| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The 2R-stereoisomers are the only forms of alpha-tocopherol that are maintained in human plasma and tissue. The activity of natural or natural-source alpha-tocopherol (RRR alpha-tocopherol), on an equal weight basis, is at least twice as high as synthetic alpha-tocopherol. This is mainly because half of the stereoisomers of synthetic alpha-tocopherol are not maintained in human plasma and are, therefore, not bioavailable. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: dl-alpha-Tocopherol is a slightly viscous, pale yellow oil. This is a synthetic form of alpha tocopherol. The activity of natural alpha-tocopherol on an equal weight basis, is at least twice as high as the synthetic form. dl-alpha-Tocopherol is used as an antioxidant in fats and oils and in animal feed. It is also used as experimental medication and as a dietary supplement. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Of 23,908 patients patch tested, 219 (0.9%) had sunscreen coded as an allergen source. The top 3 most frequent allergens in sunscreens were benzophenone-3, dl-alpha-tocopherol, and fragrance mix. Dietary supplementation with moderate dosage synthetic dl-alpha-tocopherol acetate did not significantly prolong bleeding or platelet aggregation in healthy volunteers. dl-alpha-Tocopherol provided protection against exercise-induced oxidative injury in healthy volunteers according to several reports. In vitro experiments demonstrated general inhibition of cell proliferation by dl-alpha-tocopherol, with breast and prostate cancer cells distinctly more sensitive than erythroleukemia cells. ANIMAL STUDIES: In chicks exposed to dl-alpha-tocopherol acetate for 3-8 weeks it caused prolonged prothrombin times, reticulocytosis, and a reduced hematocrit value. Supplementation of dl-alpha-tocopherol increased alpha-tocopherol concentration in cows; however, effects on reproductive efficiency were minimal. The addition of dl-alpha-tocopherol to leucocyte cultures reduced the number of chromosome breaks induced by 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene. dl-alpha-Tocopherol markedly reduced the mutagenic effect of malonaldehyde and beta-propiolactone in five strains of Salmonella typhimurium, which mutated with a frameshift mechanism. Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Vitamin E is a normal component of human milk. Maternal obesity, smoking and possibly preterm birth (<37 weeks gestational age) are associated with lower milk vitamin E levels. Lactating mothers may need to supplement their dietary intake of vitamin E to achieve the recommended daily intake of 19 mg. Daily maternal vitamin E supplementation from prenatal multivitamins can safely and modestly increase milk vitamin E levels and improve the vitamin E status of the breastfed infant compared to no supplementation. Higher daily dosages have not been studied. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Interactions Inflammatory bowel disease is often associated with iron deficiency anemia and oral iron supplementation may be required. However, iron may increase oxidative stress through the Fenton reaction and thus exacerbate the disease. This study was designed to determine in rats with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis whether oral iron supplementation increases intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress and whether the addition of an antioxidant, vitamin E, would reduce this detrimental effect. Four groups of rats that consumed 50 g/L DSS in drinking water were studied for 7 d and were fed: a control, nonpurified diet (iron, 270 mg, and dl-alpha-tocopherol acetate, 49 mg/kg); diet + iron (iron, 3000 mg/kg); diet + vitamin E (dl-alpha-tocopherol acetate, 2000 mg/kg) and the diet + both iron and vitamin E, each at the same concentrations as above. Body weight change, rectal bleeding, histological scores, plasma and colonic lipid peroxides (LPO), plasma 8-isoprostane, colonic glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and plasma vitamin E were measured. Iron supplementation increased disease activity as demonstrated by higher histological scores and heavier rectal bleeding. This was associated with an increase in colonic and plasma LPO and plasma 8-isoprostane as well as a decrease in colonic GPx. Vitamin E supplementation decreased colonic inflammation and rectal bleeding but did not affect oxidative stress, suggesting another mechanism for reducing inflammation. In conclusion, oral iron supplementation resulted in an increase in disease activity in this model of colitis. This detrimental effect on disease activity was reduced by vitamin E. Therefore, the addition of vitamin E to oral iron supplementation may be beneficial. Previous studies have shown that beta-carotene and alpha-tocopherol can act synergistically to inhibit the growth of experimentally induced oral cancer. The initial studies on the synergistic anticancer activity of antioxidants have been extended to include reduced glutathione and ascorbic acid. Sixty male hamsters (4-5 wks old) were divided into six equal groups. Groups 1-6 were treated with 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA) (0.5% solution). Group 2 received a mixture containing equal amounts of beta-carotene, dl-alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E), glutathione, and l-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) (12.5 micrograms) delivered orally by pipette. Groups 3-6 were treated with beta-carotene alone (50 micrograms), vitamin E alone (50 micrograms), glutathione (50 micrograms) alone, and vitamin C alone (50 micrograms). Animals were euthanized at 12 and 14 weeks. Tumors were counted and measured, and tumor burden was calculated for each experimental group. The mixture of antioxidants significantly reduced tumor burden, whereas the beta-carotene, vitamin E, and reduced glutathione treatments also reduced tumor burden. beta-Carotene and glutathione provided greater levels of chemoprevention than vitamin E as single agents. In contrast, vitamin C treatment produced no antitumor effect but increased tumor burden by Week 14. This mixture of antioxidants produced a significant synergistic chemoprevention of oral cancer. Ferric nitrilotriacetate (Fe-NTA) is a potent nephrotoxic agent. In this communication, we show the modulatory effect of DL-alpha-tocopherol (Vitamin-E) on ferric nitrilotriacetate (Fe-NTA)-induced renal oxidative stress, toxicity and hyperproliferative response in rats. Fe-NTA-treatment enhances the susceptibility of renal microsomal membrane for iron-ascorbate-induced lipid peroxidation and hydrogen peroxide generation which are accompanied by a decrease in the activities of renal antioxidant enzymes, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase and glutathione-S-transferase and depletion in the level of renal glutathione. Parallel to these changes, a sharp increase in blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine has been observed. In addition, Fe-NTA-treatment also enhances renal ornithine decarboxylase activity (ODC) and increases [(3)H]thymidine incorporation in renal DNA. Prophylactic treatment of animals with /vitamin E/ Vit.E daily for 1 week prior to the administration of Fe-NTA resulted in the diminution of Fe-NTA-mediated damage. Enhanced susceptibility of renal microsomal membrane for lipid peroxidation induced by iron-ascorbate and hydrogen peroxide generation were significantly reduced (P < 0.05). In addition, the depleted level of glutathione and inhibited activities of antioxidant enzymes recovered to significant levels (P < 0.05). Similarly, the enhanced blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine levels which are indicative of renal injury showed a reduction of about 50% at a higher dose of Vit.E. The pretreatment of rats with Vit.E reduced the Fe-NTA-mediated induction in ODC activity and enhancement in [(3)H]thymidine incorporation in DNA. The protective effect of Vit.E was dose dependent. In summary, our data suggest that Vit.E is an effective chemopreventive agent in kidney and may suppress Fe-NTA-induced renal toxicity. Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation of C3H/HeN mice induces skin cancer and an immunosuppression that prevents the host from rejecting antigenic UV-induced tumors. The capacity of topical vitamin E (dl-alpha-tocopherol) to prevent photocarcinogenesis or the immunosuppression induced by UV irradiation was assessed. Skin cancer incidence in UV-irradiated mice was 81% at 33 weeks after the first UV exposure; application to mice of 25 mg vitamin E three times per week for three weeks before UV irradiation, and throughout the experiment, reduced this incidence to 42% (p = 0.0065, log rank test). Immunoenhancement by vitamin E was assessed by comparing levels of immunosuppression by splenocytes from normal or UV-irradiated mice, with and without topical vitamin E treatment. Transfer of splenocytes from UV-irradiated mice to naive mice prevented the recipients from rejecting a UV-induced tumor challenge, whereas splenocytes from UV-irradiated mice treated with vitamin E did not prevent recipients from rejecting a similar tumor challenge. Phenotypic analysis of splenocytes used in the passive transfer assay, conducted with a biotin-avidin-immunoperoxidase technique, revealed that vitamin E treatment of mice undergoing UV irradiation prevented the UV-induced down regulation of Ia expression in splenocytes and increased the proportion of Lyt-2+ and L3T4+ splenocytes. Therefore, chronically applied vitamin E can effectively reduce cancer formation and immunosuppression induced by UV irradiation. Prevention of UV-induced down regulation of Ia expression may have contributed to this immunomodulation. For more Interactions (Complete) data for dl-alpha-Tocopherol (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
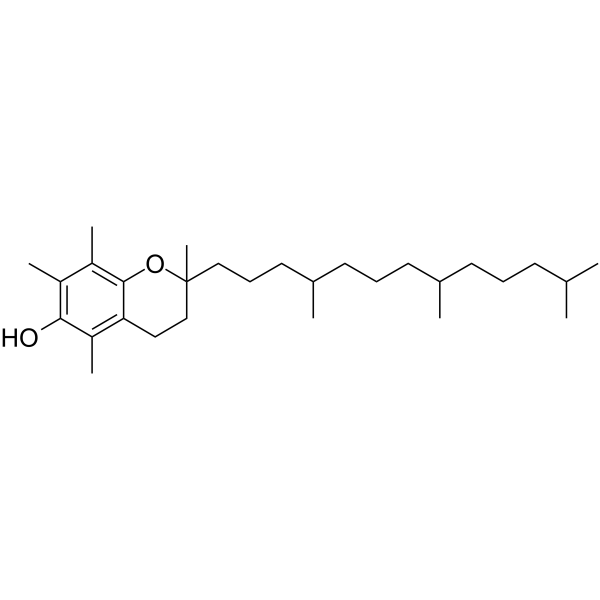
2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-6-ol is a tocopherol.
DL-alpha-Tocopherol has been reported in Albifimbria verrucaria, Sida acuta, and other organisms with data available. dl-alpha-Tocopherol is a synthetic form of vitamin E, a fat-soluble vitamin with potent antioxidant properties. Considered essential for the stabilization of biological membranes (especially those with high amounts of polyunsaturated fatty acids), d-alpha-Tocopherol is a potent peroxyl radical scavenger and inhibits noncompetitively cyclooxygenase activity in many tissues, resulting in a decrease in prostaglandin production. Vitamin E also inhibits angiogenesis and tumor dormancy through suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene transcription. (NCI04) See also: Alpha-Tocopherol (annotation moved to); Tocopherol (annotation moved to); Vitamin E (annotation moved to). Therapeutic Uses EXPL THER We evaluated the effects of vitamin E (dl-alpha-tocopherol) on mutagen sensitivity levels in a randomized placebo-controlled pilot trial. In brief, a dietary supplement of 1000 mg/day vitamin E or a placebo was randomly administered for 3 months to melanoma outpatients clinically free of the disease. Plasma vitamin E and mutagen sensitivity levels were measured at baseline and at the end of the trial after 3 months. At baseline, we found no significant differences in plasma vitamin E and mutagen sensitivity levels between the two groups. We also measured dietary intake at baseline and found dietary vitamin E to be a poor predictor of plasma levels of vitamin E. After 3 months of supplementation, we found that plasma levels of alpha-tocopherol increased significantly (P = 0.0005) in the vitamin E compared to the placebo group. We also found a non-significant, but consistent decrease in plasma gamma-tocopherol concentrations in the vitamin E supplemented compared to the placebo group. We did not find any significant difference between the vitamin E and placebo groups in mutagen sensitivity levels either at baseline or after 3 months of supplementation. We conclude that short term vitamin E supplementation, although it causes increased blood levels of alpha-tocopherol, does not provide protection against bleomycin-induced chromosome damage. EXPL THER Epidemiological studies have demonstrated an inverse relationship between vitamin E intake and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk. In contrast, randomized controlled trials have reported conflicting results as to whether vitamin E supplementation reduces atherosclerosis progression and CVD events. The study population consisted of men and women > or =40 years old with an LDL cholesterol level > or =3.37 mmol/L (130 mg/dL) and no clinical signs or symptoms of CVD. Eligible participants were randomized to DL-alpha-tocopherol 400 IU per day or placebo and followed every 3 months for an average of 3 years. The primary trial end point was the rate of change in the common carotid artery far-wall intima-media thickness (IMT) assessed by computer image-processed B-mode ultrasonograms. A mixed effects model using all determinations of IMT was used to test the hypothesis of treatment differences in IMT change rates. Compared with placebo, alpha-tocopherol supplementation significantly raised plasma vitamin E levels (P<0.0001), reduced circulating oxidized LDL (P=0.03), and reduced LDL oxidative susceptibility (P<0.01). However, vitamin E supplementation did not reduce the progression of IMT over a 3-year period compared with subjects randomized to placebo. The results are consistent with previous randomized controlled trials and extend the null results of vitamin E supplementation to the progression of IMT in healthy men and women at low risk for CVD. EXPL THER The glycation of proteins and elevated triglyceride (TG) levels are two of the major risk factors in the development of complications of diabetes. Previous studies have found some beneficial effects of supplementation of pharmacological doses (900-2000 IU/day) of vitamin E in Type II diabetic patients. This study examined whether supplementation with a modest dose of vitamin E (100 IU/day) had any effect on blood glucose, glycated hemoglobin (GHb), TG or red cell counts in Type I diabetic patients. 35 diabetic patients were supplemented with either DL-alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E) capsules (orally, 100 IU/day) or a placebo for 3 months in a double-blind clinical trial. Fasting blood was collected from each diabetic patient before and after vitamin E or placebo supplementation. Data were analyzed using paired "t" tests and the Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test. Levels of GHb (mean +/- SEM) were 11.5 +/- 0.4 and 12.8 +/- 0.9% (p < 0.05); glucose, 8.8 +/- 1.2 and 11.6 +/- 1.3 mM; and TG, 2.2 +/- 0.2 and 2.9 +/- 0.3 mM (p < 0.03) after vitamin E supplementation versus before supplementation. There were no differences in these parameters after supplementation with the placebo. There was no effect on blood RBC, hematocrit, and hemoglobin levels after supplementation of vitamin E or the placebo. There were no differences in ages and duration of diabetes between placebo and vitamin E-supplemented groups. This study suggests that modest vitamin E supplementation (100 IU/day) can significantly lower blood GHb and TG levels and does not have any effect on red cell indices in Type I diabetic patients. EXPL THER Dietary components may be both causal and protective in cases of pancreatic carcinoma, but the preventive potential of single constituents has not been evaluated. The /study/ report the effects of alpha-tocopherol and beta-carotene supplementations on the rates of incidence of and mortality from pancreatic carcinoma in a randomized, controlled trial. The 29,133 participants in the Alpha-Tocopherol Beta-Carotene Cancer Prevention (ATBC) Study were male smokers who were ages 50-69 years at the time they were randomized into 1 of the following 4 intervention groups: dl-alpha-tocopherol (AT; 50 mg/day), beta-carotene (BC; 20 mg/day), both AT and BC, and placebo. The daily supplementation lasted for 5-8 years. Incident cancers were identified through the national Finnish Cancer Registry and death certificates of the Statistics Finland. Results were analyzed by supplementation with Cox regression models. Effects of both supplementations were statistically nonsignificant. The rate of incidence of pancreatic carcinoma was 25% lower for the men who received beta-carotene supplements (n = 38) compared with the rate for those who did not receive beta-carotene (n = 51) (95% CI, -51% to 14%). Supplementation with alpha-tocopherol (n = 51) increased the rate of incidence by 34% (95% CI, -12% to 105%) compared with the rate for those who did not receive alpha-tocopherol. Mortality from pancreatic carcinoma during the follow-up, adjusted for stage and anatomic location of the tumor, was 19% (95% CI, -47% to 26%) lower among those who received beta-carotene and 11% (95% CI, -28% to 72%) higher among those who received alpha-tocopherol as compared with those who did not receive supplementation. Supplementation with beta-carotene or alpha-tocopherol does not have a statistically significant effect on the rate of incidence of pancreatic carcinoma or the rate of mortality caused by this disease. For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for dl-alpha-Tocopherol (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 分子式 |
C29H50O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
430.7061
|
| 精确质量 |
430.381
|
| CAS号 |
10191-41-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
DL-alpha-Tocopherol-13C3;DL-alpha-Tocopherol-d9;131230-17-6
|
| PubChem CID |
2116
|
| 外观&性状 |
Colorless to light yellow liquid
|
| 密度 |
0.9±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
485.9±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
2-4°C
|
| 闪点 |
210.2±24.4 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.495
|
| LogP |
11.9
|
| tPSA |
29.46
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
12
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
503
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O1C2C(C([H])([H])[H])=C(C([H])([H])[H])C(=C(C([H])([H])[H])C=2C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]1(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])O[H]
|
| InChi Key |
GVJHHUAWPYXKBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C29H50O2/c1-20(2)12-9-13-21(3)14-10-15-22(4)16-11-18-29(8)19-17-26-25(7)27(30)23(5)24(6)28(26)31-29/h20-22,30H,9-19H2,1-8H3
|
| 化学名 |
2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-ol
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~100 mg/mL (~232.17 mM)
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~232.17 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.80 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (5.80 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.80 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (232.17 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3217 mL | 11.6087 mL | 23.2175 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4643 mL | 2.3217 mL | 4.6435 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2322 mL | 1.1609 mL | 2.3217 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。