| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Topoisomerase II; Topoisomerase IV
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Enoxacin 是一种用作抗菌化合物的氟喹诺酮类药物,通过与 miRNA 生物合成蛋白 TAR RNA 结合蛋白 2 (TRBP) 结合,增强具有肿瘤抑制功能的 miRNA 的产生。依诺沙星与 DNA 活性位点结合并改变酶的断裂/团聚活性。在没有 ATP 的情况下,Enoxacin 会刺激松弛和超螺旋形式的 DNA 裂解,而 CcdB 仅在许多 ATP 依赖性断裂和团聚循环后才诱导裂解。 Enoxacin 剂量依赖性地减少用 1,25-二羟基维生素 D(3) 刺激的小鼠骨髓培养物中分化的破骨细胞数量,以及破骨细胞活性标记物和骨切片上形成的吸收腔隙的数量。依诺沙星在不改变成骨细胞形成的浓度下抑制破骨细胞形成。 Enoxacin 剂量依赖性地减少由 RANK-L 刺激的破骨细胞前体产生的表达抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶 (TRAP) 活性的多核细胞的数量。依诺沙星通过一种新机制直接抑制破骨细胞形成,而不影响细胞活力,该机制涉及翻译后加工的变化和几种在破骨细胞功能中具有已知作用的蛋白质的运输。 Enoxacin 能够降低细胞活力、诱导细胞凋亡、导致细胞周期停滞并抑制前列腺癌 (PCa) 细胞系的侵袭性。 Enoxacin 还可有效恢复前列腺癌 (PCa) 细胞系中 miRNA 的整体表达。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
依诺沙星(AT 2266;100 µM;2 µl;连续 3 天(第 12、13 和 14 天)每天注射入耳一次)可增加 Lv-siGFP 敲低 GFP mRNA 的能力(从 80% 至 60%;40%)保留 GFP mRNA 水平);然而,在 GFP 转基因系 C57BL/6-Tg(ACTB-EGFP)1Osb/J(10 d 龄)中,单独使用表达 shGFP 的慢病毒(Lv-siGFP;注射到耳朵中 10 天)对 GFP 表达没有影响[3 ]。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Rapidly absorbed following oral administration, with an absolute oral bioavailability of approximately 90%. Metabolism / Metabolites Hepatic. Some isozymes of the cytochrome P-450 hepatic microsomal enzyme system are inhibited by enoxacin. After a single dose, greater than 40% was recovered in urine by 48 hours as unchanged drug. Biological Half-Life Plasma half-life is 3 to 6 hours. |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Fluoroquinolones have traditionally not been used in infants because of concern about adverse effects on the infants' developing joints. However, recent studies indicate little risk. The calcium in milk might prevent absorption of the small amounts of fluoroquinolones in milk, but insufficient data exist to prove or disprove this assertion. Use of enoxacin is probably acceptable in nursing mothers with monitoring of the infant for possible effects on the gastrointestinal flora, such as diarrhea or candidiasis (thrush, diaper rash). However, it is preferable to use an alternate drug for which safety information is available. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Enoxacin is approximately 40% bound to plasma proteins in healthy subjects and is approximately 14% bound to plasma proteins in patients with impaired renal function. |
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
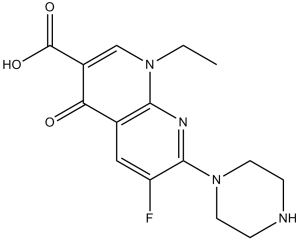
Enoxacin is a 1,8-naphthyridine derivative that is 1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine with an ethyl group at the 1 position, a carboxy group at the 3-position, an oxo sustituent at the 4-position, a fluoro substituent at the 5-position and a piperazin-1-yl group at the 7 position. An antibacterial, it is used in the treatment of urinary-tract infections and gonorrhoea. It has a role as an antibacterial drug and a DNA synthesis inhibitor. It is a monocarboxylic acid, an amino acid, a 1,8-naphthyridine derivative, a N-arylpiperazine, a quinolone antibiotic and a fluoroquinolone antibiotic.
A broad-spectrum 6-fluoronaphthyridinone antibacterial agent (fluoroquinolones) structurally related to nalidixic acid. A broad-spectrum 6-fluoronaphthyridinone antibacterial agent that is structurally related to NALIDIXIC ACID. See also: Enoxacin Sesquihydrate (is active moiety of). Drug Indication For the treatment of adults (≥18 years of age) with the following infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms: (1) uncomplicated urethral or cervical gonorrhea due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae, (2) uncomplicated urinary tract infections (cystitis) due to Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus epidermidis, or Staphylococcus saprophyticus, and (3) complicated urinary tract infections due to Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus epidermidis, or Enterobacter cloacae. Mechanism of Action Enoxacin exerts its bactericidal action via the inhibition of the essential bacterial enzyme DNA gyrase (DNA Topoisomerase II). Pharmacodynamics Enoxacin is a quinolone/fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Enoxacin is bactericidal and its mode of action depends on blocking of bacterial DNA replication by binding itself to an enzyme called DNA gyrase, which allows the untwisting required to replicate one DNA double helix into two. Enoxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Enoxacin may be active against pathogens resistant to drugs that act by different mechanisms. |
| 分子式 |
C15H17FN4O3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
320.32
|
|
| 精确质量 |
320.128
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 56.24; H, 5.35; F, 5.93; N, 17.49; O, 14.98
|
|
| CAS号 |
74011-58-8
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
84294-96-2
|
|
| PubChem CID |
3229
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
569.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
220-224ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
298.4±30.1 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.599
|
|
| LogP |
0.55
|
|
| tPSA |
87.46
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
23
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
521
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
FC1C([H])=C2C(C(C(=O)O[H])=C([H])N(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])C2=NC=1N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
IDYZIJYBMGIQMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H17FN4O3/c1-2-19-8-10(15(22)23)12(21)9-7-11(16)14(18-13(9)19)20-5-3-17-4-6-20/h7-8,17H,2-6H2,1H3,(H,22,23)
|
|
| 化学名 |
1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1219 mL | 15.6094 mL | 31.2188 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6244 mL | 3.1219 mL | 6.2438 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3122 mL | 1.5609 mL | 3.1219 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04840823 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Enoxacin Drug: Placebo |
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis | McGill University | March 26, 2021 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
|
|
|
|
|