根据制造商的说明书,使用Superscript cDNA合成试剂盒由1.0mg PolyA+mRNA合成第一链cDNA。然后使用GeneAmp 5700序列检测系统进行聚合酶链式反应(PCR)。PCR混合物由2.0μl样品cDNA溶液(100 ng/ml)、25.0μl SYBR Green Mastermix、0.3μl正义和反义引物和蒸馏水组成,最终体积为50.0μl。反应如下进行:在94°C下4分钟,然后在95°C下15 s和60°C下60 s的40个循环。甘油醛3-磷酸脱氢酶(GAPDH)被扩增作为内部对照。通过使用比较参数阈值周期计算mRNA水平,并对GAPDH进行归一化。引物的核苷酸序列如下:对于RANTES,5’-CCCTCACATCCTCATGCA-3’(有义)和5’-TCTCTCTGGTGCACACAC-3’(反义),对于eotaxin,5‘-CCCTTTCTGTTGCTGACAAG-3’(有意义)和5‘-GAGGTCCTGGATGTGGCTA-3’(无义),以及对于GAPDH,5’-GTCTCTGGGTGTGTGTGGCAG-3’和5’-CCTTTTCTGTGGCACAAG-3‘(反义的)[2]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: 30 male SD (SD (Sprague-Dawley)) rats (8 weeks old; 200-250 g) [1]
Doses: 0.4 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral (pharmacokinetic/PK/PK analysis) Experimental Results: Cmax, AUC0-t, AUC0-∞ and t1 /2 were 0.34μg/mL, 3.26μg·h/mL, 3.67μg·h/mL and 2.34 hrs (hrs (hours)) respectively. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following a 5mg oral dose of levocetirizine, a Cmax of 0.27±0.04µg/mL with a Tmax of 0.75±0.50h. The AUC of levocetirizine is 2.31±0.50µg\*h/mL. Taking levocetirizine with food does not affect the AUC but delays Tmax by 1.25 hours and lowers Cmax by 36%. 168 hours post dose an average of 85.4% of a radiolabeled dose was recovered with an average of 80.8% in the urine and 9.5% in the feces. In the urine, 77% of the dose was recovered as unchanged drug, 0.5% as the M8 and M9 metabolites, 0.4% as the M10a metabolite, 0.4% as the M10b metabolite, 0.3% as the M3 metabolite, 0.3% as the M4 and M5 metabolite, 0.2% as the M2 metabolite, and 0.1% as the M1 metabolite. In the feces, 9.0% of the dose was recovered as unchanged drug, 1.0% as the M4 and M5 metabolite, and 0.1% as the M1 metabolite. The volume of distribution of levocetirizine is 0.33±0.02L/kg. The average clearance of levocetirizine is 0.57±0.18mL/min/kg. Metabolism / Metabolites Levocetirizine is poorly metabolized with 85.8% of an oral dose being excreted as the unchanged drug. Levocetirizine can be metabolized to a dihydrodiol (M2), an N-oxide (M3), a hydroxymethoxy derivative (M4), a hydroxy derivative (M5), an O-dealkylated derivative (M6), a taurine conjugate (M8), and an N-dealkylated and aromatic hydroxylated derivative (M9). The M5 metabolite can be glucuronidated to form the M1 metabolite and the M9 metabolite can form 4-chloro-4'-hydroxybenzhydryl mercapturates (M10a and M10b). Biological Half-Life The average half life of levocetirizine is 7.05±1.54 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Levocetirizine is the R-enantiomer of cetirizine. Based on limited information from cetirizine and levocetirizine, levocetirizine appears to be acceptable during breastfeeding. Larger doses or more prolonged use may cause drowsiness and other effects in the infant or decrease the milk supply, particularly in combination with a sympathomimetic such as pseudoephedrine or before lactation is well established. International guidelines recommend cetirizine, the racemic form of the drug, as an acceptable choice if an antihistamine is required during breastfeeding. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information on levocetirizine was not found as of the revision date. In one telephone follow-up study, mothers reported irritability and colicky symptoms in 10% of infants exposed to various antihistamines, and drowsiness was reported in 1.6% of infants. None of the reactions required medical attention. A nursing mother taking levocetirizine 5 mg daily reported no adverse effects in her breastfed infant. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Antihistamines in relatively high doses given by injection can decrease basal serum prolactin in nonlactating women and in early postpartum women. However, suckling-induced prolactin secretion is not affected by antihistamine pretreatment of postpartum mothers. Whether lower oral doses of levocetirizine have the same effect on serum prolactin or whether the effects on prolactin have any consequences on breastfeeding success have not been studied. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. Protein Binding Plasma protein binding of levocetirizine was on average 96.1% 1 hour post dose and 91.9% 6 hours post dose. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
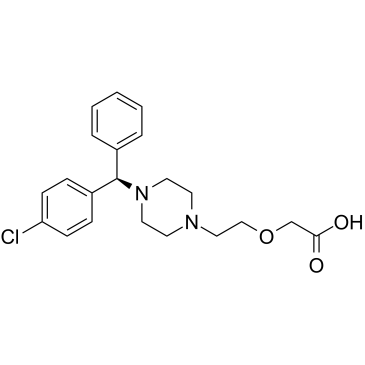
2-[2-[4-[(R)-(4-chlorophenyl)-phenylmethyl]-1-piperazinyl]ethoxy]acetic acid is a diarylmethane.
Levocetirizine is a selective histamine H1 antagonist used to treat a variety of allergic symptoms. It is the R enantiomer of [cetirizine]. Levocetirizine has greater affinity for the histamine H1 receptor than cetirizine. Levocetirizine was granted FDA approval in 1995. Levocetirizine is a Histamine-1 Receptor Antagonist. The mechanism of action of levocetirizine is as a Histamine H1 Receptor Antagonist. Levocetirizine is a third generation, non-sedating, selective histamine H1 receptor antagonist, with antihistamine, anti-inflammatory and potential anti-angiogenic activities. Levocetirizine competes with endogenous histamine for binding at peripheral H1-receptor sites on the effector cell surface. This prevents the negative symptoms associated with histamine release and an allergic reaction. In addition, as histamine plays an important role in angiogenesis during an allergic inflammatory reaction, blocking the action of histamine may modulate the expression of proangiogenic factors and thus may prevent angiogenesis. As a third-generation histamine H1 receptor antagonist, levocetirizine has fewer side effects than most second-generation antihistamines. See also: Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride (has salt form); Cetirizine (annotation moved to). Drug Indication Levocetirizine is indicated to treat symptoms of perennial allergic rhinitis and uncomplicated skin manifestations of chronic idiopathic urticaria. It is also used over the counter for a variety of mild allergy symptoms. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Levocetirizine selectively inhibits histamine H1 receptors. This action prevents histamine from activating this receptor and causing effects like smooth muscle contraction, increased permeability of vascular endothelium, histidine uptake in basophils, stimulation of cough receptors, and stimulation of flare responses in the nervous system. |
| 分子式 |
C21H25N2O3CL
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
388.8878
|
| 精确质量 |
388.155
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 64.86; H, 6.48; Cl, 9.12; N, 7.20; O, 12.34
|
| CAS号 |
130018-77-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Cetirizine;83881-51-0;Cetirizine dihydrochloride;83881-52-1;Cetirizine-d4;1219803-84-5;Cetirizine-d8;774596-22-4;Levocetirizine dihydrochloride;130018-87-0;Cetirizine-d4 dihydrochloride;Cetirizine-d8 dihydrochloride;2070015-04-0;Levocetirizine-d4 dihydrochloride;Levocetirizine-d4;1133210-23-7
|
| PubChem CID |
1549000
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as white to off-white solids at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
542.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
205-208°C (dec.)
|
| 闪点 |
281.6±28.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.589
|
| LogP |
2.16
|
| tPSA |
53.01
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
27
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
443
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
C1=CC=C(C=C1)[C@H](C2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl)N3CCN(CC3)CCOCC(=O)O
|
| InChi Key |
ZKLPARSLTMPFCP-OAQYLSRUSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H25ClN2O3/c22-19-8-6-18(7-9-19)21(17-4-2-1-3-5-17)24-12-10-23(11-13-24)14-15-27-16-20(25)26/h1-9,21H,10-16H2,(H,25,26)/t21-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
Acetic acid, (2-(4-((R)-(4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl)-1-piperazinyl)ethoxy)-
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~257.14 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.43 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.43 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.43 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5714 mL | 12.8571 mL | 25.7142 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5143 mL | 2.5714 mL | 5.1428 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2571 mL | 1.2857 mL | 2.5714 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT01567501 | Completed | Drug: Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride tablets 5 mg Drug: Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride |
Fed | IPCA Laboratories Ltd. | 2012-02 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01563081 | Completed | Drug: Levocetirizine Drug: Levocetirizine |
Rhinitis | GlaxoSmithKline | 2012-04 | Phase 3 |
| NCT01000792 | Completed | Drug: Levocetirizine Drug: Levocetirizine |
Allergic Rhinitis | Clinical Research International Limited | 2009-11 | Phase 3 |
| NCT01640535 | Completed | Drug: Montelukast + Levocetirizine Drug: Levocetirizine Drug: Montelukast |
Perennial Allergic Rhinitis | Hanmi Pharmaceutical Company Limited | 2012-06 | Phase 3 |
| NCT03555890 | Completed | Drug: Levocetirizine IRT 5 mg Drug: Levocetirizine ODT 5 mg |
Rhinitis | GlaxoSmithKline | 2018-05-18 | Phase 1 |