| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Ornithine decarboxylase
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
依氟鸟氨酸是鸟氨酸脱羧酶的一种特异性、不可逆的抑制剂,被认为通过抑制毛囊中的这种酶来减缓头发生长[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
过去五十年来唯一被批准用于治疗人类非洲锥虫病的新药是依氟鸟氨酸。它主要用作对 melarsoprol 没有反应的布氏冈比亚锥虫感染的备用药物 [1]。当谈到减少毛发过多的参与者面部毛发的生长时,15% 依氟鸟氨酸霜的效果优于安慰剂。经过 24 周的治疗疗程后,58% 的依氟鸟氨酸患者和 34% 的安慰剂受试者的面部多毛症至少有所改善 [2]。当将依氟鸟氨酸乳膏施用到预先经过微针处理的小鼠皮肤区域时,依氟鸟氨酸的毛发生长抑制活性显着增加[3]。高血压14天后,依氟鸟氨酸治疗缩窄性高血压大鼠导致KCI和去甲肾上腺素收缩强度正常化以及乙酰胆碱松弛[4]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
在使用沙门氏菌和两种酵母菌株的体外研究中,依氟鸟氨酸没有引起突变[1]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
使用Franz扩散池进行依氟鸟氨酸的体外渗透研究[3]。
|
| 动物实验 |
In vivo efficacy study was performed in a mouse model by monitoring the re-growth of hair in the lower dorsal skin of mice after the eflornithine cream was applied onto an area pretreated with microneedles. The skin and the hair follicles in the treated area were also examined histologically[3].
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following oral administrations of eflornithine, peak plasma concentrations of eflornithine (Cmax) were achieved (Tmax) 3.5 hours post-dosing. The Cmax and AUC (area under the concentration-time curve) of eflornithine were not affected by food (high fat and high calories). Administration of crushed tablets in a standard pudding admixture had no effect on eflornithine exposure (Cmax and AUC6h). The mean percutaneous absorption of eflornithine in women with unwanted facial hair, from a 13.9% w/w cream formulation, is < 1% of the radioactive dose, following either single or multiple doses under conditions of clinical use, that included shaving within 2 hours before radiolabeled dose application in addition to other forms of cutting or plucking and tweezing to remove facial hair. Steady state was reached within four days of twice-daily application. Following twice-daily application of 0.5 g of the cream (total dose 1.0 g/day; 139 mg as anhydrous eflornithine hydrochloride), under conditions of clinical use in women with unwanted facial hair (n=10), the steady-state Cmax, Ctrough and AUC12hr were approximately 10 ng/mL, 5 ng/mL, and 92 ng hr/mL, respectively, expressed in terms of the anhydrous free base of eflornithine hydrochloride. At steady state, the dose-normalized peak concentrations (Cmax) and the extent of daily systemic exposure (AUC) of eflornithine following twice-daily application of 0.5 g of the cream (total dose 1.0 g/day) is estimated to be approximately 100- and 60-fold lower, respectively, when compared to 370 mg/day once-daily oral doses. This compound is not known to be metabolized and is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine. Eflornithine volume of distribution (Vz/F) is 24.3 L. The clearance (CL/F) of eflornithine is 5.3 L/h. The mean percutaneous absorption of eflornithine in women with unwanted facial hair, from a 13.9% w/w cream formulation, is < 1% of the radioactive dose, following either single or multiple doses under conditions of clinical use, that included shaving within 2 hr before radiolabeled dose application in addition to other forms of cutting or plucking and tweezing to remove facial hair. Following twice daily application of 0.5 g of the cream (total dose 1.0 g/day; 139 mg as anhydrous eflornithine hydrochloride), under conditions of clinical use in women with unwanted facial hair (n=10), the steady-state Cmax, Ctrough and AUC12hr were approximately 10 ng/mL, 5 ng/mL, and 92 nghr/mL, respectively, expressed in terms of the anhydrous free base of eflornithine hydrochloride. At steady state, the dose-normalized peak concentrations (Cmax) and the extent of daily systemic exposure (AUC) of eflornithine following twice-daily application of 0.5 g of the cream (total dose 1.0 g/day) is estimated to be approximately 100- and 60-fold lower, respectively, when compared to 370 mg/day once-daily oral doses. Eflornithine is not metabolized and is excreted unchanged in urine. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Eflornithine (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites This compound is not known to be metabolized and is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine. Biological Half-Life The terminal plasma elimination half-life of eflornithine was 3.5 hours, and the apparent steady-state plasma half-life of eflornithine was approximately 8 hours. The apparent steady-state plasma t1/2 of eflornithine was approximately 8 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Maternal intravenous eflornithine 400 mg/kg daily for 7 days did not cause any adverse serious effects in breastfed infants. After topical application, eflornithine is poorly absorbed so it is not likely to reach the bloodstream of the infant or cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A cohort of 33 infants who were breastfed (extent not stated) by hospitalized mothers taking nifurtimox was followed in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Thirty mothers took a full course of 30 doses of oral nifurtimox 15 mg/kg daily and all received 14 doses of intravenous eflornithine 400 mg/kg daily for 7 days for human African trypanosomiasis. (sleeping sickness). Nursing mothers also took a median of 4 other concomitant medications, including amoxicillin, ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, aspirin, and diclofenac (1 patient each); hydrocortisone, promethazine and quinine (2 patients each); levamisole (6 patients); sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (8 patients); dipyrone (13 patients); acetaminophen (16 patients); and mebendazole (17 patients). No serious adverse events were reported in any of the breastfed infants. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Eflornithine does not specifically bind to human plasma proteins. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Burri C, et al. Eflornithine for the treatment of human African trypanosomiasis. Parasitol Res. 2003 Jun;90 Supp 1:S49-52.
[2]. Balfour JA, et al. Topical eflornithine. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2001;2(3):197-201; discussion 202. [3]. Kumar A, et al. A method to improve the efficacy of topical eflornithine hydrochloride cream. Drug Deliv. 2016 Jun;23(5):1495-501. [4]. Lipke DW, et al. Eflornithine alters changes in vascular responsiveness associated with coarctation hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1997 Apr;19(3):297-312 |
| 其他信息 |
Eflornithine is a fluoroamino acid that is ornithine substituted by a difluoromethyl group at position 2. It has a role as a trypanocidal drug. It is a fluoroamino acid and an alpha-amino acid. It is functionally related to an ornithine.
Eflornithine is an irreversible ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor originally developed as a treatment for human African trypanosomiasis. Further research has also implicated ornithine decarboxylase in other conditions like facial hirsutism and cancer, especially when ornithine decarboxylase is highly upregulated in tumor cells. Additionally, ornithine decarboxylase is activated by c-myc or interacts with ras, both very well-known oncogenes, thus increasing the interest in targeting ornithine carboxylase as a potential cancer treatment. In 1960 and 2000, the FDA approved eflornithine under the brand names ORNIDYL and VANIQUA for the treatment of African trypanosomiasis and hirsutism, respectively, but has since been discontinued. Subsequently, on December 14, 2023, the FDA approved eflornithine again but under the brand name IWILFIN as an oral maintenance therapy to reduce the risk of relapse in adult and pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma who have demonstrated at least a partial response to prior multiagent, multimodality therapy, including anti-GD2 immunotherapy. This approval is based on positive results obtained from a multi-site, single-arm, externally controlled study of children with high-risk neuroblastoma, where a 52% reduction in the risk of relapse and a 68% reduction in the risk of death were observed. Eflornithine is an Antiprotozoal and Decarboxylase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of eflornithine is as a Decarboxylase Inhibitor. Eflornithine is a difluoromethylated ornithine compound with antineoplastic activity. Eflornithine irreversibly inhibits ornithine decarboxylase, an enzyme required for polyamine biosynthesis, thereby inhibiting the formation and proliferation of tumor cells. Polyamines are involved in nucleosome oligomerization and DNA conformation, creating a chromatin environment that stimulates neoplastic transformation of cells. This agent has been shown to induce apoptosis in leiomyoma cells. (NCI04) An inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase, the rate limiting enzyme of the polyamine biosynthetic pathway. See also: Eflornithine Hydrochloride (has salt form). Drug Indication Eflornithine is indicated to reduce the risk of relapse in adult and pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma (HRNB) who have demonstrated at least a partial response to prior multiagent, multimodality therapy including anti-GD2 immunotherapy. It was also previously indicated for the treatment of female hirsutism and African trypanosomiasis but has since been discontinued. FDA Label Treatment of facial hirsutism in women. Mechanism of Action Eflornithine is an irreversible inhibitor of the enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), the first and rate-limiting enzyme in the biosynthesis of polyamines and a transcriptional target of MYCN. Polyamines are involved in the differentiation and proliferation of mammalian cells and are important for neoplastic transformation. There are no studies examining the inhibition of the enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) in human skin following the application of topical eflornithine. However, there are studies in the literature that report the inhibition of ODC activity in skin following oral eflornithine. It is postulated that topical eflornithine hydrochloride irreversibly inhibits skin ODC activity. This enzyme is necessary in the synthesis of polyamines. Animal data indicate that inhibition of ornithine decarboxylase inhibits cell division and synthetic functions, which affect the rate of hair growth. VANIQA has been shown to retard the rate of hair growth in non-clinical and clinical studies. Eflornithine (alpha-difluoromethylornithine) hydrochloride has hair growth retarding properties. The mechanism(s) by which topically applied eflornithine hydrochloride reduces hair growth has not been fully elucidated. Results of several studies using oral eflornithine hydrochloride indicate that the drug may inhibit ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), an enzyme that catalyzes the biosynthesis of intracellular polyamines required for cell division and differentiation. Limited animal data indicate that such inhibition of cell division and differentiation may affect the rate of hair growth. The manufacturer of topical eflornithine hydrochloride states that there are no published studies in humans on the ODC inhibitory potential of topical eflornithine hydrochloride. |
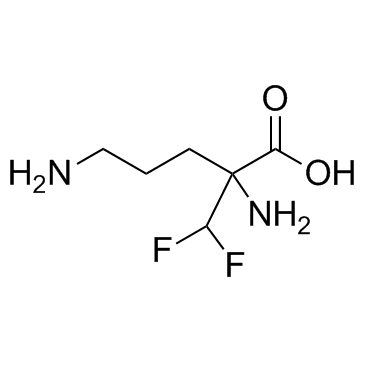
| 分子式 |
C6H12F2N2O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
182.16848
|
| 精确质量 |
182.087
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 39.56; H, 6.64; F, 20.86; N, 15.38; O, 17.57
|
| CAS号 |
70052-12-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Eflornithine hydrochloride hydrate;96020-91-6;L-Eflornithine monohydrochloride;69955-42-6;Eflornithine hydrochloride;68278-23-9;L-Eflornithine;66640-93-5
|
| PubChem CID |
3009
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light yellow solid
|
| 密度 |
1.293g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
347ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
163.7ºC
|
| LogP |
1.173
|
| tPSA |
89.34
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
12
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
166
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
NC(CCCN)(C(F)F)C(O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
VLCYCQAOQCDTCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C6H12F2N2O2/c7-4(8)6(10,5(11)12)2-1-3-9/h4H,1-3,9-10H2,(H,11,12)
|
| 化学名 |
2,5-diamino-2-(difluoromethyl)pentanoic acid.
|
| 别名 |
CPP-1X DFMO MDL 71782 MDL-71782 MDL71782 RMI71782
RMI-71782 RMI 71782 Difluoromethylornithine Eflornithine
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~83.33 mg/mL (~457.43 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.4894 mL | 27.4469 mL | 54.8938 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0979 mL | 5.4894 mL | 10.9788 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5489 mL | 2.7447 mL | 5.4894 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。