| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Beta1 Adrenergic Receptor
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:倍他洛尔能够保护视网膜神经元。倍他洛尔可减弱 NMDA 诱导的 45Ca2+ 流入,而 β-肾上腺素受体激动剂则无效。当包含倍他洛尔 (10 μM) 时,谷氨酸诱导的 LDH 释放几乎被完全阻止。倍他洛尔 (100 μM) 对于防止皮质培养物中缺氧诱导的 LDH 释放非常有效。细胞测定:将 16-18 日龄胎鼠的分离皮质细胞培养在 35 mm 培养皿中,在补充有 L-谷氨酰胺 (4 mM)、葡萄糖 (6 g/L)、青霉素 (100 U/mL) 的 DMEM 中培养)、链霉素 (100 μg/mL) 和 10% 激素补充培养基,由转铁蛋白 (1 mg/mL)、胰岛素 (250 μg/mL)、腐胺 (600 μM)、亚硒酸钠 (0.3 μM)、黄体酮 (0.2 μM) 组成和雌二醇 (0.1 pM),在 37 °C、5% CO2/95% O2 的气氛中持续 7 天。然后将培养物转移至不含激素补充培养基的培养基中。将 L-谷氨酸添加到培养基中并在含氧量正常的条件下再孵育 4 小时。倍他洛尔与 L-谷氨酸同时添加到培养物中。在其他实验中,培养物在 37°C 下处于缺氧条件(95% N2/5% CO2)下 5 小时。在缺氧之前添加倍他洛尔。然后通过将细胞置于常氧条件(95% O2/5% CO2)下 3 小时来实现再氧合。通过测量缺氧/复氧或谷氨酸暴露后乳酸脱氢酶 (LDH) 释放到细胞培养物上清液中来评估细胞损伤。通过在 340 nm 处跟踪 NADH 代谢 2 分钟,以分光光度法测定 LDH 活性。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
与可卡因戒断期间仅用生理盐水治疗的动物相比,在可卡因戒断期间用倍他洛尔治疗的动物表现出焦虑样行为的显著减弱,其特征是张开双臂的时间增加,进入张开双臂的次数增加。相比之下,倍他洛尔在长期用生理盐水治疗的对照动物中没有产生抗焦虑样作用。此外,在可卡因戒断早期使用倍他洛尔治疗显著降低了杏仁核中β1肾上腺素能受体蛋白的表达,使其水平与对照组动物相当。
结论:本研究结果表明,β洛尔对可卡因诱导的焦虑的抗焦虑样作用可能与它对在停药早期上调的杏仁核β1肾上腺素能受体的影响有关。这些数据支持倍他洛尔作为一种潜在的有效药物疗法,在戒断早期治疗可卡因戒断引起的焦虑。[1]
当在缺血前和再灌注日将倍他洛尔腹腔注射到大鼠中时,钙结合蛋白和 ChAT 免疫反应性的变化减少,并且防止了 b 波的减少。倍他洛尔的加入可以部分防止 NMDA 和缺氧/葡萄糖引起的变化。 |
||
| 细胞实验 |
将 16-18 日龄胎鼠的分离皮质细胞培养在 35 mm 培养皿中的 DMEM 中,添加 L-谷氨酰胺 (4 mM)、葡萄糖 (6 g/L)、青霉素 (100 U/mL)、链霉素 (100 μg/mL) 和 10% 激素补充培养基,含有亚硒酸钠 (0.3 μM)、黄体酮 (0.2 μM)、腐胺 (600 μM)、转铁蛋白 (1 mg/mL)、胰岛素 (250 μg/mL)、腐胺 ( 600 μM)、黄体酮 (0.2 μM) 和雌二醇 (0.1 pM)。之后,将培养物转移到不含激素补充剂的培养基中。添加L-谷氨酸后,将混合物在含氧量正常的条件下再孵育4小时。 L-谷氨酸和倍他洛尔同时添加到培养物中。在缺氧条件下,95% N2/5% CO2 在 37 °C 下持续 5 小时,应用于其他实验中的培养物。首先出现缺氧,然后出现贝索洛尔。接下来,将细胞更换为含氧量正常的细胞(95% O2/5% CO2)三小时,以实现再氧合。测量缺氧/复氧或谷氨酸暴露后细胞培养物上清液中乳酸脱氢酶 (LDH) 的释放是评估细胞损伤的有用方法。通过在 340 nm 处监测 NADH 代谢两分钟,用分光光度法测量 LDH 活性。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Absorption of an oral dose is complete. There is a small and consistent first-pass effect resulting in an absolute bioavailability of 89% ± 5% that is unaffected by the concomitant ingestion of food or alcohol. Metabolism / Metabolites Primarily hepatic. Approximately 15% of the dose administered is excreted as unchanged drug, the remainder being metabolites whose contribution to the clinical effect is negligible. Biological Half-Life 14-22 hours |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Betaxolol therapy has been associated with a low rate of mild-to-moderate elevations of serum aminotransferase levels which are usually asymptomatic and transient and resolve even with continuation of therapy. There have been no well documented cases of clinically apparent, acute liver injury attributable to betaxolol. Thus, hepatotoxicity due to betaxolol must be very rare, if it occurs at all. Most commonly used beta-blockers have been linked to rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury, typically with onset within 2 to 12 weeks, a hepatocellular pattern of liver enzyme elevations, rapid recovery on withdrawal, and little evidence of hypersensitivity (rash, fever, eosinophilia) or autoantibody formation. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because of its relatively extensive excretion into breastmilk and minimal reported experience during breastfeeding, other beta-blocking agents may be preferred for systemic use, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Ophthalmic use of betaxolol by the mother should pose little risk to the breastfed infant, although some guidelines state that gel formulations are preferred over solutions. To substantially diminish the amount of drug that reaches the breastmilk after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A study of mothers taking beta-blockers during nursing found a numerically, but not statistically significant increased number of adverse reactions in those taking any beta-blocker. Although the ages of infants were matched to control infants, the ages of the affected infants were not stated. None of the mothers were taking betaxolol. Beta-adrenergic blocking drugs with breastmilk excretion characteristics similar to betaxolol have caused adverse effects in breastfed newborns. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information on the effects of beta-blockade or betaxolol during normal lactation was not found as of the revision date. A study in 6 patients with hyperprolactinemia and galactorrhea found no changes in serum prolactin levels following beta-adrenergic blockade with propranolol. Protein Binding 50% |
||
| 参考文献 | |||
| 其他信息 |
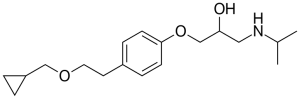
Betaxolol is a propanolamine that is 3-aminopropane-1,2-diol in which the hydrogen of the primary hydoxy is substituted by a 4-[2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)ethyl]phenyl group and one of the hydrogens attached to the amino group is substituted by isopropyl. It is a selective beta1-receptor blocker and is used in the treatment of glaucoma as well as hypertension, arrhythmias, and coronary heart disease. It is also used to reduce non-fatal cardiac events in patients with heart failure. It has a role as a beta-adrenergic antagonist, an antihypertensive agent and a sympatholytic agent.
A cardioselective beta-1-adrenergic antagonist with no partial agonist activity. Betaxolol is a beta-Adrenergic Blocker. The mechanism of action of betaxolol is as an Adrenergic beta-Antagonist. Betaxolol is a cardioselective beta-blocker used in the treatment of hypertension. Betaxolol has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent drug induced liver injury. Betaxolol is a racemic mixture and selective beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist with antihypertensive and anti-glaucoma activities and devoid of intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. Betaxolol selectively and competitively binds to and blocks beta-1 adrenergic receptors in the heart, thereby decreasing cardiac contractility and rate. This leads to a reduction in cardiac output and lowers blood pressure. When applied topically in the eye, this agent reduces aqueous humor secretion and lowers the intraocular pressure (IOP). In addition, betaxolol prevents the release of renin, a hormone secreted by the kidneys that causes constriction of blood vessels. A cardioselective beta-1-adrenergic antagonist with no partial agonist activity. See also: Betaxolol Hydrochloride (has salt form). Drug Indication For the management of hypertension. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Betaxolol selectively blocks catecholamine stimulation of beta(1)-adrenergic receptors in the heart and vascular smooth muscle. This results in a reduction of heart rate, cardiac output, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and possibly reflex orthostatic hypotension. Betaxolol can also competitively block beta(2)-adrenergic responses in the bronchial and vascular smooth muscles, causing bronchospasm. Pharmacodynamics Betaxolol is a competitive, beta(1)-selective (cardioselective) adrenergic antagonist. Betaxolol is used to treat hypertension, arrhythmias, coronary heart disease, glaucoma, and is also used to reduce non-fatal cardiac events in patients with heart failure. Activation of beta(1)-receptors (located mainly in the heart) by epinephrine increases the heart rate and the blood pressure, and the heart consumes more oxygen. Drugs such as betaxolol that block these receptors therefore have the reverse effect: they lower the heart rate and blood pressure and hence are used in conditions when the heart itself is deprived of oxygen. They are routinely prescribed in patients with ischemic heart disease. In addition, beta(1)-selective blockers prevent the release of renin, which is a hormone produced by the kidneys which leads to constriction of blood vessels. Betaxolol is lipophilic and exhibits no intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) or membrane stabilizing activity. |
| 分子式 |
C18H29NO3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
307.43
|
|
| 精确质量 |
307.21
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 70.32; H, 9.51; N, 4.56; O, 15.61
|
|
| CAS号 |
63659-18-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Betaxolol hydrochloride; 63659-19-8; Levobetaxolol hydrochloride; 116209-55-3; Betaxolol-d5; 1189957-99-0; 63659-18-7; 93221-48-8 (S-isomer free base); 116209-55-3 (S-isomer HCl)
|
|
| PubChem CID |
2369
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.067 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
448ºC at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
61-63°C
|
|
| 闪点 |
224.7ºC
|
|
| LogP |
2.784
|
|
| tPSA |
50.72
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
11
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
22
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
286
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
O(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])OC([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])O[H])C([H])([H])C1([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
NWIUTZDMDHAVTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H29NO3/c1-14(2)19-11-17(20)13-22-18-7-5-15(6-8-18)9-10-21-12-16-3-4-16/h5-8,14,16-17,19-20H,3-4,9-13H2,1-2H3
|
|
| 化学名 |
1-[4-[2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)ethyl]phenoxy]-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.13 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.13 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.13 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2528 mL | 16.2639 mL | 32.5277 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6506 mL | 3.2528 mL | 6.5055 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3253 mL | 1.6264 mL | 3.2528 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT01660620 | Completed | Drug: topical betaxolol Drug: Betaxolol |
Development of Side Effects From Betaxolol |
Smith-Kettlewell Eye Research Institute |
April 2011 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00061542 | Completed | Drug: BETOPTIC S (betaxolol HCl) Drug: Timolol Gel-forming Solution (TGFS) |
Glaucoma Ocular Hypertension |
Alcon Research | January 2003 | Phase 3 |
| NCT02617459 | Completed | Drug: Levobetaxolol eye drops Drug: Betaxolol eye drops |
Primary Open-angle Glaucoma Ocular Hypertension |
Zhaoke (Guangzhou) Ophthalmology Pharmaceutical Ltd. |
January 4, 2019 | Phase 3 |
 Effect of betaxolol on the DNA fragmentation of HCE cells.Int J Ophthalmol. 2014; 7(1): 14–21. Effect of betaxolol on the DNA fragmentation of HCE cells.Int J Ophthalmol. 2014; 7(1): 14–21. |
|---|
 |
|