| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
HIVADA (IC50 = 2.5 nM); OAT3 (IC50 = 0.41 μM); OAT1 (IC50 = 0.81 μM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在体外,cabotegravir (GSK-1265744) 阻断 HIV-1 整合酶催化的链转移反应,IC50 为 3.0 nM。 PBMC 中 NL432 和 HIV-1 Ba-L 的抗病毒 EC50 分别为 0.34 nM 和 0.22 nM。在使用 A 型自失活病毒的 PHIV 实验中,EC50 为 0.5 nM,使用 CellTiter-Glo 确定 MT-4 细胞中的 EC50 为 0.57 nM,使用 MTT 确定为 1.3 nM [3]。
卡博替韦(CAB;GSK1265744)是一种强效的HIV整合酶抑制剂,目前正在临床开发中,作为口服导入片和长效注射剂,用于治疗和预防HIV感染。2.这项工作研究了CAB是否是外排转运蛋白的底物,CAB与药物代谢酶和转运蛋白相互作用以引起临床药物相互作用的可能性,以及CAB对CYP3A4探针底物咪达唑仑在人体内的药代动力学的影响。3.CAB是Pgp和BCRP的底物;然而,其高内在膜通透性限制了这些转运蛋白对其肠道吸收的影响。4.在临床相关浓度下,CAB不会抑制或诱导体外评估的任何CYP或UGT酶,也不会对咪达唑仑的临床药代动力学产生影响。5.CAB是OAT1(IC50 0.81µM)和OAT3(IC50 0.41µM)的抑制剂,但不抑制或仅弱抑制Pgp、BCRP、MRP2、MRP4、MATE1、MATE2-K、OATP1B1、OATP1B3、OCT1、OCT2或BSEP。根据监管指南和定量推断,CAB引起临床显著药物相互作用的倾向较低,但与OAT1或OAT3底物联合给药除外。[2] GSK1265744的体外抗病毒特性和作用机制是通过整合酶测定、抗性传代实验和细胞测定建立的,这些细胞测定使用对其他类别的抗HIV-1药物和早期INSTI具有抗性的定点分子(SDM)HIV克隆。GSK1265744在相同的培养条件下以低或亚纳米效率抑制HIV复制,选择性指数至少为22000。推断为100%人血清的蛋白质调整半最大抑制浓度(PA-EC50)为102 nM。当病毒在GSK1265744存在下传代时,在长达112天的培养中没有观察到EC50相对于野生型变化超过10倍(FC)的高度抗性突变体。GSK1265744显示出对含有拉替拉韦(RAL)抗性Y143R、Q148K、N155H和G140S/Q148H特征变体的SDM克隆的活性(FC小于6.1),而这些突变体在RAL的EC50中具有较高的FC(11至>130)。当GSK1265744与代表性的抗HIV药物联合使用时,观察到相加或协同作用,没有观察到拮抗作用[3]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Cabotegravir 在小鼠体内的半相滴注时间长达 54 天[1]。 Cabotegravir(25 或 50 mg/kg;静脉注射;单次或两次剂量)可防止猕猴 (Macaques) 感染 SIVmac251 [4]。
在小鼠中,capetreavir 的半衰期长达 54 天 [1]。当猕猴(Macaques)感染 SIVmac251 时,它们会受到cabotegravir 的保护(静脉注射;单剂量或两次;25 或 50 mg/kg)[4]。
长效肠外(LAP)抗逆转录病毒药物在治疗和预防HIV-1感染方面引起了相当大的兴趣。一种新的LAP是cabotegravir (CAB),这是一种高效的整合酶抑制剂,半衰期长达54天,允许每隔一个月进行一次肠外给药。尽管有这种出色的表现,但大剂量给药、注射部位反应和低体液药物浓度会影响病毒感染者和易感人群的广泛使用。为了改善药物输送特性,我们创造了一种肉豆蔻酰化CAB前药(MCAB)。MCAB形成晶体,这些晶体被配制成大小和形状稳定的纳米颗粒(NMCAB),有助于单核细胞-巨噬细胞的进入、滞留和网状内皮系统的储存制剂。药物释放动力学与对HIV-1挑战的持续保护并行。BALB/cJ小鼠单次肌肉注射45mg/kg后,NMCAB的药代动力学特征是CAB-LAP记录的4倍。这些观察结果与恒河猴的重复测量结果相吻合。这些结果与人类成年淋巴细胞重构NOD/SCID/IL2Rγc-/-小鼠中病毒限制性的改善相结合,使我们得出结论,NMCAB可以改善当前CAB-LAP制剂的生物分布和病毒清除情况。[1] 目的:研究人员在基于每行为感染概率的模拟输血模型中评估了cabotegravir(CAB;GSK1265744或GSK744)长效(LA)作为暴露前预防(PrEP)对静脉注射SIV挑战的有效性。 设计:CAB LA是一种InSTI,配制为200 mg/mL可注射纳米颗粒悬浮液,是一种有效的暴露前预防(PrEP)剂,可防止猕猴直肠和阴道SHIV传播。 方法:三组恒河猴(n=8/组)在第2周肌肉注射CAB LA,静脉注射17 AID50 SIVmac251。第1组在第0周和第4周注射50mg/kg,以评估模拟性传播的猕猴研究中使用的CAB LA剂量的保护效果。第2组在第0周注射50mg/kg,以评估第二次注射CAB LA以防止静脉挑战的必要性。第3组在第0周注射25mg/kg,在第4周注射50mg/kg,以将攻击时的CAB血浆浓度与保护作用相关联。另外五只猕猴作为对照仍未得到治疗。 结果:CAB LA具有高度的保护作用,24只CAB LA治疗的猕猴中有21只仍然是病毒血症,保护率为88%。病毒攻击时的血浆CAB浓度似乎比第二次CAB LA注射维持治疗性血浆浓度更重要。 结论:这些结果支持CAB LA作为注射吸毒者PrEP的临床研究[4]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
体外链转移试验。[3]
如前所述,使用重组HIV in在链转移试验中测量了cabotegravir(GSK1265744)和其他INSTIs的抑制浓度。通过在37°C下将2μM纯化的重组整合酶与0.66μM生物素化供体DNA-4 mg/ml链霉抗生物素蛋白包被的SPA珠在25 mM吗啉丙磺酸钠(pH 7.2)、23 mM NaCl和10 mM MgCl2中孵育5分钟,形成整合酶和生物素化供体DNA链霉抗抗生物素素蛋白包封的闪烁邻近测定(SPA)珠的复合物。将这些珠粒旋转,并在37°C下与稀释的INSTIs预孵育60分钟。接下来,加入3H标记的靶DNA底物,使底物终浓度为7 nM,并将链转移反应混合物在37°C下孵育25至45分钟,这使得供体DNA向放射性标记靶DNA的链转移呈线性增加。使用Wallac MicroBeta闪烁板阅读器读取信号。 PHIV检测。[3] 使用自灭活PHIV慢病毒载体在单轮试验中测量化合物的抗病毒活性。CIP4细胞(2×104个细胞/孔)感染PHIV,足以在检测中产生约50000个相对光单位。将感染的细胞加入96孔、黑色、透明的底板中,加入不同浓度的cabotegravir (GSK1265744),并孵育2天。使用Steady-Glo试剂 在光度计中测量萤光素酶活性。 人血清和血清蛋白的影响。[3] 在PHIV和MT-4检测系统中评估了人血清白蛋白(HSA)(20或40 mg/ml)、α1-酸性糖蛋白(AAG)(2 mg/ml)和人血清(HS)(使用高达30%或50%,外推至100%)对cabotegravir(GSK1265744)抗病毒活性的影响。为了评估蛋白质结合的影响,如前所述,在MT-4细胞中的HIV复制试验中添加不同浓度的人血清来测试抗病毒活性。通过将PBMC中的EC50乘以倍数偏移值来估算蛋白质调整的半最大有效浓度(PA-EC50)。 |
| 细胞实验 |
活力测定[3]
细胞类型: MT-4 细胞 测试浓度: 0-32 nM 孵育时间: 4 或 5 天 实验结果:显示出抗病毒活性,EC50 为 1.3 nM。 评估抗逆转录病毒活性的细胞模型[1] 利用单核细胞衍生巨噬细胞(MDM)。如前所述,获得人外周血单核细胞并进行培养。简而言之,单核细胞是通过HIV-1/2和乙型肝炎血清阴性供体血细胞的白细胞分离获得的,然后通过逆流离心淘析纯化。洗脱的单核细胞在添加了10%热灭活混合人血清、10µg/mL环丙沙星、50µg/mL庆大霉素和1000 U/mL重组巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的DMEM中作为贴壁细胞培养。细胞在5%CO2培养箱中保持在37°C。7天后,分化的巨噬细胞用不同浓度(0.06-1000nM)的天然cabotegravir (GSK1265744)/CAB或MCAB处理30分钟,然后以0.1个感染性病毒颗粒/细胞的多重感染率(MOI)进行HIV-1ADA攻击。攻击后4小时,用无菌磷酸盐缓冲盐水(PBS)洗涤细胞三次,然后用感染前使用的相同浓度的每种化合物孵育。细胞用含有相同药物浓度的DMEM培养基再培养7天,每隔一天更换一半培养基。如前所述,在挑战HIV逆转录酶(RT)活性测定7天后收集上清液。为了测定纳米制剂的抗逆转录病毒活性,MDM用含有100µM药物的NMCAB、CAB LAP或NCAB处理8小时,然后用3次PBS洗涤以去除任何细胞外药物。在预定的时间点(第0、2、5、10和15天),用MOI为0.1的HIV-1ADA攻击MDM 4小时。病毒攻击后7天,分析培养基的RT活性,同时用4%PFA固定粘附的MDM,并通过免疫细胞化学评估HIV-1p24蛋白表达。 细胞毒性试验。[3] 在增殖的人白血病和淋巴瘤细胞系(IM-9、U-937、MT-4和Molt-4)以及刺激和未刺激的人外周血单个核细胞中,用cabotegravir(GSK1265744)进行了体外生长抑制(细胞毒性)研究。作为细胞生长的替代指标,使用CellTiter-Glo萤光素酶试剂定量ATP水平。 细胞力学研究。[3] 为了确定cabotegravir(GSK1265744)是否通过整合酶抑制机制在细胞检测中抑制HIV复制,在INSTI或非核苷逆转录酶抑制剂(NNRTI)存在的情况下,使用定量PCR方法在单轮感染检测中测量了MT-4细胞中HIV NL432 DNA物种合成的影响,如前所述,并进行了细微修改。简而言之,用NL432质粒转染293T细胞以产生感染性病毒,上清液通过0.45-μm孔径的过滤器过滤,并用DNase I处理。用稀释的化合物将MT-4细胞感染HIV-1 NL432病毒1小时,并在孵育6或18小时后收集。所有细胞均与0.5μM浓度的蛋白酶抑制剂(PI)利托那韦一起孵育,以将HIV复制限制在一个周期内。孵育6小时后,对样本进行总DNA PCR检测晚期RT产物。用巢式Alu PCR检测整合的前病毒,用两个LTR PCR检测两个LTR环,在孵育18小时时取样。使用ABI Prism 7900HT-3序列检测系统分析反应。 cabotegravir(GSK1265744)的交叉电阻分析。[3] cabotegravir(GSK1265744)针对in、RT和蛋白酶(PR)编码区突变的分子克隆进行了评估。INSTI-、核苷逆转录酶抑制剂(NRTI)和NNRTI抗性突变体通过基于HeLa-CD4细胞的报告分析进行分析,而PI抗性突变体通过MT-4细胞的感染性进行分析,如前所述监测RT活性。HIV-1野生型感染性分子克隆pNL432用于定点突变,以产生含有突变的HIV克隆。构建了50个INSTI抗性突变体。将RT编码区内具有K101E、K103N、E138K、Y181C、M184I、M184V、Y188L、K101E/M184I,E138K/M184I D67/K70R/T215Y和R4(V75I/F77L/F116Y/Q151M)置换的分子克隆用作NRTI或NNRTI抗性病毒,并使用携带蛋白酶编码区M46I/I47V/I50V和L24I/M46I/L63P/A71V/G73S/V82T突变的PI抗性突变体。随后使用Lipofectamine 2000用质粒转染293T细胞以产生感染性病毒。转染后2至3天收获上清液,在-80°C下作为无细胞培养上清液储存,并用于每次测定。 MT-4细胞中的联合抗病毒活性测定。[3] 如前所述,确定了cabotegravir(GSK1265744)的体外组合活性关系。在有和没有批准的代表性抗HIV药物阿德福韦或利巴韦林的稀释液的情况下,以棋盘式稀释方式测试了多种浓度的cabotegravir(GSK1265744)。通过基于剂量加和性的计算分析了化合物的相互作用。将含有最高浓度化合物的孔与含有最高浓度两种化合物的孔进行比较,以表明组合效应是由于使用的药物而不是毒性。如前所述,使用MT-4系统格式进行了检测。分数抑制浓度(FIC)值在-0.1至-0.2范围内表示弱协同作用,接近-0.5的值表示强协同作用,0.1至0.2的正值表示弱拮抗作用。如前所述,使用线性回归检查了抗乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)和抗丙型肝炎病毒(HCV)药物阿德福韦和利巴韦林对cabotegravir(GSK1265744)EC50的影响(30)。由于HIV-1 IIIB MT-4系统是基于CXCR4的,因此使用HIV-1 Ba-L-感染的MAGI-CCR5细胞和Gal Screen试剂以棋盘稀释形式评估了CCR5抑制剂Maraviroc的化学发光终点。按照Prichard的描述,使用MacSynergy II程序对数据进行分析。在-50至50范围内的协同体积定义了相加性,<-50定义了拮抗性,>50定义了协同作用。 |
| 动物实验 |
In female pigtail macaques model that intravaginal inoculated simian/human immunodeficiency virus twice a week for up to 11 weeks, GSK744 injection prevented the macaques from being infected by virus while placebo controls were infected after a 4 median vaginal challenges with SHIV which reminded that GSK744 may be a potential preexposure prophylaxis drug for prevention via inhibiting HIV integrase
Pharmacokinetics (PK) and biodistribution (BD) of NMCAB in BALB/cJ mice [1] Male BALB/cJ mice were dosed intramuscularly with NMCAB or CAB LAP 45 mg cabotegravir (GSK1265744)/CAB equivalents, followed by weekly blood collection in heparinized tubes via cheek bleeding. Plasma was collected via centrifugation at 2000 × g for 5 min for the drug quantitation by ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) (see supplementary method). At day 28 and day 58 after nano-formulation injection, 5 mice in each treatment group were sacrificed and tissues including liver, lung, spleen, lymph node were collected for drug quantitation by UPLC-MS/MS (see supplementary method). To identify potential drug depots for NMCAB, PK at early time points was assessed in male BALB/cJ mice after a single intramuscular injection of NMCAB or CAB LAP (45 mg CAB equivalents/kg). At predetermined time points (15 min, 1, 2, 4, and 8 h and 1, 3, 7, 10 and 14 days), 25 mL of whole blood was collected and levels of both cabotegravir (GSK1265744)/CAB and MCAB were determined. Tissues were collected at days 1, 3, 7 and 14 for drug quantitation by UPLC-MS/MS. NMCAB PK in rhesus macaques [1] Two male Chinese rhesus macaques (3 years old; 4.0 and 4.7 kg) were anesthetized with 10 mg/kg ketamine and injected intramuscularly with NMCAB at 45 mg cabotegravir (GSK1265744)/CAB equivalents/kg in 2.1 and 2.5 mL, respectively. Blood was collected into potassium EDTA tubes before drug administration, and at days 4, 7, 11, and 18 after the administration, and biweekly thereafter. Plasma was obtained for CAB and MCAB drug quantitation and metabolic panels, while peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were obtained for complete blood counts. Studies of viral restriction in humanized adult lymphocyte mice [1] Male 6–8-week-old NOD/SCID/IL2Rγc−/− (NSG) mice were injected intramuscularly with NMCAB or cabotegravir (GSK1265744)/CAB LAP at 45 mg CAB equivalents/kg. Eleven days after nanoformulation treatments, mice were reconstituted by intraperitoneal injection with 25 × 106 human peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) obtained by leukapheresis and centrifugal elutriation. Eleven days after reconstitution, mice were challenged with 104 50% tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50) HIV-1ADA by intraperitoneal injections. Mice were sacrificed 10 days after viral challenge. The experimental timeline is shown in Fig. 7A. Peripheral blood was collected at days 10 (prior to PBL reconstitution), 21 (prior to HIV-1 challenge), and 32 (10 days post HIV-1 challenge) for flow cytometry analysis of human pan-CD45, CD3, CD4 and CD8 immune markers. Plasma was collected via centrifugation at 2000 × g for 5 min for drug quantitation by UPLC-MS/MS. HIV-1 RNA was analyzed in day 32 plasma samples using the Roche Amplicor and Taqman-48 system with HIV-1 kit V 2.0 according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Tissues were collected for CAB concentrations by UPLC/MS/MS, viral RNA and DNA quantitation by semi-nested real-time PC, and immunohistochemical staining for HIV-1p24 antigen as described previously. Efficacy of cabotegravir (GSK1265744)/CAB LA in preventing SIV intravenous transmission [4] The efficacy of CAB LA against intravenous SIV transmission was evaluated in three groups of Indian rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) (n=8/group) injected IM with cabotegravir (GSK1265744)/CAB LA and challenged intravenously with 17 AID50 SIVmac251 on week 2. Group 1 was injected with 50 mg/kg CAB LA on week 0 and 4, the same dosing regimen used in previous studies assessing CAB LA prevention efficacy against mucosal transmission. Group 2 was injected with 50 mg/kg of CAB LA on week 0 to understand the relative importance of CAB concentrations at the time of challenge and negating the potential benefit of a second injection that would prevent infection distal to the time of challenge as had been seen in the high-dose challenge experiments in female rhesus macaques. Group 3 was injected with 25 mg/kg CAB LA on week 0 and 50 mg/kg CAB LA on week 4 to determine the importance of CAB concentration at the time of challenge while maintaining the second injection thereby modifying a single variable, peak drug concentrations at the time of intravenous challenge. CAB LA is a 200 mg/mL nanosuspension that was administered based on body weights measured at the time of dosing (5.4 to 11.3 kg) with the dose split into four injections, two per quadriceps. Five additional macaques remained untreated as controls. Systemic infection was monitored weekly for 20 weeks after the last CAB LA administration by detection of SIV RNA in plasma using real-time RT-PCR assay with a sensitivity of 40 SIV RNA copies/mL as previously described. PBMC proviral DNA amplification was performed as previously described. Serology was performed utilizing SIVmac251 gp120-coated plates. cabotegravir (GSK1265744)/CAB plasma concentration analyses were performed as previously described. Integrase sequence analyses from bulk plasma virus was performed as previously described. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Oral cabotegravir has a Tmax of 3 hours, reaches a Cmax of 8.0 µg/mL, and has an AUC of 145 µg\*h/mL. Intramuscular extended-release cabotegravir has a Tmax of 7 days, reaches a Cmax of 8.0 µg/mL, and has an AUC of 1591 µg\*h/mL. An oral radiolabelled dose of cabotegravir is 58.5% recovered in the feces and 26.8% recovered in the urine. Data regarding the volume of distribution of cabotegravir is not readily available. Data regarding the clearance of cabotegravir is not readily available. Clearance in dogs was 0.34 mL/min/kg and in cynomolgus monkeys was 0.32 mL/min/kg. Metabolism / Metabolites Cabotegravir is O-glucuronidated to the M1 and M2 metabolites, with 67% of glucuronidation performed by UGT1A1, and 33% by UGT1A9. Biological Half-Life The mean half life of oral cabotegravir is 41 hours. The mean half life of intramuscular extended-release cabotegravir is 5.6-11.5 weeks. Background: GSK1265744 is an HIV integrase strand transfer inhibitor selected for clinical development. Objective: This first-time-in-human and phase IIa investigation assessed GSK1265744 antiviral activity, pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability in healthy and HIV-1–infected subjects. Methods: This double-blind, placebo-controlled study consisted of a dose escalation of single (part A) and multiple (part B) oral doses in 48 healthy subjects and an oral dose (part C) in 11 HIV-1–infected subjects. In part A, 2 cohorts of 9 subjects received either 5 and 25 mg or 10 and 50 mg. In part B, 3 cohorts of 10 subjects received 5, 10, or 25 mg once daily for 14 days. In part C and the phase IIa study, subjects received 5 or 30 mg once daily for 10 days. Results: Dose-proportional increases in drug exposure were observed in healthy and HIV-1–infected subjects. In healthy subjects, pharmacokinetic variability was low following single or repeat dosing (coefficient of variation, 13%-34% and 15%-23%, respectively). Mean plasma half-life was 31.5 hours. GSK1265744 monotherapy significantly reduced plasma HIV-1 RNA from baseline to day 11 in HIV-1–infected subjects receiving 5 or 30 mg versus placebo (P < .001); mean decrease was 2.2 to 2.3 log10 copies/mL, respectively. Study drug was generally well tolerated with no clinically relevant trends in laboratory values, vital signs, or electrocardiograms. Conclusions: GSK1265744 was well tolerated in healthy and HIV-1–infected subjects. Results demonstrate once-daily doses of 5 or 30 mg exceeded minimum target therapeutic concentrations and produced a significant reduction in plasma HIV-1 RNA viral load. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1310/hct1405-192?src=recsys |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No published information is available on the use of cabotegravir during breastfeeding. Achieving and maintaining viral suppression with antiretroviral therapy decreases breastfeeding transmission risk to less than 1%, but not zero. Individuals with HIV who are on antiretroviral therapy with a sustained undetectable viral load and who choose to breastfeed should be supported in this decision. If a viral load is not suppressed, banked pasteurized donor milk or formula is recommended. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Hepatotoxicity In large clinical trials, switching antiretroviral therapy of HIV infection to the combination of parenteral injections of long acting cabotegravir and rilpivirine was associated with alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevations in up to 7% of patients, but levels above 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) arose in only 1% to 2% of subjects. The elevations were typically transient, asymptomatic, and rarely required dose modification or discontinuation. While clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice was reported to occur in early studies, there were no such cases in the large, preregistration trials of long acting, parenteral cabotegravir and rilpivirine used for treatment of HIV infection or in the large trials of long acting cabotegravir used as prophylaxis against acquiring HIV infection. The use of injections every 4 or 8 weeks has been found to improve compliance and to be preferable to daily oral therapy by many patients requiring long term antiretroviral therapy. Since approval of cabotegravir for use as maintenance therapy and for prophylaxis against HIV infection, there have been no case reports of clinically apparent hepatotoxicity associated with its use. Interestingly, in the large preregistration trials of parenteral cabotegravir and rilpivirine as replacement therapy of HIV infection, cases of acute hepatitis A, B and C were reported as adverse events, occurring largely in patients who had been switched to the parenteral regimen compared to control subjects who were continued on oral agents. The reasons for these differences were unclear. Importantly, neither cabotegravir or rilpivirine have activity against hepatitis B virus (HBV), and one possibility has been that reactivation of hepatitis B may occur after withdrawal of oral antiretroviral agents that have activity against HBV, such as tenofovir, emtricitabine, and lamivudine. For this reason, patients starting long- acting parenteral regimens of cabotegravir and rilpivirine should be screened for hepatitis B virus markers and potential risks of stopping agents with activity against HBV should be considered. In addition, persons with HIV without protective antibodies to HAV and HBV should be offered hepatitis A and B virus vaccination. Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No published information is available on the use of cabotegravir during breastfeeding. Achieving and maintaining viral suppression with antiretroviral therapy decreases breastfeeding transmission risk to less than 1%, but not zero. Individuals with HIV who are on antiretroviral therapy with a sustained undetectable viral load and who choose to breastfeed should be supported in this decision. If a viral load is not suppressed, banked pasteurized donor milk or formula is recommended. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Cabotegravir is >99.8% bound to proteins in plasma, usually alubmin. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
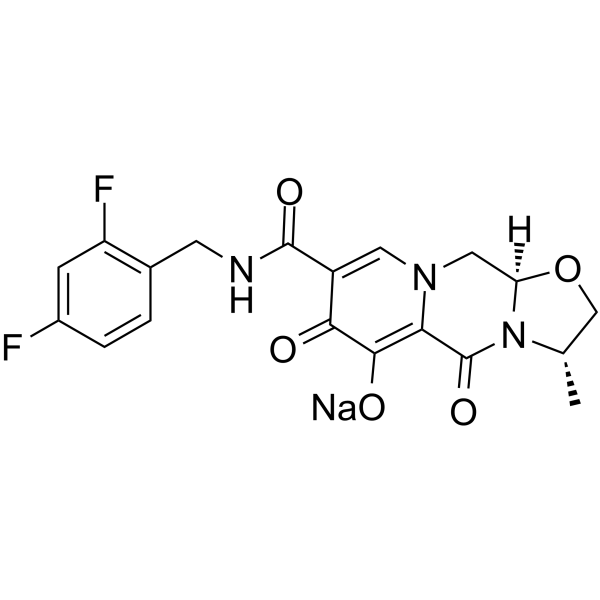
Cabotegravir sodium is an organic sodium salt that is the monosodium salt of cabotegravir. Used for treatment of HIV-1. It has a role as a HIV-1 integrase inhibitor. It contains a cabotegravir(1-).
Cabotegravir is a prescription medicine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It is approved as two different dosage forms under two different brand names for the following uses: Cabotegravir oral tablet (brand name: Vocabria) For the short-term treatment of HIV infection in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older who weigh at least 77 lb (35 kg) and who meet certain requirements, as determined by a health care provider. When used for HIV treatment, cabotegravir is always used with the HIV medicine rilpivirine (brand name: Edurant). For short-term PrEP to reduce the risk of HIV infection in adults and adolescents who weigh at least 77 lb (35 kg), are HIV negative, and are at risk of getting HIV. Oral cabotegravir for PrEP should always be used in combination with safer sex practices, such as using condoms, to reduce the risk of getting other sexually transmitted infections. Long-acting injectable cabotegravir (brand name: Apretude) For HIV PrEP to reduce the risk of HIV infection in adults and adolescents who weigh at least 77 lb (35 kg), are HIV negative, and are at risk of getting HIV. Long-acting injectable cabotegravir for PrEP should always be used in combination with safer sex practices, such as using condoms, to reduce the risk of getting other sexually transmitted infections. Drug Indication Vocabria tablets are indicated in combination with rilpivirine tablets for the short-term treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in adults who are virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA) Pharmacodynamics Cabotegravir is an inhibitor of HIV integrase, which reduces viral replication. It has a long duration of action as the oral tablet is given daily and the intramuscular suspension is given monthly. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of hypersensitivity, hepatotoxicity, and depression. Cabotegravir is a monocarboxylic acid amide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of (3S,11aR)-6-hydroxy-3-methyl-5,7-dioxo-2,3,5,7,11,11a-hexahydro[1,3]oxazolo[3,2-a]pyrido[1,2-d]pyrazine-8-carboxylic acid with the amino group of 2,4-difluorobenzylamine. Used (as its sodium salt) for treatment of HIV-1. It has a role as a HIV-1 integrase inhibitor. It is a difluorobenzene, a secondary carboxamide, a monocarboxylic acid amide and an organic heterotricyclic compound. It is a conjugate acid of a cabotegravir(1-). Cabotegravir is a prescription medicine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It is approved as two different dosage forms under two different brand names for the following uses: Cabotegravir oral tablet (brand name: Vocabria) For the short-term treatment of HIV infection in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older who weigh at least 77 lb (35 kg) and who meet certain requirements, as determined by a health care provider. When used for HIV treatment, cabotegravir is always used with the HIV medicine rilpivirine (brand name: Edurant). For short-term PrEP to reduce the risk of HIV infection in adults and adolescents who weigh at least 77 lb (35 kg), are HIV negative, and are at risk of getting HIV. Oral cabotegravir for PrEP should always be used in combination with safer sex practices, such as using condoms, to reduce the risk of getting other sexually transmitted infections. Long-acting injectable cabotegravir (brand name: Apretude) Cabotegravir, or GSK1265744, is an HIV-1 integrase inhibitor that is prescribed with the non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, [rilpivirine]. Early research into cabotegravir showed it had lower oral bioavailability than [dolutegravir], which resulted in the development of long acting monthly intramuscular injection formulation for cabotegravir. Cabotegravir was granted FDA approval on 21 January 2021 in combination with rilpivirine to treat HIV-1 infection in virologically suppressed individuals. While previously administered once monthly only, this combination product was granted FDA approval for dosing every two months on February 01, 2022 and without the need for an oral lead-in period prior. Cabotegravir is a Human Immunodeficiency Virus Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of cabotegravir is as a HIV Integrase Inhibitor, and Organic Anion Transporter 1 Inhibitor, and Organic Anion Transporter 3 Inhibitor. Cabotegravir is an antiviral agent that inhibits the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) integrase and is used in combination with rilpivirine, a non-nucleoside HIV reverse transcription inhibitor, in the treatment of HIV infection and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). The fixed combination of cabotegravir and rilpivirine is typically given intramuscularly once monthly and has been linked to a low rate of serum aminotransferase elevations during therapy and to rare episodes of acute, clinically apparent liver injury. Cabotegravir is a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI), that is used for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to reduce the risk of sexually acquired HIV-1 infection. Upon gluteal intramuscular administration, cabotegravir binds to the active site of HIV integrase and inhibits the activity of HIV integrase, an HIV-1 coded enzyme that is necessary for viral replication. Inhibition of integrase prevents the integration of HIV-1 DNA into host genomic DNA. CABOTEGRAVIR is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of IV (across all indications) that was first approved in 2021 and has 3 approved and 1 investigational indication. Drug Indication Oral cabotegravir is indicated in combination with [rilpivirine] for the short-term treatment of HIV-1 in virologically suppressed adults with no history of treatment failure to assess tolerability of cabotegravir or who have missed an injected dose of cabotegravir. Intramuscular extended-release cabotegravir in combination with rilpivirine is indicated as a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older weighing at least 35 kg to replace the current antiretroviral regimen in those who are virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL) on a stable antiretroviral regimen with no history of treatment failure and with no known or suspected resistance to either cabotegravir or rilpivirine. An extended-release injectable suspension formulation of cabotegravir is also indicated for the prevention of sexually-acquired HIV-1 infection (i.e. for pre-exposure prophylaxis, PrEP) in at-risk adults and adolescents weighing at least 35kg. Apretude is indicated in combination with safer sex practices for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to reduce the risk of sexually acquired HIV-1 infection in high-risk adults and adolescents, weighing at least 35 kg (see sections 4. 2, 4. 4 and 5. 1). Vocabria tablets are indicated in combination with rilpivirine tablets for the short-term treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in adults who are virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA |
| 分子式 |
C19H16N3O5F2-.NA+
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
427.33404
|
| 精确质量 |
427.095
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.40; H, 3.77; F, 8.89; N, 9.83; Na, 5.38; O, 18.72
|
| CAS号 |
1051375-13-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Cabotegravir;1051375-10-0;Cabotegravir-d3 sodium
|
| PubChem CID |
46215800
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| tPSA |
102
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
820
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
C[C@H]1CO[C@H]2N1C(=O)C3=C(C(=O)C(=CN3C2)C(=O)NCC4=C(C=C(C=C4)F)F)[O-].[Na+]
|
| InChi Key |
AEZBWGMXBKPGFP-KIUAEZIZSA-M
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H17F2N3O5.Na/c1-9-8-29-14-7-23-6-12(16(25)17(26)15(23)19(28)24(9)14)18(27)22-5-10-2-3-11(20)4-13(10)21;/h2-4,6,9,14,26H,5,7-8H2,1H3,(H,22,27);/q;+1/p-1/t9-,14+;/m0./s1
|
| 化学名 |
sodium;(3R,6S)-12-[(2,4-difluorophenyl)methylcarbamoyl]-6-methyl-8,11-dioxo-4-oxa-1,7-diazatricyclo[7.4.0.03,7]trideca-9,12-dien-10-olate
|
| 别名 |
Cabotegravir sodium; 1051375-13-3; Vocabria; GSK1265744B; GSK-1265744B;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~6.25 mg/mL (~14.63 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3401 mL | 11.7006 mL | 23.4011 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4680 mL | 2.3401 mL | 4.6802 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2340 mL | 1.1701 mL | 2.3401 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。