| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
MMP-2;HIV-1
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
硫酸茚地那韦(0-50 μM;18 小时)抑制 PBMC 中淋巴细胞细胞周期的 G0/G1 期,降低细胞增殖淋巴肿大的能力[1]。
在体外,硫酸茚地那韦(40 μM– 40 nM;5 天)抑制 Huh7 和 SK-HEP-1 肝癌细胞侵袭细胞并激活 MMPs-2 的能力(40 μM–40 nM;48 小时)[2]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
硫酸茚地那韦(70 mg/kg;ig;每天一次,持续 3 周)可抑制体内肝癌细胞的生长[2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞系:PBMC(来自健康和感染 HIV 的志愿者)
浓度:0-50 µM 孵育时间:18 小时(预处理;用抗 CD3 刺激另外 48 小时) 结果:封闭抗CD3以剂量依赖性方式诱导细胞周期进程。导致淋巴细胞增殖反应的剂量依赖性减少。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal Model: Nude mice(s.c. into Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells)[2].
Dosage: 70 mg/kg Administration: Oral gavage; once a day for 3 weeks. Result: Delaied the growth of s.c. implanted hepatocarcinoma xenografts in nude mice compared with placebo. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
In a study in HIV-infected children 4-17 years of age receiving an antiretroviral regimen that included oral indinavir (initial dosage of 500 mg/sq m every 8 hours; subsequent dosage averaging 2043 mg/sq m daily in 3 or 4 doses); peak and trough plasma concentrations averaging 7.3 and 0.29 ug/ml, respectively. Indinavir is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with peak levels achieved in approximately 1 hour. Unlike other drugs in this class, food can adversely affect indinavir bioavailability; a high-calorie, high-fat meal reduces plasma concentrations by 75%. Indinavir is excreted principally in the feces, both as unabsorbed drug and metabolites. Following oral administration of 400 mg of radiolabeled indinavir, 83% of the dose is recovered in feces (19.1% as unchanged drug) and 19% is recovered in urine (9.4% as unchanged drug). Following oral administration of a single 700- or 1000-mg dose of indinavir, 10.4 or 12%, respectively, is excreted unchanged in urine. To characterize steady-state indinavir pharmacokinetics in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma, 8 adults infected with human immunodeficiency virus underwent intensive cerebrospinal fluid sampling while receiving indinavir (800 mg every 8 hours) plus nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Nine and 11 serial cerebrospinal fluid and plasma samples, respectively, were obtained from each subject. Free indinavir accounted for 94.3% of the drug in cerebrospinal fluid and 41.7% in plasma. Mean values of cerebrospinal fluid peak concentration, concentration at 8 hours, and area under the concentration-time profile calculated over the interval 0 to 8 hours (AUC(0-8)) for free indinavir were 294 nmol/L, 122 nmol/L, and 1616 nmol/L x hr, respectively. The cerebrospinal fluid-to-plasma AUC(0-8) ratio for free indinavir was 14.7% +/- 2.6% and did not correlate with indexes of blood-brain barrier integrity or intrathecal immune activation. Indinavir achieves levels in cerebrospinal fluid that should contribute to control of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in this compartment. The cerebrospinal fluid-to-plasma AUC (0-8) ratio suggests clearance mechanisms in addition to passive diffusion across the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier, perhaps by P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for INDINAVIR SULFATE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Indinavir is metabolized to at least 7 metabolites including 1 glucuronide conjugate and 6 oxidative metabolites. Major metabolic pathways identified include glucuronidation at the pyridine nitrogen, pyridine N-oxidation, para-hydroxylation of the phenylmethyl group, 3-hydroxylation of the indan, and N-depyridomethylation. In vitro studies indicate that cytochrome P-450 isoenzyme CYP3A4 is the major enzyme involved in the formation of the oxidative metabolites. Biological Half-Life In a study in adults with cirrhosis and mild to moderate hepatic impairment, the elimination half-life of the drug was prolonged to 2.8 hours. The plasma half-life of indinavir averages 1.8 hours. In HIV-infected children 4-17 years of age receiving an antiretroviral regimen that included oral indinavir, plasma half-life of the drug averaged 1.1 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Indinavir is no longer marketed in the US. Published experience with indinavir during breastfeeding is limited, but some infants may achieve high levels of the drug in breastmilk. Indinavir is not a recommended agent during breastfeeding. Achieving and maintaining viral suppression with antiretroviral therapy decreases breastfeeding transmission risk to less than 1%, but not zero. Individuals with HIV who are on antiretroviral therapy with a sustained undetectable viral load and who choose to breastfeed should be supported in this decision. If a viral load is not suppressed, banked pasteurized donor milk or formula is recommended. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Gynecomastia has been reported among men receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. Gynecomastia is unilateral initially, but progresses to bilateral in about half of cases. No alterations in serum prolactin were noted and spontaneous resolution usually occurred within one year, even with continuation of the regimen. Some case reports and in vitro studies have suggested that protease inhibitors might cause hyperprolactinemia and galactorrhea in some male patients, although this has been disputed. The relevance of these findings to nursing mothers is not known. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. Interactions Studies have not been done with the cytochrome p450 CYP3A4 substrates astemizole, cisapride, midazolam, terfenadine, and triazolam; because competition for CYP3A4 by indinavir could result in inhibition of the metabolism of these medications and elevated plasma concentrations, there is a potential for serious and/or life-threatening side effects; concurrent use of indinavir with any of these medications is not recommended. Concurrent administration /of cimetidine and indinavir/ does not affect the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) of indinavir. Amprenavir interferes with the metabolism of rifabutin and significantly increases rifubutin serum concentrations; it is recommended that the dose of rifabutin be reduced by at least half of the recommended dose; rifabutin decreases the AUC of amprenavir by 15%; patients should be monitored for neutropenia once a week and as clinically indicated if rifabutin is given concurrently with amprenavir. Concurrent use /with clarithromycin/ results in a 29% increase in the AUC of indinavir and a 53% increase in the AUC of clarithromycin; dosing modification is not required. For more Interactions (Complete) data for INDINAVIR SULFATE (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Dog Intraperitoneal > 640 mg/kg LD50 Dog oral > 640 mg/kg LD50 Mouse Intraperitoneal > 5 g/kg LD50 Mouse oral > 5 g/kg For more Non-Human Toxicity Values (Complete) data for INDINAVIR SULFATE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
HIV Protease Inhibitors. Indinavir with antiretroviral agents is indicated for the treatment of HIV infection. /Included in US product labeling/ Drug Warnings Nephrolithiasis/urolithiasis, which may present as flank pain with or without hematuria (including microscopic hematuria), has been reported in about 9% of adults and 29% of pediatric patients receiving indinavir. The most frequent adverse effects associated with indinavir therapy involve the GI tract. ...In treatment-naive HIV-infected adults, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea occurred in 16.6, 11.7, 8.4, and 3.3%, respectively, and acid regurgitation, anorexia, dyspepsia, increased appetite, and taste perversion occurred in 1.5-2.7% of patients receiving indinavir monotherapy. In patients in study 028 receiving indinavir in conjunction with zidovudine, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea occurred in 16, 31.9, 17.8, and 3%, respectively, and acid regurgitation, anorexia, dyspepsia, increased appetite, and taste perversion occurred in 1.5-8.4% of patients. ...Safety and efficacy of indinavir in pediatric patients have not been established. Indinavir has been used in a limited number of HIV-infected children 3 months of age or older without unusual adverse effects. However, nephrolithiasis/urolithiasis has been reported more frequently in pediatric patients receiving indinavir (29%) than in adults receiving the drug (9.2%). Asymptomatic hyperbilirubinemia (i.e., total serum bilirubin concentrations exceeding 2.5 mg/dL) has occurred in about 14% of patients receiving indinavir in clinical studies. Asymptomatic bilirubinemia usually has been reported as elevated indirect bilirubin and has been associated with increased serum AST (SGOT) or ALT (SGPT) concentrations only rarely (i.e., in less than 1% of patients receiving the drug). Acute hepatitis sometimes resulting in hepatic failure and death have been reported in a few patients receiving indinavir in conjunction with other drugs. ...Jaundice was reported in 1.5-2.1% of patients receiving indinavir. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for INDINAVIR SULFATE (21 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
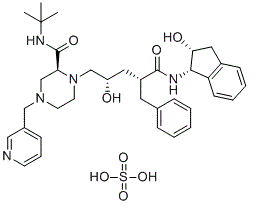
| 分子式 |
C36H49N5O8S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
711.87
|
| 精确质量 |
711.33
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 60.74; H, 6.94; N, 9.84; O, 17.98; S, 4.50
|
| CAS号 |
157810-81-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Indinavir;150378-17-9;Indinavir sulfate ethanolate;2563866-80-6
|
| PubChem CID |
5462355
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 沸点 |
877.9ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
150-153ºC
|
| 闪点 |
484.7ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
5.56E-33mmHg at 25°C
|
| LogP |
3.952
|
| tPSA |
201.01
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
6
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
11
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
12
|
| 重原子数目 |
50
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1030
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
5
|
| SMILES |
O=C([C@@H](C[C@H](O)CN(CCN(CC1=CN=CC=C1)C2)[C@@H]2C(NC(C)(C)C)=O)CC3=CC=CC=C3)N[C@H]4C(C=CC=C5)=C5C[C@H]4O.O=S(O)(O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
NUBQKPWHXMGDLP-BDEHJDMKSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C36H47N5O4.H2O4S/c1-36(2,3)39-35(45)31-24-40(22-26-12-9-15-37-21-26)16-17-41(31)23-29(42)19-28(18-25-10-5-4-6-11-25)34(44)38-33-30-14-8-7-13-27(30)20-32(33)43;1-5(2,3)4/h4-15,21,28-29,31-33,42-43H,16-20,22-24H2,1-3H3,(H,38,44)(H,39,45);(H2,1,2,3,4)/t28-,29+,31+,32-,33+;/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2S)-1-[(2S,4R)-4-benzyl-2-hydroxy-5-[[(1S,2R)-2-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-yl]amino]-5-oxopentyl]-N-tert-butyl-4-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)piperazine-2-carboxamide sulfate
|
| 别名 |
trade name: Crixivan; DRG-0233; DRG0233; L-735 524 sulfate; DRG 0233; MK-639 sulfate; L 735 524; MK 639; L735 524; MK639;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL ( ~140.47 mM )
H2O :~50 mg/mL (~70.24 mM ) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.51 mM) 配方 5 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (140.48 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.4048 mL | 7.0238 mL | 14.0475 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2810 mL | 1.4048 mL | 2.8095 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1405 mL | 0.7024 mL | 1.4048 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Protease-inhibitor interactions.J Mol Biol.2005 Dec 9;354(4):789-800. |
The catalytic site of PRL24I–p2/NC at 1.1 Å resolution.J Mol Biol.2005 Dec 9;354(4):789-800. |
Structural differences at sites of mutation.J Mol Biol.2005 Dec 9;354(4):789-800. |