| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
cytotoxicity in LoVo cells ( IC50 = 15.8 μM ); cytotoxicity in HT-29 cells ( IC50 = 5.17 μM ); Topo I
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
伊立替康和吉非替尼研究还发现可以显着减少 MDA-MB-231 细胞迁移和增殖。 [2]
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在异种移植模型中治疗 TNBC 亚型细胞时,吉非替尼和伊立替康具有很好的协同作用。[/2]
|
| 细胞实验 |
在 20 cm2 培养皿中,按指数生长的细胞接种每个细胞系理想数量的细胞(LoVo 细胞为 20,000 个,HT-29 细胞为 100,000 个)。两天后,他们接受浓度递增的伊立替康或 SN-38 治疗,进行单细胞倍增期(LoVo 细胞为 24 小时,HT-29 细胞为 40 小时)。 0.15 M NaCl 洗涤后,将细胞在正常培养基中再培养两次倍增,然后使用胰蛋白酶-EDTA 将其与支持物分离并使用血细胞计数器进行计数。与不含药物培养的细胞相比,导致生长抑制 50% 的药物浓度估计为 IC50 值。
|
| 动物实验 |
One cycle of therapy consists of five days of 5 mg/kg of iminotecan administered intraperitoneally (IV) at a volume of 0.1 cc of the suitable solution, on two separate weeks. The administration of the medication is followed by a seven-day rest period. In an eight-week period, rats receive three cycles. Under the same intratumoral injection guidelines as group II animals, control animals receive 0.1 cc of sterile 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption
The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) when a dose of 125 mg/m^2 is given to patients with solid tumours is 1660 ng/mL. The AUC (0-24) is 10,200 ng·h/mL. The Cmax when a dose of 340 mg/m^2 is given to patients with solid tumours is 3392 ng/mL. The AUC (0-24) is 20,604 ng·h/mL. Route of Elimination The cumulative biliary and urinary excretion of irinotecan and its metabolites (SN-38 and SN-38 glucuronide) over a period of 48 hours following administration of irinotecan in two patients ranged from approximately 25% (100 mg/m2) to 50% (300 mg/m2). Volume of Distribution The volume of distribution of terminal elimination phase is 110 L/m^2 when a dose of 125 mg/m^2 is given to patients with solid tumours. The volume of distribution of terminal elimination phase is 234 L/m^2 when a dose of 340 mg/m^2 is given to patients with solid tumours. Clearance 13.3 L/h/m^2 [Dose of 125 mg/m^2, patients with solid tumours] 13.9 L/h/m^2 [Dose of 340 mg/m^2, patients with solid tumours] View More
Pharmacokinetic parameters for irinotecan and SN-38 were determined in 2 pediatric solid-tumor trials at dose levels of 50 mg/sq m (60-min infusion, n=48) and 125 mg/sq m (90-min infusion, n=6). Irinotecan clearance (mean + or - S.D.) was 17.3 + or - 6.7 L/h/sq m for the 50 mg/sq m dose and 16.2 + or - 4.6 L/h/sq m for the 125 mg/sq m dose, which is comparable to that in adults. Dose-normalized SN-38 AUC values were comparable between adults and children. Minimal accumulation of irinotecan and SN-38 was observed in children on daily dosing regimens (daily X 5 every 3 weeks or (daily X 5) X 2 weeks every 3 weeks).
Metabolism / Metabolites Hepatic. The metabolic conversion of irinotecan to the active metabolite SN-38 is mediated by carboxylesterase enzymes and primarily occurs in the liver. SN-38 is subsequently conjugated predominantly by the enzyme UDP-glucuronosyl transferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) to form a glucuronide metabolite. ... SN38 levels achieved in humans are about 100-fold lower than corresponding irinotecan levels, but these concentrations are important since SN38 is 100- to 1,000-fold more cytotoxic than the parent compound. SN38 is 95% bound to plasma proteins. SN38 plasma decay follows closely that of the parent compound. Irinotecan is extensively metabolized in the liver. The bipiperidinocarbonyloxy group of irinotecan is first removed by a carboxyesterase to yield the corresponding carboxylic acid and SN38. This metabolite can be converted into SN38 glucuronide by UDP-glucuronyltransferase (1.1 isoform). A recently identified metabolite is the 7-ethyl-10-[4-N-(5-aminopentanoic acid)-1-piperidino]-carbonyloxy-camptothecin (APC), which is formed by the action of cytochrome P450 3A4. Numerous other unidentified metabolites are detected in bile and urine. ... PMID:9932079 Bull Cancer (12): 11-20 (1998) Irinotecan, a camptothecin analogue, is a prodrug which requires bioactivation to form the active metabolite SN-38. SN-38 acts as a DNA topoisomerase I poison. ... Irinotecan is subjected to be shunted between CYP3A4 mediated oxidative metabolism to form two inactive metabolites APC or NPC and tissue carboxylesterase mediated hydrolysis to form SN-38 which is eventually detoxified via glucuronidation by UGT1A1 to form SN-38G. The pharmacology of this compound is further complicated by the existence of genetic inter-individual differences in activation and deactivation enzymes of irinotecan (e.g., CYP3A4, CYP3A5, UGT1A1) and sharing competitive elimination pathways with many concomitant medications, such as anticonvulsants, St. John's Wort, and ketoconazole. Efflux of the parent compound and metabolites out of cells by several drug transporters (e.g., Pgp, BCRP, MRP1, MRP2) also occurs. This review highlights the latest findings in drug activation, transport mechanisms, glucuronidation, and CYP3A-mediated drug-drug interactions of irinotecan in order to unlock some of its complicated pharmacology and to provide ideas for relevant future studies into optimization of this promising agent. PMID:12570720 Ma MK, McLeod HL; Curr Med Chem 10 (1): 41-9 (2003) Irinotecan serves as a water-soluble precursor of the lipophilic metabolite SN-38. SN-38 is formed from irinotecan by carboxylesterase-mediated cleavage of the carbamate bond between the camptothecin moiety and the dipiperidino side chain. SN-38 is approximately 1000 times as potent as irinotecan as an inhibitor of topoisomerase I purified from human and rodent tumor cell lines. In vitro cytotoxicity assays show that the potency of SN-38 relative to irinotecan varies from 2- to 2000-fold. However, the plasma area under the concentration versus time curve (AUC) values for SN-38 are 2% to 8% of irinotecan and SN-38 is 95% bound to plasma proteins compared to approximately 50% bound to plasma proteins for irinotecan. The precise contribution of SN-38 to the activity of Camptosar is thus unknown. Both irinotecan and SN-38 exist in an active lactone form and an inactive hydroxy acid anion form. A pH-dependent equilibrium exists between the two forms such that an acid pH promotes the formation of the lactone, while a more basic pH favors the hydroxy acid anion form. Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 62 ed., Montvale, NJ 2008, p. 2594 The metabolic conversion of irinotecan to the active metabolite SN-38 is mediated by carboxylesterase enzymes and primarily occurs in the liver. SN-38 is subsequently conjugated predominantly by the enzyme UDP-glucuronosyl transferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) to form a glucuronide metabolite. UGT1A1 activity is reduced in individuals with genetic polymorphisms that lead to reduced enzyme activity such as the UGT1A1*28 polymorphism. Approximately 10% of the North American population is homozygous for the UGT1A1*28 allele. In a prospective study, in which irinotecan was administered as a single-agent on a once-every-3-week schedule, patients who were homozygous for UGT1A1*28 had a higher exposure to SN-38 than patients with the wild-type UGT1A1 allele. SN-38 glucuronide had 1/50 to 1/100 the activity of SN-38 in cytotoxicity assays using two cell lines in vitro. The disposition of irinotecan has not been fully elucidated in humans. The urinary excretion of irinotecan is 11% to 20%; SN-38, <1%; and SN-38 glucuronide, 3%. The cumulative biliary and urinary excretion of irinotecan and its metabolites (SN-38 and SN-38 glucuronide) over a period of 48 hours following administration of irinotecan in two patients ranged from approximately 25% (100 mg/sq m) to 50% (300 mg/sq m). Thomson Health Care Inc.; Physicians' Desk Reference 62 ed., Montvale, NJ 2008, p. 2594 Irinotecan has known human metabolites that include 7-ethyl-10-[4-N-(5-aminopentanoic acid)-1-piperidino] carbonyloxycamptothecin and (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-[[(19S)-10,19-diethyl-14,18-dioxo-7-(4-piperidin-1-ylpiperidine-1-carbonyl)oxy-17-oxa-3,13-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.02,11.04,9.015,20]henicosa-1(21),2,4(9),5,7,10,15(20)-heptaen-19-yl]oxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid. S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560 Biological Half-Life The half life of irinotecan is about 6 - 12 hours. The terminal elimination half-life of the active metabolite, SN-38 is 10 - 20 hours. After intravenous infusion of irinotecan in humans, irinotecan plasma concentrations decline in a multiexponential manner, with a mean terminal elimination half-life of about 6 to 12 hours. The mean terminal elimination half-life of the active metabolite SN-38 is about 10 to 20 hours. The half-lives of the lactone (active) forms of irinotecan and SN-38 are similar to those of total irinotecan and SN-38, as the lactone and hydroxy acid forms are in equilibrium. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding:
30%-68% protein bound, mainly to albumin.
Interactions A total of 190 patients (49 smokers, 141 nonsmokers) treated with irinotecan (90-minute intravenous administration on a 3-week schedule) were evaluated for pharmacokinetics. Complete toxicity data were available in a subset of 134 patients receiving 350 mg/sq m or 600 mg flat-fixed dose irinotecan. In smokers, the dose-normalized area under the plasma concentration-time curve of irinotecan was significantly lower (median, 28.7 v 33.9 ng x hr/mL/mg; P = .001) compared with nonsmokers. In addition, smokers showed an almost 40% lower exposure to SN-38 (median, 0.54 v 0.87 ng x h/mL/mg; P < .001) and a higher relative extent of glucuronidation of SN-38 into SN-38G (median, 6.6 v 4.5; P = .006). Smokers experienced considerably less hematologic toxicity. In particular, the incidence of grade 3 to 4 neutropenia was 6% in smokers versus 38% in nonsmokers (odds ratio [OR], 0.10; 95% CI, 0.02 to 0.43; P < .001). There was no significant difference in incidence of delayed-onset diarrhea (6% v 15%; OR, 0.34; 95% CI, 0.07 to 1.57; P = .149). This study indicates that smoking significantly lowers both the exposure to irinotecan and treatment-induced neutropenia, indicating a potential risk of treatment failure. Although the underlying mechanism is not entirely clear, modulation of CYP3A and uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase isoform 1A1 may be part of the explanation. The data suggest that additional investigation is warranted to determine whether smokers are at increased risk for treatment failure. PMID:17563393 van der Bol JM et al; J Clin Oncol 25 (19): 2719-26 (2007) The coadministration of protease inhibitors with anticancer drugs in the management of human immunodeficiency virus-related malignancies can cause potential drug-drug interactions. The effect of lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/RTV) on the pharmacokinetics of irinotecan (CPT11) has been investigated in seven patients with Kaposi's sarcoma. Coadministration of LPV/RTV reduces the clearance of CPT11 by 47% (11.3+/-3.5 vs 21.3+/-6.3 l/h/m(2), P=0.0008). This effect was associated with an 81% reduction (P=0.02) of the AUC (area under the curve) of the oxidized metabolite APC (7-ethyl-10-[4-N-(5-aminopentanoic-acid)-1-piperidino]-carbonyloxycamptothecin). The LPV/RTV treatment also inhibited the formation of SN38 glucuronide (SN38G), as shown by the 36% decrease in the SN38G/SN38 AUCs ratio (5.9+/-1.6 vs 9.2+/-2.6, P=0.002) consistent with UGT1A1 inhibition by LPV/RTV. This dual effect resulted in increased availability of CPT11 for SN38 conversion and reduced inactivation on SN38, leading to a 204% increase (P=0.0001) in SN38 AUC in the presence of LPV/RTV. The clinical consequences of these substantial pharmacokinetic changes should be investigated. PMID:17713471 |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Irinotecan hydrochloride hydrate is a hydrate that is the trihydrate form of irinotecan hydrochloride. Onivyde is used in combination with fluorouracil and leucovorin, for the treatment of patients with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas after disease progression following gemcitabine-based therapy. It is converted via hydrolysis of the carbamate linkage to its active metabolite, SN-38, which is ~1000 times more active. It has a role as an EC 5.99.1.2 (DNA topoisomerase) inhibitor, an antineoplastic agent, an apoptosis inducer and a prodrug. It contains an irinotecan hydrochloride (anhydrous).
Irinotecan Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt of a semisynthetic derivative of camptothecin, a cytotoxic, quinoline-based alkaloid extracted from the Asian tree Camptotheca acuminata. Irinotecan, a prodrug, is converted to a biologically active metabolite 7-ethyl-10-hydroxy-camptothecin (SN-38) by a carboxylesterase-converting enzyme. One thousand-fold more potent than its parent compound irinotecan, SN-38 inhibits topoisomerase I activity by stabilizing the cleavable complex between topoisomerase I and DNA, resulting in DNA breaks that inhibit DNA replication and trigger apoptotic cell death. Because ongoing DNA synthesis is necessary for irinotecan to exert its cytotoxic effects, it is classified as an S-phase-specific agent. A semisynthetic camptothecin derivative that inhibits DNA TOPOISOMERASE I to prevent nucleic acid synthesis during S PHASE. It is used as an antineoplastic agent for the treatment of COLORECTAL NEOPLASMS and PANCREATIC NEOPLASMS. Drug Indication Treatment of metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas, in combination with 5 fluorouracil (5 FU) and leucovorin (LV), in adult patients who have progressed following gemcitabine based therapy. |
| 分子式 |
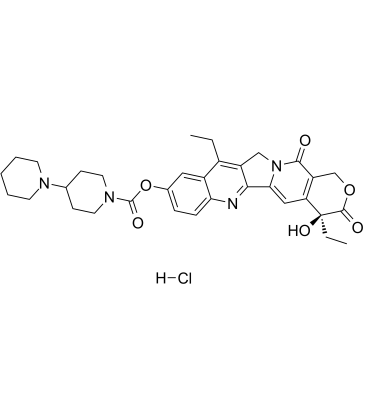
C₃₃H₃₉CLN₄O₆
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
623.14
|
| 精确质量 |
622.255
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 63.61; H, 6.31; Cl, 5.69; N, 8.99; O, 15.40
|
| CAS号 |
100286-90-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
136572-09-3 (HCl trihydrate); 1329502-92-2 (Carboxylate Sodium Salt); 143490-53-3 (Lactone Impurity); 100286-90-6 (HCl); 97682-44-5 (Free base)
|
| PubChem CID |
60837
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid powder
|
| 沸点 |
257 °C
|
| 熔点 |
250-256°C (dec.)
|
| 闪点 |
482ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
1.31E-32mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
67.7 ° (C=1, H2O)
|
| LogP |
4.768
|
| tPSA |
114.2
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
5
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
11
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
47
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1200
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
Cl[H].O(C1C([H])=C([H])C2=C(C=1[H])C(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])=C1C(C3=C([H])C4=C(C([H])([H])OC([C@@]4(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])O[H])=O)C(N3C1([H])[H])=O)=N2)C(N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])=O
|
| InChi Key |
GURKHSYORGJETM-WAQYZQTGSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C33H38N4O6.ClH/c1-3-22-23-16-21(43-32(40)36-14-10-20(11-15-36)35-12-6-5-7-13-35)8-9-27(23)34-29-24(22)18-37-28(29)17-26-25(30(37)38)19-42-31(39)33(26,41)4-2;/h8-9,16-17,20,41H,3-7,10-15,18-19H2,1-2H3;1H/t33-;/m0./s1
|
| 化学名 |
[(19S)-10,19-diethyl-19-hydroxy-14,18-dioxo-17-oxa-3,13-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.02,11.04,9.015,20]henicosa-1(21),2,4(9),5,7,10,15(20)-heptaen-7-yl] 4-piperidin-1-ylpiperidine-1-carboxylate;hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
CPT-11 hydrochloride; Irinotecan hydrochloride; 100286-90-6; Irinotecan Hcl; Topotecin; Campto; Camptothecin 11; CPT-11; Camptothecin 11 hydrochloride
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: 100~125 mg/mL (160.5~200.6 mM)
H2O: ~3.3 mg/mL (~5.3 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.34 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.34 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.34 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 5%DMSO+ 40%PEG300+ 5%Tween 80+ 50%ddH2O: 5.0mg/ml (8.02mM) 配方 5 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (16.05 mM) in 50% PEG300 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 6 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (16.05 mM) in 0.5% CMC-Na/saline water (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6048 mL | 8.0239 mL | 16.0478 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3210 mL | 1.6048 mL | 3.2096 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1605 mL | 0.8024 mL | 1.6048 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04074343 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: TAS-102 Drug: Irinotecan |
Gastric Adenocarcinoma GastroEsophageal Cancer |
University of California, Irvine | August 26, 2019 | Phase 1 |
| NCT04641871 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Irinotecan Hydrochloride Drug: Sym021 |
Metastatic Cancer Solid Tumor |
Symphogen A/S | October 12, 2020 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03567629 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Irinotecan Drug: Oxaliplatin |
mCRC | Peking University | May 29, 2018 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03323034 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Irinotecan Drug: Pevonedistat |
Recurrent Lymphoma Refractory Lymphoma |
Children's Oncology Group | January 11, 2018 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03365882 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Irinotecan Hydrochloride Biological: Cetuximab |
Colon Adenocarcinoma Rectal Adenocarcinoma |
SWOG Cancer Research Network | November 27, 2017 | Phase 2 |
|
|