| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Na+/Ca2+ channel (T-type); D2 dopamine receptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在培养的皮质神经元中,氟桂利嗪二盐酸盐对钙电流 (ICa) 扩张的 IC50 值为 1.77 μM,对钠电流 (INa) 扩张的 IC50 值为 0.94 μM [2]。在浓度为 3–10 μM 时,二盐酸氟桂利嗪(10 和 30 μM;24 盐酸氟桂利嗪 (1–30 μM))会显着损害嗜铬细胞 [4]。嗜铬细胞会受到细胞活力的显着细胞毒性影响,这在 [4] 中进行了评估小时[4]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
氟桂利嗪二盐酸盐(腹膜内注射;30 mg/kg;一次)可预防脂多糖(LPS)诱导的小鼠颈部急性肺损伤(ALI)[5]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
氟桂利嗪明显抑制顺铂诱导的细胞凋亡。出乎意料的是,氟桂利嗪增加了HEI-OC1细胞内钙([Ca2+]i)水平。然而,氟桂利嗪对顺铂的保护作用不是通过调节细胞内钙水平介导的。顺铂治疗导致HEI-OC1细胞ROS生成和脂质过氧化。氟桂利嗪不减弱ROS的产生,但抑制顺铂处理细胞的脂质过氧化和线粒体通透性转变。这一结果提示氟桂利嗪对顺铂诱导的细胞毒性的保护机制与直接抑制脂质过氧化和线粒体通透性转变有关[1]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[4]
细胞类型:嗜铬 测试浓度: 10 和 30 μM 孵育时间: 24 小时 实验结果:显示在 10 μM 浓度下细胞死亡增加的趋势,在 30 μM 浓度下细胞损失接近 100%。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male balb/c (Bagg ALBino) mouse (6-8 weeks old)) lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury [5]
Doses: 30 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection; 30 mg/kg; Experimental Results:Inhibition of LPS induction of cell influx, protein leakage, and inflammatory cytokine release. Suppress lung inflammation. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption
85% following oral administration. Metabolism / Metabolites Hepatic, to two metabolites via N-dealylation and hydroxylation. Flunarizine has known human metabolites that include p-Hydroxyflunarizine, 1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]piperazine, and bis(4-fluorophenyl)methanone. Biological Half-Life: 18 days |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Flunarizine is not approved for marketing in the United States by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, but is available in other countries. No information is available on the use of flunarizine during breastfeeding. Because of its long half-life of 19 days in children, expert opinion recommends that flunarizine not be used in migraine prophylaxis in nursing mothers. An alternate drug is preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. women TDLo oral 73 mg/kg/1Y-I BEHAVIORAL: SOMNOLENCE (GENERAL DEPRESSED ACTIVITY); BEHAVIORAL: TREMOR Italian Journal of Neurological Sciences., 10(89), 1989 [PMID:2925349] man TDLo oral 4286 ug/kg/30D BEHAVIORAL: TREMOR Neurology., 37(881), 1987 [PMID:3574697] mouse LD50 oral 960 mg/kg Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research., 37(1103), 1987 [PMID:3435581] women TDLo oral 18 mg/kg/90D-I BEHAVIORAL: TREMOR Neurology., 37(881), 1987 [PMID:3574697] Protein Binding 99% bound to plasma proteins |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Flunarizine hydrochloride is a diarylmethane.
Flunarizine is a selective calcium entry blocker with calmodulin binding properties and histamine H1 blocking activity. It is effective in the prophylaxis of migraine, occlusive peripheral vascular disease, vertigo of central and peripheral origin, and as an adjuvant in the therapy of epilepsy. |
| 分子式 |
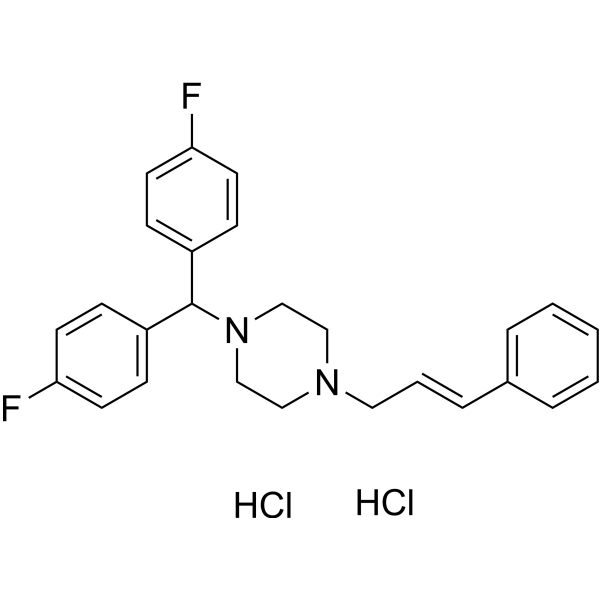
C26H26F2N2.2(HCL)
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
477.42
|
| 精确质量 |
476.159
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 65.41; H, 5.91; Cl, 14.85; F, 7.96; N, 5.87
|
| CAS号 |
30484-77-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Flunarizine;52468-60-7; 30484-77-6 (Flunarizine hydrochloride); 22348-32-9 (Flunarizine 2HCl)
|
| PubChem CID |
5282407
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 沸点 |
511.3ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
204-210ºC
|
| 闪点 |
263ºC
|
| LogP |
6.865
|
| tPSA |
6.48
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
487
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C1CN(CCN1C/C=C/C2=CC=CC=C2)C(C3=CC=C(C=C3)F)C4=CC=C(C=C4)F.Cl.Cl
|
| InChi Key |
RXKMOPXNWTYEHI-RDRKJGRWSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H26F2N2.2ClH/c27-24-12-8-22(9-13-24)26(23-10-14-25(28)15-11-23)30-19-17-29(18-20-30)16-4-7-21-5-2-1-3-6-21;;/h1-15,26H,16-20H2;2*1H/b7-4+;;
|
| 化学名 |
1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-[(E)-3-phenylprop-2-enyl]piperazine;dihydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
Flunarizine dihydrochloride; flunarizine hydrochloride; 30484-77-6; Flunarizine 2HCl; Flunarizine HCl; 27064-95-5; Flunarizine (dihydrochloride); 1-(Bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl)-4-cinnamylpiperazine dihydrochloride;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~104.73 mM)
H2O : ~1 mg/mL (~2.09 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.24 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.24 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.24 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (20.95 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0946 mL | 10.4730 mL | 20.9459 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4189 mL | 2.0946 mL | 4.1892 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2095 mL | 1.0473 mL | 2.0946 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|
|