| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
EGFR; HER2; HER3
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
(-)-表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 (EGCG, 10-60 μM) 以剂量依赖性方式抑制 WRO 和 FB-2 细胞的发育 [1]。 (-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate(10–60 μM,0–24 小时)可提高 p21 和 p53 的表达,并降低细胞周期蛋白 D1、AKT 和 ERK1/2 的磷酸化 [1]。据报道,(10–60 μM,12 小时)-表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯对细胞运动和迁移的影响[1]。根据生化实验,(-)-表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(0 – 20 μM,或大约 0 – 20 分钟)以浓度和时间依赖性方式抑制 GLUD1/2 和 IDH1 活性 [2]。 (-)- 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(0-35 μg/mL,24-72 小时)促进细胞凋亡,减少 G0/G1 期细胞增殖,并抑制结直肠癌细胞(LoVo、SW480、HT-29 和 HCT)的增殖-8 个细胞)[3]。在成骨细胞中,LPS 诱导的 COX-2 和 mPGES-1 mRNA 表达以及前列腺素 E2 合成受到 (-)-表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(30 μM,3-24 小时)的抑制 [4]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
(-)-表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯在原位移植范例中腹腔内给药(5-20 mg/kg),每天一次,持续 14 天,可抑制肿瘤的生长 [3]。当表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯以 0.5 mg/小鼠的单剂量注射到实验性牙周炎模型小鼠的下牙龈时,(-)- LPS 引起的骨矿物质密度 (BMD) 损失受到抑制和减少 [3]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
GLUD1/2和IDH酶测定[2]
IDH1在pDEST15中表达为谷胱甘肽S-转移酶(GST)融合蛋白,并如所述在谷胱甘肽珠上纯化。纯化的牛GLUD1/2购自Serva。通过向100μM NADP+、2 mM MgCl2、0.5 mM异柠檬酸盐和100 mM Tris-HCl(pH 7.4)的混合物中加入4μg IDH1酶来引发酶反应。在磷酸盐缓冲液(pH 8.0)中,在含有0.1 U牛GLUD1/2酶、500μM NAD+、10 mM谷氨酸和2 mM ADP的反应中测量GLUD1/2活性。通过在Omega Fluostar上以20秒的间隔实时监测340nm处的NADPH或NADH吸光度来测量NADPH和NADH的化学计量生产。 DNA双链断裂(DSB)检测[2] 将细胞(有或没有AGI-5198培养)以300000个细胞/孔的密度铺在6孔板上,并放置过夜。与Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)孵育24小时后. (0、50或100μM),用0、2或4 Gy照射细胞。30分钟后,在含有1 mM苯甲基磺酰氟(PMSF)的1×RIPA缓冲液中制备细胞质提取物。对细胞提取物进行超声处理以释放核蛋白。蛋白质样品(25μg)在10%SDS-PAGE凝胶上电泳,并在硝化纤维上电印迹。用抗γH2AX抗体和抗γ微管蛋白(C20)对印迹进行染色,然后用IRDye680或IRDye800标记适当的二抗。使用Odyssey系统对信号进行可视化和量化。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖测定[1]
细胞类型: FB-2 和 WRO 细胞(血清饥饿 48 小时) 测试浓度: 10、40、60微米。 孵育时间: 4 天 实验结果: 10 μM 时抑制基底细胞增殖(FB-2 中为 40%,WRO 中为 35%),抑制40 和 60 μM 时的细胞数量(增加 68% 至 73%)。 蛋白质印迹分析[1] 细胞类型: FB-2 细胞 测试浓度: 10、40、60 μM。 孵育时间:24小时 实验结果:细胞周期蛋白D1水平降低,AKT和ERK1/2磷酸化。诱导 p21 和 p53、E-钙粘蛋白、N-钙粘蛋白、波形蛋白和 α5-整合素的表达。 细胞迁移测定 [1] 细胞类型: FB-2 和 WRO 细胞(血清饥饿 48 小时) 测试浓度: > 10、40、60 μM。 孵育时间:12小时 实验结果:FB-2和WRO细胞的迁移活性降低。 RT-PCR[4] 细胞类型:小鼠原代成骨细胞(1 ng/ml LPS 处理) 测试浓度: 30 μM 孵育时间: 3、6、12、24 h 实验结果: 抑制 LPS 诱导的 COX-2 和 mPGES-1 表达mRNA、前列腺素 E2 的产生。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Orthotopic transplant BALB/c nude mice model[3]
Doses: 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg, one time/day for 14 days. Route of Administration: Intragastrical administration. Experimental Results: Inhibited tumors growth with no liver or lung metastases. Animal/Disease Models: Model of experimental periodontitis, LPS (25 μg/mouse)[4] Doses: 0.5 mg/mouse, a single dose. Route of Administration: Injected into the mouse lower gingiva Experimental Results: Inhibited the LPS-induced loss of bone mineral density (BMD ) in mice. Subcutaneous orthotopic colorectal cancer transplant model and medical treatment[3] The HT-29 colorectal cancer cell line with green fluorescence was established.7 BALB/c nude mice, 20 male and 20 female, that ranged from 4- to 6-weeks-old were fed in a special pathogenic free animal facility. The feed was sterilized using cobalt 60. As described above, the subcutaneous orthotopic colorectal cancer transplant model was established successfully. At 2 weeks postsurgery, 39 out of the 40 nude mice presented with tumors. Based on the volume of the tumors, the 39 mice with tumors were divided into four groups: a control group (n = 9); a group that received 5 mg/kg of Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) (n = 10); a group that received 10 mg/kg of Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) (n = 10); and a group that received 20 mg/kg of Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) (n = 10). In the therapeutic groups, Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) was administrated intragastrically, and in the control group, 100 uL of physiological saline was administrated intragastrically, once daily for 14 days. After the treatment of the mice with Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) for 4 weeks, the growth and metastasis of the primary tumors were continuously monitored using a fluorescent imaging system. After 4 weeks, the primary tumors were weighed and immediately put into liquid nitrogen (−196°C) and 2 to 3 hours later, these specimens were stored at −80°C. In addition, the other parts of the primary tumor and metastases were fixed in 4% formaldehyde.[3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Metabolism / Metabolites
(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate has known human metabolites that include (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate, 3p-hydroxy-glucuronide and (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate, 4p-hydroxy-glucuronide. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
(-)-epigallocatechin 3-gallate is a gallate ester obtained by the formal condensation of gallic acid with the (3R)-hydroxy group of (-)-epigallocatechin. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent, an antioxidant, a Hsp90 inhibitor, a neuroprotective agent, a plant metabolite, a geroprotector and an apoptosis inducer. It is a gallate ester, a polyphenol and a member of flavans. It is functionally related to a (-)-epigallocatechin.
Epigallocatechin gallate has been investigated for the treatment of Hypertension and Diabetic Nephropathy. (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate has been reported in Camellia sinensis, Eschweilera coriacea, and other organisms with data available. Epigallocatechin Gallate is a phenolic antioxidant found in a number of plants such as green and black tea. It inhibits cellular oxidation and prevents free radical damage to cells. It is under study as a potential cancer chemopreventive agent. Well-differentiated papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma are the most frequent types of thyroid cancer and the prognosis is generally favorable however, a number of patients develops recurrences. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a major catechin in green tea, was shown to possess remarkable therapeutic potential against various types of human cancers, although data on thyroid cancer cells are still lacking. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of EGCG on the proliferation and motility of human thyroid papillary (FB-2) and follicular (WRO) carcinoma cell lines. Our results demonstrate that EGCG (10, 40, 60 μM) treatment inhibited the growth of FB-2 and WRO cells in a dose-dependent manner. These changes were associated with reduced cyclin D1, increased p21 and p53 expression. Furthermore, EGCG suppressed phosphorylation of AKT and ERK1/2. In addition EGCG treatment results in reduction of cell motility and migration. Changes in motility and migration in FB-2 were associated with modulation in the expression of several proteins involved in cell adhesion and reorganization of actin cytoskeleton. After 24 h EGCG caused an increase of the E-cadherin expression and a concomitant decrease of SNAIL, ZEB and the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor TWIST. Besides expression of Vimentin, N-cadherin and α5-integrin was down-regulated. These data well correlate with a reduction of MMP9 activity as evidenced by gelatin zymography. Our findings support the inhibitory role of EGCG on thyroid cancer cell proliferation and motility with concomitant loss of epithelial-to-mesenchymal cell transition markers.[1] Background: Mutations in isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) occur in various types of cancer and induce metabolic alterations resulting from the neomorphic activity that causes production of D-2-hydroxyglutarate (D-2-HG) at the expense of α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) and NADPH. To overcome metabolic stress induced by these alterations, IDH-mutated (IDH mut ) cancers utilize rescue mechanisms comprising pathways in which glutaminase and glutamate dehydrogenase (GLUD) are involved. We hypothesized that inhibition of glutamate processing with the pleiotropic GLUD-inhibitor epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) would not only hamper D-2-HG production, but also decrease NAD(P)H and α-KG synthesis in IDH mut cancers, resulting in increased metabolic stress and increased sensitivity to radiotherapy. View More
Methods: We performed 13C-tracing studies to show that HCT116 colorectal cancer cells with an IDH1 R132H knock-in allele depend more on glutaminolysis than on glycolysis for the production of D-2-HG. We treated HCT116 cells, HCT116-IDH1 R132H cells, and HT1080 cells (carrying an IDH1 R132C mutation) with EGCG and evaluated D-2-HG production, cell proliferation rates, and sensitivity to radiotherapy.
Aims: To explore the inhibitory effects of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) on the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells and on the gene expression of Notch signaling. Methods: The colorectal cancer cells and orthotopic colorectal cancer transplant model were treated with EGCG, and MTT assay was used to test the inhibitory role of EGCG in the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells. Results: MTT assay indicated that EGCG inhibited the proliferation of these four cell lines when the time and concentration increased, and EGCG enhanced the apoptotic rate of these four cell lines. The dosage was positively correlated to the apoptotic rate, and EGCG inhibited the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells by influencing cell cycle. In-vivo study suggested that on the seventh day, the volume of tumors reduced after administrating with 5, 10 and 20 mg/kg of EGCG. At the twenty-eighth day, the volume of tumors was significantly different in three EGCG treatment groups as compared to the control group (P < 0.05), and TUNEL assay indicated that the apoptosis of cancer cells in EGCG treated groups was markedly higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). In these cell lines, the expressions of HES1 and Notch2 in EGCG treated groups were remarkably lower than that in the control group (P < 0.05). The expression of JAG1 decreased in SW480 cells (P =0.019), HT-29 cells and HCT-8 cells, but increased in LoVo cells at mRNA level. The expression of Notch1 was upregulated in these four cell lines, but its expression was significantly upregulated only in LoVo and SW480 cells (P < 0.05). Conclusion: In-vitro and in-vivo studies showed that EGCG inhibited the proliferation, induced the apoptosis and affected the cell cycle of colorectal cancer cells. After treating with EGCG, the expressions of HES1 and Notch2 was obviously inhibited, this indicated that EGCG inhibited colorectal cancer by inhibiting HES1 and Notch2.[3] Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a major polyphenol in green tea, possesses antioxidant properties and regulates various cell functions. Here, we examined the function of EGCG in inflammatory bone resorption. In calvarial organ cultures, lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced bone resorption was clearly suppressed by EGCG. In osteoblasts, EGCG suppressed the LPS-induced expression of COX-2 and mPGES-1 mRNAs, as well as prostaglandin E2 production, and also suppressed RANKL expression, which is essential for osteoclast differentiation. LPS-induced bone resorption of mandibular alveolar bones was attenuated by EGCG in vitro, and the loss of mouse alveolar bone mass was inhibited by the catechin in vivo.[4] |
| 分子式 |
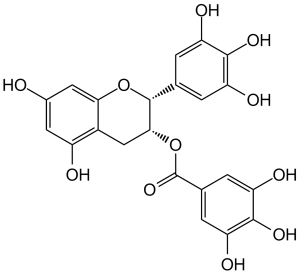
C22H18O11
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
458.37
|
|
| 精确质量 |
458.084
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 57.65; H, 3.96; O, 38.40
|
|
| CAS号 |
989-51-5
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
(-)-Epigallocatechin;970-74-1;(-)-Gallocatechin gallate;4233-96-9;(-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate (Standard);989-51-5;(+/-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate-13C3
|
|
| PubChem CID |
65064
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to pink solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.9±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
909.1±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
222-224°C
|
|
| 闪点 |
320.0±27.8 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.857
|
|
| 来源 |
polyphenol in green tea
|
|
| LogP |
2.08
|
|
| tPSA |
197.37
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
8
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
11
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
667
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
|
| SMILES |
O1C2=C([H])C(=C([H])C(=C2C([H])([H])[C@]([H])([C@@]1([H])C1C([H])=C(C(=C(C=1[H])O[H])O[H])O[H])OC(C1C([H])=C(C(=C(C=1[H])O[H])O[H])O[H])=O)O[H])O[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
WMBWREPUVVBILR-WIYYLYMNSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H18O11/c23-10-5-12(24)11-7-18(33-22(31)9-3-15(27)20(30)16(28)4-9)21(32-17(11)6-10)8-1-13(25)19(29)14(26)2-8/h1-6,18,21,23-30H,7H2/t18-,21-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
[(2R,3R)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)chroman-3-yl] 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.54 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.54 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.54 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 9.09 mg/mL (19.83 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶 (<60°C). 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1816 mL | 10.9082 mL | 21.8164 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4363 mL | 2.1816 mL | 4.3633 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2182 mL | 1.0908 mL | 2.1816 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。