| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
LRRK1/Leucine rich repeat kinase 1
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
IN04被选为体外评估破骨细胞(OC)的生物学效应。在体外下拉试验中,16 nM的INO4完全阻断了ATP与hLRRK1 KD的结合。在分化和凹坑试验中,虽然用IN04和DMSO处理的OC在骨切片上的OC数量相当,但IN04处理的OC显著削弱了它们吸收骨的能力。与DMSO相比,骨切片上的凹坑面积在5μM和10μM时分别减少了43%和83%。个别坑看起来更小、更浅。F-actin染色显示,DMSO处理的OC显示清晰的肌动蛋白环,F-actin形成外周密封区。相比之下,IN04处理的OC显示细胞质中的F-actin紊乱,F-actin未能在骨切片上形成密封区。IN04治疗对OC衍生偶联因子的产生和成骨细胞结节的形成没有影响。这些数据表明,IN04是LRRK1的强效抑制剂,抑制OC功能,对OC形成没有影响[1]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
体外抑制ATP结合试验[1]
IN04根据制造商的说明(ATP-Affpur试剂盒III),通过ATP琼脂糖下拉试验评估ATP对hLRRK1-KD结合的抑制作用。简而言之,首先将50 ng重组hLRRK1 KD与不同浓度的IN04抑制剂(3.2 nM、16、nM、80 nM、0.4μM和5.0μM)或相同体积的DMSO在冰上500μl 1x结合缓冲液中孵育15分钟。孵育后,将50μl平衡的ATP琼脂糖加入反应中,在4°C下通过端对端混合孵育反应1小时,然后在1x洗涤缓冲液中洗涤珠子4次。使用2x LDS样品缓冲液洗脱蛋白质,在90°C下加热5分钟,用10%NuPage-Bis-tris凝胶通过蛋白质印迹法用抗6xHis抗体进行分析,如前所述. |
| 细胞实验 |
体外OC形成[1]
根据制造商的说明,用磁性CD11b微珠阳性分离来自5周龄C57BL/6J小鼠脾脏的原代CD11b+单核细胞。简而言之,在用红细胞裂解缓冲液去除红细胞后,将1ml MACS缓冲液中的108个脾细胞与150μl CD11b微珠在4°C下孵育15分钟。然后用含有0.5%BSA和2 mM EDTA的15 ml PBS洗涤缓冲液洗涤细胞,离心并重新悬浮在500μl洗涤缓冲液中。然后将细胞悬浮液装载到放置在MACS分离器磁场中的MACS®柱上。磁性标记的CD11b+单核细胞在3次洗涤并从分离器中取出后,用柱塞洗脱和冲洗。将分离的CD11b+单核细胞在添加了10%胎牛血清(FBS)、青霉素(100单位/ml)、链霉素(100μg/ml)和M-CSF(20 ng/ml)的α-MEM中在37°C的5%CO2中维持3天,以刺激单核细胞增殖。然后在含有LRRK1抑制剂IN04的培养基中诱导细胞分化。培养基每2天更换一次。通过计数TRAP染色阳性、具有至少三个核的多核细胞来评估破骨发生。成熟OC尺寸由配备Lieca STP6000显微镜和Image J的Lieca Application Suite X软件测量。 |
| 动物实验 |
Bone resorption pit and actin ring formation assays [1]
Slices from bovine cortical bone were placed in 48-well plates and cells were differentiated on top of the bone slices as described previously. Cells on bone slices were digested with trypsin at 37°C overnight. Multinucleated cells were further removed by 5-minute sonication in 1M ammonia. Air-dried bone slices were stained with hematoxylin. The entire surface of each bone slice was examined and the total resorbed area per bone slice was quantified using ImageJ software. Resorption pits were also visualized by nano-CT at a 0.66 μM voxel dimension. The pit area and pit depth on bone slices were quantified with ImageJ software and TXM Reconstructor, respectively. Cells on bone slices were also stained with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated phalloidin for F-actin and DAPI for nuclei staining. Actin ring formation, sealing zone, and 3D OC images were visualized by Olympus Fluoview 3000 confocal microscopy. Nodule assay[1] Bone marrow stromal cells isolated from the femurs and the tibias of the mice were grown to 80% confluence. The cells were then treated with a mineralization medium containing 10 mM β-glycerophosphate, 50 μg/ml ascorbic acid, and 10% FBS for 24 days. The cells were washed, fixed, and stained with 40 mM alizarin red (pH 4.2). The mineralized area was measured as described previously [1]. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Since the 3D structure of Lrrk1 is not available, we used TAK1 as a template to build 3D structures of hLRRK1 KD for drug screening. Thus, it is possible that IN04 may inhibit enzymatic activity of TAK1 or other MAPKKK family members. Although we minimized off-target effects by eliminating the compounds that also interact with other known kinases (e.g., p38 MAP kinase, PKC, GSK, c-Src, and B-RAF kinase) and focused on compounds that suppress OC activity by disrupting cytoskeleton rearrangement, but not through affecting OC differentiation, further characterization of the kinase selectivity of IN04 are still needed with experimental high-throughput approaches such as kinase binding assays by the KINOMEscanTM methodology and activity-based enzymatic assays by the KiNativTM technology. In vivo testing in ovariectomized osteoporotic mice or inflammatory bone mouse models with high bone turnover is also needed to confirm that IN04 inhibits bone resorption with no effect on bone formation and to determine whether IN04 has better pharmacologic efficacy than bisphosphonates in treating osteoporosis. It will be our future direction to conjugate IN04 inhibitor with penetrating oligopeptide (DSS)6 to target active OCs on bone surface. Lastly, a crystallographic structure of LRRK1 needs to be resolved for refinement of potential LRRK1 inhibitors and for high throughput screening of more specific and selective inhibitors. [1]
|
| 分子式 |
C20H19N3O6S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
429.4464
|
| 精确质量 |
429.099
|
| CAS号 |
838816-57-2
|
| PubChem CID |
1259183
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.39±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
|
| 折射率 |
1.628
|
| LogP |
4.59
|
| tPSA |
138
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
571
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C=CC=CC=1C(C1C=CC=CC=1)N1CCN(CCOCC(=O)O)CC1
|
| InChi Key |
MCQJCSNFOKHYLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H19N3O6S/c1-26-15-8-13(9-16(10-15)27-2)18-22-23-20(29-18)30-11-17(24)21-14-6-4-5-12(7-14)19(25)28-3/h4-10H,11H2,1-3H3,(H,21,24)
|
| 化学名 |
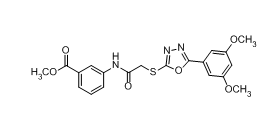
methyl 3-[[2-[[5-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl]sulfanyl]acetyl]amino]benzoate
|
| 别名 |
IN04; IN 04; 838816-57-2; Methyl 3-(2-((5-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)thio)acetamido)benzoate; Methyl3-(2-((5-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)thio)acetamido)benzoate; CBKinase1_012394; CBKinase1_024794; IN-04
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3286 mL | 11.6428 mL | 23.2856 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4657 mL | 2.3286 mL | 4.6571 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2329 mL | 1.1643 mL | 2.3286 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。