| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |

| 靶点 |
Macrolide antibiotic
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
恶性疟原虫在硬脂酸红霉素存在下不能发育,硬脂酸红霉素的 IC50 和 IC90 值分别为 58.2 μM 和 104.0 μM [1]。除了其抗炎和抗氧化特性外,硬脂酸红霉素(10 μM、100 μM;24 小时、72 小时)还可显着降低 TNF-α (p<0.01) 和 Iba-1 (p<0.01) 的表达,防止 4-HNE (p<0.01) 和 8-OHdG (p<0.01) 的形成 [4]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
硬脂酸红霉素(胃插管;0.1-50 mg/kg;30-120 天)在 5 mg/kg 的剂量下可减少肿瘤生长并延长小鼠的生存期 [3]。硬脂酸红霉素(胃插管;5 mg/kg)即使在接种后 120 天也能维持小鼠的存活,而 50 mg/kg 的剂量会使荷瘤小鼠的平均存活期缩短 4-5 天[3]。硬脂酸红霉素(ih;单次注射;50 mg/kg)对脑缺血再灌注损伤模型大鼠具有保护作用[4]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定 [4]
细胞类型: 胚胎初级皮层神经元(来自 17 日龄 Sprague-Dawley 大鼠的大脑皮层) 测试浓度: 10, 100 μM 孵育时间: 24、72 小时 实验结果: 提高培养神经元的活力 3 小时(体外细胞氧糖剥夺(OGD)小时)。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Female ddY mice (6 weeks old) with EAC cells or CDF mice (6 weeks old) with P388 cells [3]
Doses: 0.1 mg/kg; 0.5 mg/kg; 10 mg/kg ; 30 mg/kg; 50 mg/kg Route of Administration: gastric intubation; 30-120 days Experimental Results: After the 5 mg/kg dose, tumor growth was diminished and the average survival time of mice was prolonged, but the 50 mg/kg dose shortened the load. MST of tumor mice. Animal/Disease Models: Male SD (SD (Sprague-Dawley)) rats (8 weeks old, 250-300 g) [4] Doses: 50 mg/kg Route of Administration: Single subcutaneous injection Experimental Results: Reduce infarct volume and edema volume, and improve neurological deficits. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
PEAK CONCN IN PLASMA...0.3-0.5 UG/ML 4 HR AFTER ORAL ADMIN OF 250 MG OF BASE & ARE 0.3-1.9 UG/ML AFTER...500-MG TABLET. VARIOUS ESTERS OF ERYTHROMYCIN HAVE BEEN PREPARED TO...IMPROVE STABILITY & FACILITATE ABSORPTION. ...CONCN OF ERYTHROMYCIN IN PLASMA ARE LITTLE DIFFERENT IF STEARATE IS GIVEN ORALLY. ...DIFFUSES READILY INTO INTRACELLULAR FLUIDS, & ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY... ACHIEVED AT...ALL SITES EXCEPT BRAIN & CSF. ...ONE OF FEW ANTIBIOTICS THAT PENETRATES INTO PROSTATIC FLUID, CONCN ARE APPROX 40% OF...PLASMA. EXTENT OF BINDING...TO PLASMA PROTEINS VARIES...PROBABLY EXCEEDS 70% IN ALL.../FORMS OF DRUG/. /ERYTHROMYCIN/ ERYTHROMYCIN BASE IS ADEQUATELY ABSORBED FROM UPPER PART OF SMALL INTESTINE; IT IS INACTIVATED BY GASTRIC JUICE... FOOD IN STOMACH DELAYS ITS ULTIMATE ABSORPTION. /ERYTHROMYCIN/ ERYTHROMYCIN TRAVERSES PLACENTAL BARRIER; & CONCN OF DRUG IN FETAL PLASMA ARE ABOUT 5-20% OF THOSE IN MATERNAL CIRCULATION. /ERYTHROMYCIN/ For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ERYTHROMYCIN STEARATE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites IT IS HYDROLYZED IN SMALL INTESTINE & IN TISSUES TO YIELD ERYTHROMYCIN. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because of the low levels of erythromycin in breastmilk and safe administration directly to infants, it is acceptable in nursing mothers. The small amounts in milk are unlikely to cause adverse effects in the infant. Monitor the infant for irritability and possible effects on the gastrointestinal flora, such as diarrhea, candidiasis (thrush, diaper rash). One case report and unconfirmed epidemiologic evidence indicates that hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants might occur with maternal use of erythromycin during the first two weeks of breastfeeding; however, if it occurs, the frequency is very low and others have questioned this relationship. Infant side effects are unlikely with topical application for acne, although topical application to the nipple may increase the risk of diarrhea in the infant. Only water-miscible cream or gel products should be applied to the breast because ointments may expose the infant to high levels of mineral paraffins via licking.[1] ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Pyloric stenosis, vomiting, sedation, poor sucking and poor weight gain probably related to erythromycin in breastmilk was reported in a 3-week-old infant.[4] A cohort study of infants diagnosed with infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis found that affected infants were 2.3 to 3 times more likely to have a mother taking a macrolide antibiotic during the 90 days after delivery. Stratification of the infants found the odds ratio to be 10 for female infants and 2 for male infants. All of the mothers of affected infants nursed their infants. Seventy-two percent of the macrolide prescriptions were for erythromycin. However, the authors did not state which macrolide was taken by the mothers of the affected infants.[5] A study comparing the breastfed infants of mothers taking amoxicillin to those taking a macrolide antibiotic found no instances of pyloric stenosis. However, most of the infants exposed to a macrolide in breastmilk were exposed to roxithromycin. Only 2 of the 55 infants exposed to a macrolide were exposed to erythromycin. Adverse reactions occurred in 12.7% of the infants exposed to macrolides which was similar to the rate in amoxicillin-exposed infants. Reactions included rash, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and somnolence.[6] A retrospective database study in Denmark of 15 years of data found a 3.5-fold increased risk of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in the infants of mothers who took a macrolide during the first 13 days postpartum, but not with later exposure. The proportion of infants who were breastfed was not known, but probably high. The proportion of women who took each macrolide was also not reported.[7] In one telephone follow-up study, mothers reported diarrhea 2 infants and irritability in 2 infants out of 17 infants whose mothers were taking erythromycin during breastfeeding. None of the reactions required medical attention.[8] Two meta-analyses failed to demonstrate a relationship between maternal macrolide use during breastfeeding and infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis.[9][10] ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Interactions A 77-YR-OLD WOMAN IS REPORTEDLY MAINTAINED ON 7.5 MG OF WARFARIN DAILY IN WHOM THE ADMIN OF ORAL ERYTHROMYCIN STEARATE, 500 MG 4 TIMES A DAY, RESULTED IN A PROTHROMBIN TIME OF 64 SECONDS (CONTROL, 11 SECONDS). |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Erythromycin stearate appears as fluffy colorless powder or fine white powder. (NTP, 1992)
Erythromycin stearate is an aminoglycoside. Erythromycin Stearate is the stearate salt form of erythromycin, a broad-spectrum, topical macrolide antibiotic with antibacterial activity. Erythromycin stearate diffuses through the bacterial cell membrane and reversibly binds to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome. This prevents bacterial protein synthesis. Erythromycin stearate may be bacteriostatic or bactericidal in action, depending on the concentration of the drug at the site of infection and the susceptibility of the organism involved. See also: Erythromycin (has active moiety). Mechanism of Action ...INHIBIT PROTEIN SYNTH BY BINDING TO 50 S RIBOSOMAL SUBUNITS OF SENSITIVE MICROORGANISMS. ... ASSOC BETWEEN ERYTHROMYCIN & RIBOSOME IS REVERSIBLE BUT TAKES PLACE ONLY WHEN 50 S SUBUNIT IS FREE FROM TRNA MOLECULES BEARING NASCENT PEPTIDE CHAINS. PRODN...OF HIGHLY POLYMERIZED HOMOPEPTIDES IS SUPPRESSED. /ERYTHROMYCIN/ THE NONIONIZED FORM OF THE DRUG IS CONSIDERABLY MORE PERMEABLE TO CELLS, & THIS PROBABLY EXPLAINS INCREASED ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY THAT IS OBSERVED AT ALKALINE PH. /ERYTHROMYCIN/ Therapeutic Uses ITS ACTIONS & USES ARE IDENTICAL TO THOSE OF ERYTHROMYCIN. ERYTHROMYCIN MAY BE USEFUL FOR DISSEMINATED GONOCOCCAL DISEASE IN PREGNANT PT WHO IS ALLERGIC TO PENICILLIN... 13 PT...TREATED WITH 500 MG OF ERYTHROMYCIN... STEARATE, GIVEN ORALLY EVERY 6 HR FOR 5 DAYS, SHOWED RAPID CLINICAL & BACTERIOLOGICAL RESPONSES. ANTIBACTERIAL AGENT MEDICATION (VET): ANTIBACTERIAL AGENT Drug Warnings ...ERYTHROMYCIN & ITS DERIV SELDOM CAUSE SERIOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS. |
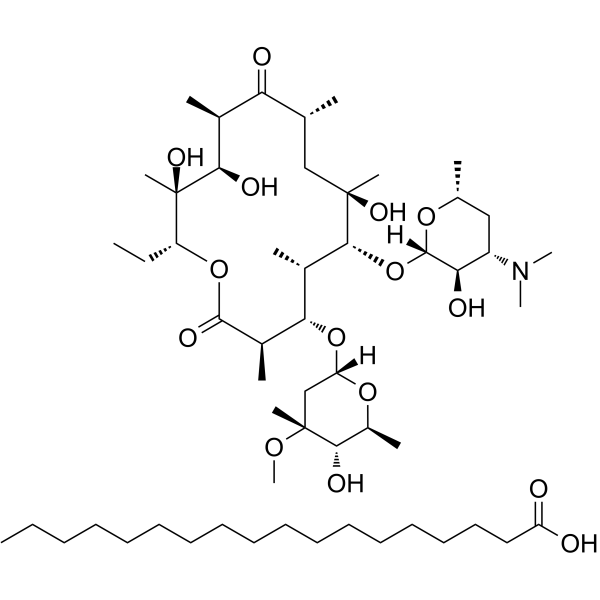
| 分子式 |
C55H103NO15
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
1018.40
|
| 精确质量 |
1003.717
|
| CAS号 |
643-22-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Erythromycin;114-07-8;Erythromycin lactobionate;3847-29-8;Erythromycin (aspartate);30010-41-4;Erythromycin thiocyanate;7704-67-8;Erythromycin A dihydrate;59319-72-1
|
| PubChem CID |
12559
|
| 外观&性状 |
CRYSTALS
WHITE OR SLIGHTLY YELLOW CRYSTALS OR POWDER |
| 密度 |
1.112g/cm3
|
| 熔点 |
77-79ºC
|
| 闪点 |
523.101ºC
|
| 折射率 |
1.518
|
| LogP |
8.118
|
| tPSA |
231.21
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
6
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
16
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
23
|
| 重原子数目 |
71
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1380
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
18
|
| SMILES |
CC[C@@H]1[C@](C)([C@@H]([C@@H](C)C(=O)[C@H](C)C[C@](C)([C@@H]([C@@H](C)[C@@H]([C@@H](C)C(=O)O1)O[C@H]2C[C@](C)([C@H]([C@H](C)O2)O)OC)O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@H](C[C@@H](C)O3)N(C)C)O)O)O)O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)O
|
| InChi Key |
YAVZHCFFUATPRK-YZPBMOCRSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C37H67NO13.C18H36O2/c1-14-25-37(10,45)30(41)20(4)27(39)18(2)16-35(8,44)32(51-34-28(40)24(38(11)12)15-19(3)47-34)21(5)29(22(6)33(43)49-25)50-26-17-36(9,46-13)31(42)23(7)48-26;1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18(19)20/h18-26,28-32,34,40-42,44-45H,14-17H2,1-13H3;2-17H2,1H3,(H,19,20)/t18-,19-,20+,21+,22-,23+,24+,25-,26+,28-,29+,30-,31+,32-,34+,35-,36-,37-;/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
(3R,4S,5S,6R,7R,9R,11R,12R,13S,14R)-6-[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-[(2R,4R,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyloxan-2-yl]oxy-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyl-oxacyclotetradecane-2,10-dione;octadecanoic acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2942000000
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.9819 mL | 4.9097 mL | 9.8193 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1964 mL | 0.9819 mL | 1.9639 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0982 mL | 0.4910 mL | 0.9819 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。