| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
VEGFR1 (IC50 = 170 nM); VEGFR2 (IC50 = 160 nM); VEGFR3 (IC50 = 125 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:KRN 633 是一种新型喹唑啉脲衍生物,强烈抑制 VEGFR1、VEGFR2 和 VEGFR3 受体,IC50 值分别为 170 nM、160 nM 和 125 nM。它对非 RTK 表现出较低的抑制活性,例如 PDGF 受体(PDGFRα 和 β、c-Kit、乳腺肿瘤激酶和内膜内皮细胞激酶酪氨酸激酶)(IC50 = 965、9850、4330、9200 和 9900 nM, KRN 633 有效抑制 HUVEC 中配体 VEGF 诱导的 VEGFR2 磷酸化,IC50 为 1.16 nM。KRN 633 还抑制内皮细胞中 VEGF 依赖性而非 bFGF 依赖性 MAP 激酶磷酸化,IC50 值为 3.51 ERK1 和 ERK2 分别为 nM 和 6.08 nM。KRN633 还被证明可以抑制 VEGF 驱动的 HUVEC 增殖,IC50 为 14.9 nM,但仅在 3 μM 时微弱地抑制 FGF 驱动的增殖。KRN 633 抑制缺氧-通过抑制 Akt 和 ERK 磷酸化信号通路,以浓度依赖性方式诱导 HIF-1α 转录激活,IC50 为 3.79 μM。 激酶测定:进行无细胞激酶测定以获得针对多种药物的 IC50 值重组VEGF受体。 KRN633 的测试浓度范围为 0.3 nM 至 10 μM。所有测定均使用 1 μM ATP 一式四份进行。细胞测定:将癌细胞(A549、Ls174T、DU145、HT29、LNCap 和 PC-3 细胞系)接种在含有 10% FBS 和抗生素的培养基中,其密度已知可在测定期间呈指数生长。将细胞培养 24 小时,然后添加 KRN633(0.01 至 10 μM)或仅添加载体(培养基中含有 0.1% DMSO),然后再生长 96 小时。使用 WST-1 试剂测量细胞活力。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
尽管KRN633在体外对多种癌细胞没有细胞毒性,但由于其对肿瘤血管形成和血管通透性的抑制作用,在体内表现出优异的抗肿瘤活性。每日一次以 100 mg/kg/d 剂量施用 KRN633 可在 A549、LC-6-LCK、HT29、Ls174T、LNCap 和 Du145 细胞中产生显着的肿瘤生长抑制作用,而每日两次以 100 mg/kg 剂量施用 KRN633 可诱导约 90 HT29 肿瘤的生长抑制百分比。用 KRN 633(300 mg/kg,口服)治疗中期妊娠小鼠会减少胎儿组织的血液供应,因为胎盘和胎儿器官的血管化减少,从而增加诱发宫内生长受限 (IUGR) 的风险。
|
| 酶活实验 |
为了找到针对各种重组 VEGF 受体的 IC50 值,进行了无细胞激酶测定。 KRN633 的检测浓度范围为 0.3 nM 至 10 μM。每个测定均使用一微克 ATP 进行四次重复。
|
| 细胞实验 |
含有 10% FBS 和抗生素的培养基用于以已知在检测期间允许指数生长的密度铺板癌细胞。将细胞孵育 24 小时后,用 KRN633(0.01 至 10 μM)或仅用载体(培养基中含有 0.1% DMSO)处理它们,然后让它们再生长 96 小时。 WST-1试剂用于测量细胞的活力。
|
| 动物实验 |
Rats: Human tumor xenografts are implanted in the hind flank of BALB/cA and Jcl-nu athymic rats. When the tumors reach the average size indicated (162 to 657 mm3), rats are randomized into groups of five and treated with KRN-633 or vehicle once (qd) or twice (bid) per day at the indicated dosages. On the 14th day following the last treatment, the percentage of inhibition of tumor growth is calculated in comparison to the vehicle-treated group[1].
Mice: The mice are divided into five-group randomization once the tumors reach the average sizes of 500 to 667 mm3 or 103 to 260 mm3. Following that, they receive treatment with KRN-633 or a vehicle once (qd) or twice (bid) daily at doses ranging from 10 to 100 mg/kg. The day following the final treatment, the percentage of tumor growth inhibition (TGI) relative to the vehicle-treated group is computed[1]. Inhibition of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway during pregnancy contributes to several pathologic pregnancies, such as hypertension, preeclampsia, and intrauterine growth restriction, but its effects on the fetus have not been fully examined. To determine how inhibition of the VEGF signaling pathway affects the fetal vascular development of mid pregnancy, we treated pregnant mice daily with either the VEGF receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) tyrosine kinase inhibitor KRN633 (300 mg/kg, p.o.) or the vehicle from 13.5 to 15.5 day of pregnancy. On the 16.5 day of pregnancy, the vascular beds in the placenta and several organs of the fetus were visualized by fluorescent immunohistochemistry. All mice treated with KRN633 appeared healthy, and total numbers of fetuses per litter were unaffected. However, weights of the placenta and fetus from KRN633-treated mice were lower than those from the vehicle-treated ones. No external malformations and bleeding were observed in the placenta and fetus, whereas immunohistochemical analyses revealed that the vascular development in labyrinthine zone of placenta and fetal organs examined (skin, pancreas, kidney, and lung) were impaired by KRN633 treatment. These results suggest that inhibition of the VEGF signaling pathway during mid pregnancy suppresses vascular growth of both the placenta and fetus without obvious health impairments of mother mice and increases the risk of induction of intrauterine growth restriction.[3] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor VEGFR-2 play a central role in angiogenesis, which is necessary for solid tumors to expand and metastasize. Specific inhibitors of VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase are therefore thought to be useful for treating cancer. We showed that the quinazoline urea derivative KRN633 inhibited tyrosine phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 (IC50 = 1.16 nmol/L) in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Selectivity profiling with recombinant tyrosine kinases showed that KRN633 was highly selective for VEGFR-1, -2, and -3. KRN633 also blocked the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by VEGF, along with human umbilical vein endothelial cell proliferation and tube formation. The propagation of various cancer cell lines in vitro was not inhibited by KRN633. However, p.o. administration of KRN633 inhibited tumor growth in several in vivo tumor xenograft models with diverse tissue origins, including lung, colon, and prostate, in athymic mice and rats. KRN633 also caused the regression of some well-established tumors and those that had regrown after the cessation of treatment. In these models, the trough serum concentration of KRN633 had a more significant effect than the maximum serum concentration on antitumor activity. KRN633 was well tolerated and had no significant effects on body weight or the general health of the animals. Histologic analysis of tumor xenografts treated with KRN633 revealed a reduction in the number of endothelial cells in non-necrotic areas and a decrease in vascular permeability. These data suggest that KRN633 might be useful in the treatment of solid tumors and other diseases that depend on pathologic angiogenesis.[1]
The hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) is a heterodimeric basic helix-loop-helix transcriptional factor and the activated HIF plays pivotal roles in various pathological conditions, including inflammation and cancer. HIF-1alpha overexpression has been observed in many common human cancers, including brain, breast, colon, lung, ovary, and prostate, and HIF-mediated genes, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, are associated with tumor angiogenesis, metastasis, and invasion. Therefore, the pro-oncogenic protein HIF is a novel target of cancer therapy. We examined the effects of VEGFR inhibitors, AAL993, SU5416, and KRN633, on suppression of HIF-1alpha accumulation under the hypoxic condition. We found that VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, AAL993, SU5416, and KRN633, possess dual functions: inhibition of VEGFR signaling and HIF-1alpha expression under the hypoxic condition. The detailed mechanistic study indicated that SU5416 and KRN633 suppressed HIF-1alpha expression through inhibition of both Akt and ERK phosphorylation signaling pathways, whereas AAL993 suppressed HIF-1alpha expression through ERK inhibition without affecting Akt phosphorylation.[2] KRN-633 is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of I. |
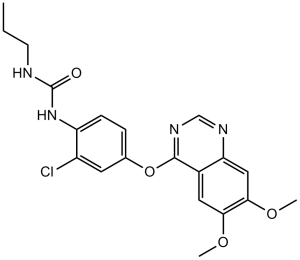
| 分子式 |
C20H21CLN4O4
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
416.86
|
|
| 精确质量 |
416.125
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 57.62; H, 5.08; Cl, 8.50; N, 13.44; O, 15.35
|
|
| CAS号 |
286370-15-8
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
9549295
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
545.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
229 °C
|
|
| 闪点 |
283.7±30.1 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.629
|
|
| LogP |
4.14
|
|
| tPSA |
98.09
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
529
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C(C([H])=C([H])C=1N([H])C(N([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)OC1C2=C([H])C(=C(C([H])=C2N=C([H])N=1)OC([H])([H])[H])OC([H])([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
VPBYZLCHOKSGRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H21ClN4O4/c1-4-7-22-20(26)25-15-6-5-12(8-14(15)21)29-19-13-9-17(27-2)18(28-3)10-16(13)23-11-24-19/h5-6,8-11H,4,7H2,1-3H3,(H2,22,25,26)
|
|
| 化学名 |
1-[2-chloro-4-(6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-yl)oxyphenyl]-3-propylurea
|
|
| 别名 |
KRN633; KRN-633; K00589a; VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor III; 1-(2-chloro-4-(6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-yloxy)phenyl)-3-propylurea; 1-{2-chloro-4-[(6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-yl)oxy]phenyl}-3-propylurea; KRN 633
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|---|
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3989 mL | 11.9944 mL | 23.9889 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4798 mL | 2.3989 mL | 4.7978 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2399 mL | 1.1994 mL | 2.3989 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。