| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
β-lactam
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在不减弱万古霉素抗菌作用的情况下,西铂(200 μg/mL;24 小时;RPTEC)治疗可防止万古霉素诱导的近端小管凋亡并增强细胞活力[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在全身感染小鼠模型(雌性小鼠,CD-1 株,20 g)中,伊培南和西司他丁共同保护小鼠免受金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌和铜绿假单胞菌感染[3]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞系:肾近端肾小管上皮细胞 (RPTEC)
浓度:200 μg/mL 孵育时间:24 小时 结果:显着改善万古霉素诱导的核细胞凋亡。 |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Cilastatin is reported by official FDA labeling to be 70% excreted in the urine, however published literature has reported values as high as 98%. Cilastatin has a volume of distribution of 14.6-20.1L. Cilastatin has a total clearance of 0.2 L/h/kg and a renal clearance of 0.10-0.16 L/h/kg. Biological Half-Life The half-life of cilastatin is approximately 1h. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Cilastatin is plasma protein binding is reported to be 35-40%. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Keynan S, et al. The renal membrane dipeptidase (dehydropeptidase I) inhibitor, cilastatin, inhibits the bacterialmetallo-beta-lactamase enzyme CphA. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995 Jul;39(7):1629-31.
[2]. S Keynan, et al. The Renal Membrane Dipeptidase (Dehydropeptidase I) Inhibitor, Cilastatin, Inhibits the Bacterial Metallo-Beta-Lactamase Enzyme CphA. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995 Jul;39(7):1629-31. [3]. Blanca Humanes, et al. Protective Effects of Cilastatin Against Vancomycin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:704382. [4]. P J Petersen, et al. In Vitro and in Vivo Activities of LJC10,627, a New Carbapenem With Stability to Dehydropeptidase I. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):203-7. |
| 其他信息 |
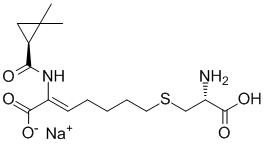
Cilastatin is the thioether resulting from the formal oxidative coupling of the thiol group of L-cysteine with the 7-position of (2Z)-2-({[(1S)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropyl]carbonyl}amino)hept-2-enoic acid. It is an inhibitor of dehydropeptidase I (membrane dipeptidase, 3.4.13.19), an enzyme found in the brush border of renal tubes and responsible for degrading the antibiotic imipenem. Cilastatin is therefore administered (as the sodium salt) with imipenem to prolong the antibacterial effect of the latter by preventing its renal metabolism to inactive and potentially nephrotoxic products. Cilastatin also acts as a leukotriene D4 dipeptidase inhibitor, preventing the metabolism of leukotriene D4 to leukotriene E4. It has a role as a protease inhibitor, an EC 3.4.13.19 (membrane dipeptidase) inhibitor, a xenobiotic and an environmental contaminant. It is a non-proteinogenic L-alpha-amino acid, a L-cysteine derivative, an organic sulfide and a carboxamide. It is a conjugate acid of a cilastatin(1-).
Cilastatin is an inhibitor of renal dehydropeptidase, an enzyme responsible for both the metabolism of thienamycin beta-lactam antibiotics as well as conversion of leukotriene D4 to leukotriene E4. Since the antibiotic, [imipenem], is one such antibiotic that is hydrolyzed by dehydropeptidase, cilastatin is used in combination with imipenem to prevent its metabolism. The first combination product containing both drugs was approved by the FDA in November of 1985 under the trade name Primaxin, marketed by Merck & Co. A newer triple-drug product was approved in July 2019 under the trade name Recarbrio which also contains [relebactam]. Cilastatin is a Renal Dehydropeptidase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of cilastatin is as a Dipeptidase Inhibitor. Cilastatin has been reported in Bos taurus and Apis cerana with data available. A renal dehydropeptidase-I and leukotriene D4 dipeptidase inhibitor. Since the antibiotic, IMIPENEM, is hydrolyzed by dehydropeptidase-I, which resides in the brush border of the renal tubule, cilastatin is administered with imipenem to increase its effectiveness. The drug also inhibits the metabolism of leukotriene D4 to leukotriene E4. See also: ... View More ... Drug Indication Cilastatin is indicated, in combination with [imipenem] with or without [relebactam], for the treatment of bacterial infections including respiratory, skin, bone, gynecologic, urinary tract, and intra-abdominal as well as septicemia and endocarditis. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Cilastatin is a renal dehydropeptidase-I inhibitor. Since the antibiotic, imipenem, is hydrolyzed by dehydropeptidase-I, which resides in the brush border of the renal tubule, cilastatin is administered with imipenem to block the metabolism of imipenem. Pharmacodynamics Cilastatin is a chemical compound which inhibits the human enzyme dehydropeptidase. Renal Dehydropeptidase degrades the antibiotic [imipenem]. Cilastatin is therefore combined intravenously with imipenem in order to protect it from dehydropeptidase and prolong its antibacterial effect. However, cilastatin in and of itself does not have any antibacterial activity. The increased renal excretion of unchanged imipenem appears to prevent proximal tubular necrosis associated with high doses of imipenem. |
| 分子式 |
C16H25N2NAO5S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
380.4348
|
| 精确质量 |
380.138
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 50.51; H, 6.62; N, 7.36; Na, 6.04; O, 21.03; S, 8.43
|
| CAS号 |
81129-83-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Cilastatin;82009-34-5
|
| PubChem CID |
6435415
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
| 沸点 |
655.5ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
350.2ºC
|
| LogP |
1.189
|
| tPSA |
157.85
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
11
|
| 重原子数目 |
24
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
519
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
C([C@H]1CC1(C)C)(=O)N/C(/C(=O)O)=C\CCCCSC[C@H](N)C(=O)O.[Na]
|
| InChi Key |
QXPBTTUOVWMPJN-QBNHLFMHSA-M
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H26N2O5S.Na/c1-16(2)8-10(16)13(19)18-12(15(22)23)6-4-3-5-7-24-9-11(17)14(20)21/h6,10-11H,3-5,7-9,17H2,1-2H3,(H,18,19)(H,20,21)(H,22,23)/q+1/p-1/b12-6-/t10-,11+/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
sodium S-((Z)-6-carboxy-6-((S)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane-1-carboxamido)hex-5-en-1-yl)-L-cysteinate
|
| 别名 |
Cilastatin Monosodium Salt ; MK 0791; MK0791; M K-0791; MK791; MK-791; MK-791; Cilastatin sodium; Recarbrio;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: (1). 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 (2). 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~72 mg/mL ( ~200.86 mM )
Water : 7~100 mg/mL(~262.86 mM ) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6286 mL | 13.1430 mL | 26.2860 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5257 mL | 2.6286 mL | 5.2572 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2629 mL | 1.3143 mL | 2.6286 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|
|
|
|
|