| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
环丙沙星 (Bay-09867) 单盐酸盐(5-50 μg/mL;0-24 小时;肌腱细胞)可抑制细胞生长并导致细胞周期停滞在 G2/M 期,用于治疗感染 [1]。环丙沙星 (Bay-09867) monoHClide 可有效抑制鼠疫耶尔森菌和炭疽杆菌,MIC90 值分别为 0.03 μg/mL 和 0.12 μg/mL [2]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在肺鼠疫小鼠模型中,环丙沙星 (Bay-09867) 单盐酸盐(30 mg/kg;腹膜内注射;24 小时;BALB/c 小鼠)对鼠疫耶尔森菌具有保护作用 [3]。通过降低 LOX 水平并提高 MMP 水平和活性,环丙沙星 (Bay-09867) 单盐酸盐(100 mg/kg;ir;每日一次,持续 4 周;C57BL/6J 小鼠)加速主动脉根部扩张,增加主动脉夹层和动脉破裂的风险。主动脉壁[4]。 Ciprofloxacin (Bay-09867) monoHClide(100 mg/kg;IR;每日一次,持续 4 周;C57BL/6J 小鼠)会导致线粒体功能障碍、细胞质 DNA 传感器信号激活、DNA 损伤并释放到细胞质中。乳酸环丙沙星会增加主动脉壁的细胞凋亡和坏死性凋亡[4]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定 [1]
细胞类型: 肌腱细胞 测试浓度: 5、10、20 和 50 µg/mL 孵育持续时间:24小时 实验结果:肌腱细胞的细胞结构减少。 细胞周期分析 [1] 细胞类型: 肌腱细胞 测试浓度: 50 µg/mL 孵育持续时间:24小时 实验结果:细胞周期停滞在G2/M期,抑制肌腱细胞的细胞分裂。 蛋白质印迹分析 [1] 细胞类型: 肌腱细胞 测试浓度: 50 µg/mL 孵育持续时间:0、6、12、17和24小时 实验结果:下调CDK-1和cyclin B蛋白及mRNA的表达。上调 PLK-1 蛋白的表达。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: balb/c (Bagg ALBino) mouse [3]
Doses: 30 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection; 24-hour Experimental Results: diminished the bacterial load in the lungs of the plague mouse model. Animal/Disease Models: C57BL/6J mice [4] Doses: 100 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day for 4 weeks Experimental Results: The aorta was destroyed, accompanied by diminished LOX expression and MMP expression and activity Increase. Animal/Disease Models: C57BL/6J mice [4] Doses: 100 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day for 4 weeks Experimental Results: Causes mitochondrial DNA and nuclear DNA damage, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS production. Increased aortic wall cell apoptosis and necroptosis. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
A 250mg oral dose of ciprofloxacin reaches an average maximum concentration of 0.94mg/L in 0.81 hours with an average area under the curve of 1.013L/h\*kg. The FDA reports an oral bioavailability of 70-80% while other studies report it to be approximately 60%. An early review of ciprofloxacin reported an oral bioavailability of 64-85% but recommends 70% for all practical uses. 27% of an oral dose was recovered unmetabolized in urine compared to 46% of an intravenous dose. Collection of radiolabelled ciprofloxacin resulted in 45% recovery in urine and 62% recovery in feces. Cirpofloxacin follws a 3 compartment distribution model with a central compartment volume of 0.161L/kg and a total volume of distribution of 2.00-3.04L/kg. The average renal clearance after a 250mg oral dose is 5.08mL/min\*kg. Following a 100mg intravenous dose, the average total clearance is 9.62mL/min\*kg, average renal clearance is 4.42mL/min\*kg, and average non renal clearance is 5.21mL/min\*kg. Based on population pharmacokinetics, bioavailability of ciprofloxacin oral suspension in children is approximately 60%. Following a single oral dose of 10 mg/kg of ciprofloxacin given as the oral suspension to children 4 months to 7 years of age, the mean peak plasma concentration was 2.4 ug/mL. There was no apparent age dependence and no increase in peak plasma concentrations following multiple doses. When extended-release tablets containing ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (ProQuin XR) are administered with food, approximately 87% of the drug is gradually released from the tablet over a 6- hour period. When administered following a meal, peak plasma concentrations are attained approximately 4.5-7 hours after the dose. Bioavailability is substantially lower if ProQuin XR tablets are given while fasting. In healthy adults receiving ProQuin XR extended-release tablets in a dosage of 500 mg once daily given following a standardized meal, peak plasma concentrations at steady state (day 3) average 0.82 mcg/mL and are attained 6.1 hours after the dose. /Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride/ Following oral administration of extended-release tablets containing ciprofloxacin hydrochloride and base (Cipro XR), peak plasma concentrations of ciprofloxacin are attained within 1-4 hours. Cipro XR tablets contain approximately 35% of the dose within an immediate-release component; the remaining 65% of the dose is contained in a slow-release matrix. Oral administration of ciprofloxacin 500 mg daily as Cipro XR extended-release tablets or 250 mg twice daily as conventional tablets results in steady-state mean peak plasma concentrations of 1.59 or 1.14 ug/mL, respectively; however, the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) is similar with both regimens. /Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride/ Peak serum concentrations of ciprofloxacin and AUCs of the drug are slightly higher in geriatric patients than in younger adults; this may occur because of increased bioavailability, reduced volume of distribution, and/or reduced renal clearance in these patients. Single-dose oral studies using ciprofloxacin conventional tablets and single- and multiple-dose IV studies indicate that, compared with younger adults, peak plasma concentrations are 16-40% higher, mean AUC is approximately 30% higher, and elimination half-life is prolonged approximately 20% in individuals older than 65 years of age. These differences can be at least partially attributed to decreased renal clearance in this age group and are not clinically important. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CIPROFLOXACIN (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Ciprofloxacin is primarily metabolized by CYP1A2. The primary metabolites oxociprofloxacin and sulociprofloxacin make up 3-8% of the total dose each. Ciprofloxacin is also converted to the minor metabolites desethylene ciprofloxacin and formylciprofloxacin. These 4 metabolites account for 15% of a total oral dose. There is a lack of available data on the enzymes and types of reactions involved in forming these metabolites. The drug is partially metabolized in the liver by modification of the piperazinyl group to at least 4 metabolites. These metabolites, which have been identified as desethyleneciprofloxacin (M1), sulfociprofloxacin (M2), oxociprofloxacin (M3), and N-formylciprofloxacin (M4), have microbiologic activity that is less than that of the parent drug but may be similar to or greater than that of some other quinolones (e.g., M3 and M4 are comparable to norfloxacin for certain organisms). Hepatic. Four metabolites have been identified in human urine which together account for approximately 15% of an oral dose. The metabolites have antimicrobial activity, but are less active than unchanged ciprofloxacin. Route of Elimination: Approximately 40 to 50% of an orally administered dose is excreted in the urine as unchanged drug. Half Life: 4 hours Biological Half-Life The average half life following a 250mg oral dose was 4.71 hours and 3.65 hours following a 100mg intravenous dose. Generally the half life is reported as 4 hours. The serum elimination half-life of ciprofloxacin in adults with normal renal function is 3-7 hours. Following IV administration in healthy adults, the distribution half-life of ciprofloxacin averages 0.18-0.37 hours and the elimination half-life averages 3-4.8 hours. The elimination half-life of the drug is slightly longer in geriatric adults than in younger adults, and ranges from 3.3-6.8 hours in adults 60-91 years of age with renal function normal for their age. Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis of pediatric patients with various infections, the predicted mean half-life of ciprofloxacin in children is approximately 4-5 hours. In patients with impaired renal function, serum concentrations of ciprofloxacin are higher and the half-life prolonged. In adults with creatinine clearances of 30 mL/minute or less, half-life of the drug ranges from 4.4-12.6 hours. t1/2 for ciprofloxacin- normal: 4 (hr), anephric: 8.5 (hr) /from table/ |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
The bactericidal action of ciprofloxacin results from inhibition of the enzymes topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV, which are required for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, strand supercoiling repair, and recombination. Interactions Serious and fatal reactions have been reported in patients receiving concurrent administration of ciprofloxacin and theophylline. These reactions have included cardiac arrest, seizure, status epilepticus, and respiratory failure. Although similar serious adverse effects have been reported in patients receiving theophylline alone, the possibility that these reactions may be potentiated by ciprofloxacin cannot be eliminated. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, serum levels of theophylline should be monitored and dosage adjustments made as appropriate. ... The effects of aluminum hydroxide ... and calcium carbonate ... on the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin /was determined in/ ... a 3 way randomized, crossover study was concluded in 12 healthy male volunteers (ages 21-45 yr) that consisted of 3 treatments: 750 mg ciprofloxacin alone, 750 mg ciprofloxacin with 3.4 g calcium carbonate or 1.8 g aluminum hydroxide admin 5 min before ciprofloxacin. The relative bioavailability of ciprofloxacin was reduced to 60% and 15% of control values when given with calcium carbonate and aluminum hydroxide, respectively. ... It was concluded that antacids containing either aluminum or calcium should not be given concurrently with ciprofloxacin. Ciprofloxacin, given to a patient successfully treated with methadone for more than 6 yrs, caused profound sedation, confusion, & respiratory depression. We suggest that this was caused by ciprofloxacin inhibition of CYP1A2 & CYP3A4 activity, 2 of the cytochrome p450 isozymes involved in the metab of methadone. Synergism does not occur in vitro when ciprofloxacin is used in conjunction with vancomycin against Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. aureus (including oxacillin-resistant S. aureus), Corynebacterium, or Listeria monocytogenes. For more Interactions (Complete) data for CIPROFLOXACIN (35 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Anti-Infective Agents; Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors Ciprofloxacin (IV, conventional tablets, oral suspension) is used in adults for the treatment of bone and joint infections, including osteomyelitis, caused by susceptible E. cloacae, ... Ps. aeruginosa, or S. marcescens. ... /Included in US product label/ Ciprofloxacin (IV, conventional tablets, oral suspension) is used in adults for the treatment of bone and joint infections, including osteomyelitis, caused by susceptible E. aerogenes, ... E. coli, K. pneumoniae, M. morganii, P. mirabilis, ... . The drug also has been used in adults for the treatment of bone and joint infections caused by susceptible S. aureus, S. epidermidis, other coagulase-negative staphylococci, or Enterococcus faecalis (formerly S. faecalis), but other anti-infectives generally are preferred for these infections. Although resistance to ciprofloxacin has been reported in some strains of oxacillin-resistant S. aureus, oral ciprofloxacin may be a useful alternative to parenteral anti-infectives for the treatment of infections caused by susceptible oxacillin-resistant staphylococci. /NOT included in US product label/ Although only limited experience is available to date, ciprofloxacin is recommended by the American Heart Association (AHA) and Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) as an alternative agent for the treatment of native or prosthetic valve endocarditis caused by fastidious gram-negative bacilli known as the HACEK group (Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Cardiobacterium hominis, Eikenella corrodens, Haemophilus aphrophilus, H. influenzae, H. parainfluenzae, H. paraphrophilus, Kingella denitrificans, K. kingae). /NOT included in US product label/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CIPROFLOXACIN (53 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings /BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including Cipro, are associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. This risk is further increased in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants. /BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including Cipro, may exacerbate muscle weakness in persons with myasthenia gravis. Avoid Cipro in patients with known history of myasthenia gravis. In 4 corneal transplantation patients treated preoperatively with ciprofloxacin ophthalmic drops, microprecipitates associated with damaged corneal epithelium were noted in 2 patients. Another patient developed a large macroprecipitate in a corneal ulcer. All specimens were examined by electron microscopy & high-pressure liquid chromatography. The crystalline precipitates were pure ciprofloxacin. The macroprecipitate demonstrated a large zone of inhibition on agar plates seeded with a susceptible organism at 24 & 48 hr. It was bioactive & bioavailable in vitro. Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions, some following the first dose, have been reported in patients receiving quinolone therapy. Some reactions were accompanied by cardiovascular collapse, loss of consciousness, tingling, pharyngeal or facial edema, dyspnea, urticaria, and itching. Only a few patients had a history of hypersensitivity reactions. Serious anaphylactic reactions require immediate emergency treatment with epinephrine. Oxygen, intravenous steroids, and airway management, including intubation, should be administered as indicated. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CIPROFLOXACIN (41 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Ciprofloxacin is a second generation fluoroquinolone that is active against many Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria. It produces its action through inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. Ciprofloxacin binds to bacterial DNA gyrase with 100 times the affinity of mammalian DNA gyrase. There is no cross resistance between fluoroquinolones and other classes of antibiotics, so it may be of clinical value when other antibiotics are no longer effective. Ciprofloxain and its derivatives are also being investigated for its action against malaria, cancers, and AIDS. |
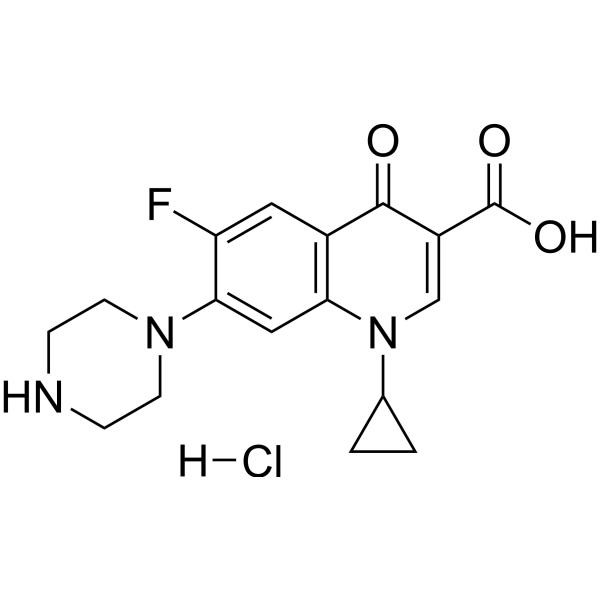
| 分子式 |
C17H19CLFN3O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
367.8025
|
| 精确质量 |
367.109
|
| CAS号 |
93107-08-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Ciprofloxacin;85721-33-1;Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride monohydrate;86393-32-0;Ciprofloxacin-d8 hydrochloride hydrate
|
| PubChem CID |
2764
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 沸点 |
581.8ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
>300ºC
|
| 闪点 |
305.6ºC
|
| LogP |
2.779
|
| tPSA |
74.57
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
24
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
571
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
MYSWGUAQZAJSOK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H18FN3O3/c18-13-7-11-14(8-15(13)20-5-3-19-4-6-20)21(10-1-2-10)9-12(16(11)22)17(23)24/h7-10,19H,1-6H2,(H,23,24)
|
| 化学名 |
1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-ylquinoline-3-carboxylic acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: (1). 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 (2). 该产品在溶液状态不稳定,请现配现用。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~12.5 mg/mL (~33.99 mM)
DMSO : ~5 mg/mL (~13.59 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.5 mg/mL (1.36 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 5.0mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.5 mg/mL (1.36 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 5.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液添加到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7189 mL | 13.5943 mL | 27.1887 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5438 mL | 2.7189 mL | 5.4377 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2719 mL | 1.3594 mL | 2.7189 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Ciprofloxacin Versus Levofloxacin in Stem Cell Transplant
CTID: NCT03850379
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Completed
Date: 2024-09-19