| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:莱特莫韦(原名MK-8828和AIC-246;商品名:Prevymis)是一种处于临床开发阶段的新型强效抗巨细胞病毒药物。 2017年11月8日,莱特莫韦被FDA批准用于预防骨髓移植后感染。尽管有现代的预防和治疗策略,人类巨细胞病毒(HCMV)仍然是一种常见的机会性病原体,与免疫功能低下个体(例如移植受者和艾滋病患者)的严重发病率和死亡率相关。目前获得许可用于治疗 HCMV 感染的所有药物均以病毒 DNA 聚合酶为靶标,并与严重的毒性问题和耐药性的出现有关。激酶检测:AIC246具有一致的抗病毒功效,并且AIC246对人巨细胞病毒具有显着的选择性。 AD169 突变株和指定的 rAIC246-1 和 rAIC246-2 对莱特莫韦 (AIC246) 高度耐药,EC50 分别为 5.6 nM、1.24 μM、0.37 μM。 Letermovir 通过涉及病毒基因产物 UL56 的特定抗病毒机制抑制 HCMV 复制。 Letermovir 通过干扰 HCMV 后代 DNA 的正确切割/包装来抑制细胞培养中的 HCMV 复制[2]。就 EC50 而言,莱特莫韦抑制当前金标准 GCV 超过 400 倍(平均值为 4.5 nM 与 2 μM),就 EC90 值而言抑制超过 2,000 倍(平均值为 6.1 nM 与 14.5 μM)[3] 。莱特莫韦与抗 HCMV 药物联合使用会产生附加的抗病毒作用,但莱特莫韦和抗 HIV 药物之间不存在相互作用。细胞测定:简而言之,将 5×103 AD169 感染的 NHDF 细胞/孔接种到 30 个 96 孔微量滴定板的孔中。允许感染在50 nM AIC246 (10×EC50)的暴露下进行,直到在一个或多个化合物处理的孔中出现CPE(表明抗性病毒突破)。未感染和未处理的细胞作为每个板上的对照。在存在 50 nM AIC246 的情况下,通过无细胞上清病毒的传代,培养物达到最大 CPE,从而完成突变病毒扩增。所得AIC246抗性子代病毒突变体通过在AIC246存在下有限稀释进行噬菌斑纯化3次。通过在没有选择压力的情况下连续传代空斑纯化的病毒(8至10次)来测试耐药性的稳定性。
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
使用小鼠异种移植模型,与安慰剂治疗的对照组相比,莱特莫韦(10-100 mg/kg/天,口服)导致移植细胞中 HCMV 滴度呈剂量依赖性降低
|
||
| 酶活实验 |
AIC246具有一致的抗病毒功效,并且AIC246对人巨细胞病毒具有显着的选择性。 AD169 突变株和指定的 rAIC246-1 和 rAIC246-2 对莱特莫韦 (AIC246) 高度耐药,EC50 分别为 5.6 nM、1.24 μM、0.37 μM。 Letermovir 通过涉及病毒基因产物 UL56 的特定抗病毒机制抑制 HCMV 复制。 Letermovir 通过干扰 HCMV 后代 DNA 的正确切割/包装来抑制细胞培养中的 HCMV 复制[2]。就 EC50 而言,莱特莫韦抑制当前金标准 GCV 超过 400 倍(平均值为 4.5 nM 与 2 μM),就 EC90 值而言抑制超过 2,000 倍(平均值为 6.1 nM 与 14.5 μM)[3] 。莱特莫韦与抗 HCMV 药物联合使用会产生附加的抗病毒作用,但莱特莫韦和抗 HIV 药物之间不存在相互作用。
|
||
| 细胞实验 |
简而言之,将5×103 AD169感染的NHDF细胞/孔接种到30个96孔微量滴定板的孔中。允许感染在50 nM AIC246 (10×EC50)的暴露下进行,直到在一个或多个化合物处理的孔中出现CPE(表明抗性病毒突破)。未感染和未处理的细胞作为每个板上的对照。在存在 50 nM AIC246 的情况下,通过无细胞上清病毒的传代,培养物达到最大 CPE,从而完成突变病毒扩增。所得AIC246抗性子代病毒突变体通过在AIC246存在下有限稀释进行噬菌斑纯化3次。通过在没有选择压力的情况下连续传代空斑纯化的病毒(8至10次)来测试耐药性的稳定性。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Letermovir has a bioavailability of 94% in healthy subjects when administered without cyclosporin, 35% in HSCT recipients when administered without cyclosporin, and 85% in HSCT recipients when administered with cyclosporin. Letermovir's Tmax is 45 min to 2.25 hours. Time to steady state has been observed to be 9-10 days. Taking Letermovir with food increases Cmax by an average of 129.82% (range of 104.35%-161.50%). No significant effect on AUC has been observed. Letemovir is taken up by the liver through OATP1B1/3 transporters. 93% is excreted in the feces with 70% as the parent drug. <2% is excreted in the urine. The mean steady state volume of distribution is 45.5L. The mean clearance is 11.25 L/h in healthy subjects. Metabolism / Metabolites Letermovir undergoes a minor degree of metabolism through UGT1A1/1A3. Biological Half-Life The mean terminal half-life was observed to be 12 hours following administration of Letemovir 480 mg IV once daily. |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In large preregistration clinical trials, ALT elevations occurred in 18.5% of letermovir vs 21.9% of placebo recipients after hematopoietic cell transplantation, and levels rose to above 5 times ULN in 3.5% vs 1.6%. The ALT elevations were generally transient, mild and asymptomatic. Recurrence of serum ALT elevations on rechallenge has been reported. In prelicensure studies, 0.5% of subjects developed jaundice and liver injury, but in the setting of hematopoietic cell transplantation other more likely causes for liver injury were present in all, and none could be convincingly attributed to letermovir therapy. Since the approval of letermovir and its general availability, there have been no reported cases of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice associated with its use; however, the total clinical experience with letermovir therapy has been limited. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of letermovir during breastfeeding. Because letermovir is 99% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be very low. However, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Letermovir has been observed to be 99% bound to plasma proteins at concentrations of 0.2-50 mg/L _in vitro_. |
||
| 参考文献 | |||
| 其他信息 |
Letermovir recieved approval from the FDA on November 8th, 2017 for use in prophylaxis of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients. It is the first of a new class of CMV anti-infectives called DNA terminase complex inhibitors. Letermovir has recieved both priority and orphan drug status from the FDA. It is currently marketed under the brand name Prevymis.
Letermovir is a Cytomegalovirus DNA Terminase Complex Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of letermovir is as a DNA Terminase Complex Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 3A Inhibitor, and Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide 1B1 Inhibitor, and Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide 1B3 Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 2C8 Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 2C9 Inducer, and Cytochrome P450 2C19 Inducer. Letermovir is an antiviral agent which targets the DNA terminal transferase complex of the cytomegalovirus (CMV) and which is used to prevent CMV reactivation in immunocompromised patients. Letermovir has been associated with mild-to-moderate serum aminotransferase elevations during therapy but has not been linked to cases of clinically apparent acute liver injury. Letermovir is an orally bioavailable, non-nucleoside, 3,4-dihydroquinazolinyl acetic acid and inhibitor of the pUL56 subunit of the viral terminase complex of cytomegalovirus (CMV), with potential CMV-specific antiviral activity. Upon oral administration, letermovir binds to the pUL56 subunit of the viral terminase complex of CMV and prevents the cleavage of concatemeric DNA into monomeric genome length DNA. As this agent interferes with viral DNA processing and subsequent viral DNA packaging into procapsids, CMV replication is blocked and CMV infection is prevented. Drug Indication Letermovir is indicated for prophylaxis against cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection and disease in adult recipients of an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) who are CMV-seropositive. It is also indicated for prophylaxis against CMV disease in adult kidney transplant recipients who are at risk (i.e. donor CMV-seropositive/recipient CMV-seronegative). FDA Label Prevymis is indicated for prophylaxis of cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation and disease in adult CMV-seropositive recipients [R+] of an allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT). Consideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antiviral agents. Prevention of cytomegalovirus infection Mechanism of Action CMV relies on a DNA terminase complex consisting of multiple subunits (pUL51, pUL56, and pUL89) for processing of viral DNA. Viral DNA is produced in a single repeating strand which is then cut by the DNA terminase complex into individual viral genomes which can then be packaged into mature viral particles. Letemovir inhibits the activity of this complex to prevent production of mature viral genomes and the production of viable viral particles. The exact nature of Letemovir's binding to this complex is not currently known. Initially, the observation of resistance-causing mutations in pUL56 suggested this subunit was the location of Letemovir binding. However, resistance mutations have now been observed in pUL51, pUL56, and pUL89. It is possible that changes in amino acid sequence in one subunit could result in conformational changes to interacting subunits affecting Letemovir binding or that Letemovir interacts with multiple subunits of the complex but evidence towards either of these distinctions has not yet been seen. pUL89 is known to contain the endonuclease activity of the complex but because all members of the complex are necessary for targeting as well as protection from proteosomal degradation, it is difficult to discern if Letemovir inhibits pUL89's activity directly. Pharmacodynamics Letermovir inhibits the activity of the DNA terminase complex of CMV thereby preventing the cutting of viral DNA into mature length genomes for packaging into viral particles. Letemovir inhibits the DNA terminase complex with an EC50 of 2.1nM. |
| 分子式 |
C29H28F4N4O4
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
572.56
|
|
| 精确质量 |
572.204
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 60.84; H, 4.93; F, 13.27; N, 9.79; O, 11.18
|
|
| CAS号 |
917389-32-3
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
45138674
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
706.5±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
381.1±35.7 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.601
|
|
| LogP |
3.47
|
|
| tPSA |
77.84
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
41
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
931
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
C([C@H]1C2C=CC=C(C=2N=C(N2CCN(C3C=CC=C(OC)C=3)CC2)N1C1C=C(C(F)(F)F)C=CC=1OC)F)C(=O)O
|
|
| InChi Key |
FWYSMLBETOMXAG-QHCPKHFHSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C29H28F4N4O4/c1-40-20-6-3-5-19(16-20)35-11-13-36(14-12-35)28-34-27-21(7-4-8-22(27)30)23(17-26(38)39)37(28)24-15-18(29(31,32)33)9-10-25(24)41-2/h3-10,15-16,23H,11-14,17H2,1-2H3,(H,38,39)/t23-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
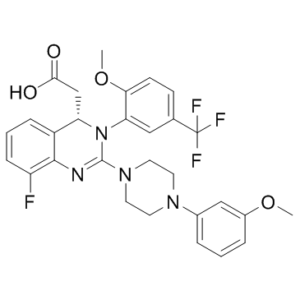
(S)-2-(8-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-(4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-yl)acetic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
MK-8828; MK 8828; MK8828; AIC-246; AIC 246; AIC246; Letermovir; Prevymis
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL ( ~174.65 mM )
Ethanol : ~100 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.37 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.37 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.37 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.37 mM) 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7465 mL | 8.7327 mL | 17.4654 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3493 mL | 1.7465 mL | 3.4931 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1747 mL | 0.8733 mL | 1.7465 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Anti-HCMV activities and cytotoxicities for letermovir in combination with GCV (A), CDV (B), FOS (C), and ACV (D).Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2015;59(6):3140-8. |
|---|
Efficacy analysis of two-drug combinations by use of the Bliss independence model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2015;59(6):3140-8. |
(A) Effects of therapeutic drug concentrations of selected anti-HIV drugs on the letermovir EC50value for inhibition of HCMV replication. (B) Effects of a clinically relevant letermovir dose on the EC50values of the indicated anti-HIV drugs for inhibition of HIV-1 replication.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2015;59(6):3140-8. |