| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
ERα (IC50 = 26 nM); ERβ (IC50 = 99 nM)[1]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
GP130 D1 结构域与小分子 GP130 抑制剂苯多昔芬结合 [1]。当 IL-6 和 IL-11 触发 GP130/STAT3 通路信号传导中的 STAT3 磷酸化时,苯多昔芬会阻断这一过程 [1]。在人胰腺癌细胞中,zedoxifene(10 μM–20 μM;2 小时)可抑制细胞因子引起的 STAT3 磷酸化 [2]。当人类胰腺癌细胞暴露于苯佐昔芬 (5–20 μM) 过夜时会发生凋亡 [2]。 IL-6 引起的 STAT3 核转位可被苯多昔芬抑制 [2]。通过阻断 GP130,苯多昔芬可阻止胰腺癌细胞迁移 [2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在未成熟大鼠子宫模型中, 巴多昔芬0.5和5.0 mg/kg)对子宫湿重的增加作用小于乙炔雌二醇(10微克/kg)或雷洛昔芬(0.5和5.0 mg/kg)。组织学分析显示,同时使用巴多昔芬也能减少雷洛昔芬刺激的子宫内膜上皮细胞和子宫肌层细胞肥大。在去卵巢大鼠中,与对照组相比,巴多昔芬与6周时骨矿物质密度显著增加有关,与去卵巢动物的样本相比,L4椎骨样本的抗压强度更好。在吗啡成瘾大鼠血管舒缩活性模型中,单独使用保骨剂量的巴多昔芬与17 - β -雌二醇对血管舒缩活性增加的抑制作用无关。醋酸巴多昔芬是一种很有前景的治疗骨质疏松症的新方法,与目前临床上使用的选择性雌激素受体调节剂相比,它对子宫和血管舒缩的影响可能更小。需要对照临床试验数据来证实这些效果。
巴泽多昔芬抑制小鼠体内模型capan-1肿瘤生长[2] 在小鼠模型中,醋酸巴多昔芬(5 mg/kg;搞笑;每日,持续18天)在体内抑制Capan-1肿瘤生长[2]。 在本研究中,研究人员验证了巴多昔芬是否在体内和体外抑制肿瘤生长。Capan-1细胞(3 × 106)注射方法如前面材料和方法所述。初始植入1周后,当肿瘤大小达到0.05 ~ 0.1cm3时,给予治疗组巴多昔芬5 mg/kg,对照组给予DMSO,连续18 d。如图6A所示,与载药组相比,巴多昔芬明显抑制肿瘤生长。巴多昔芬处理组肿瘤组织样本P-STAT3Y705降低,caspase-3被诱导(图6A),提示巴多昔芬可以抑制胰腺癌异种移植瘤的生长,诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡。 |
| 酶活实验 |
配体结合[1]
使用先前描述的[3H]-17β-雌二醇,采用固相竞争放射配体结合法评估醋酸巴多昔芬(BZA)与人ERα和ERβ的相互作用。 STAT3 DNA结合试验[2] 将BxPC-3细胞接种于10cm板上,用5-10 μmol/L的巴多昔芬或DMSO处理24h。细胞核提取试剂盒 按照制造商的方案制备细胞核提取液。采用STAT3 DNA结合ELISA试剂盒(Active Motif),采用ELISA方法分析核提取物的STAT3 DNA结合活性。在450nm处读取吸光度。 细胞因子或生长因子诱导STATs磷酸化[2] 将PANC-1、AsPC-1和hpf - ii胰腺癌细胞接种于10厘米板中,留置过夜。第二天晚上,这些细胞被血清饥饿。然后不处理细胞或用巴泽多西芬(5 ~ 20 μmol/L)或DMSO处理细胞。2小时后,未处理和巴多昔芬处理的细胞被IL6 (50 ng/mL)、IL11 (50 ng/mL)、OSM (50 ng/mL)或INFγ (50 ng/mL)刺激30分钟。收集细胞,用Western blot分析p-STAT3Y705或p-STAT1Y701。 |
| 细胞实验 |
蛋白质印迹分析[2]
细胞类型: AsPC-1 细胞 测试浓度: 10 μM、20 μM 孵育时间: 2小时 实验结果:抑制IL-6、IL-11或OSM (50 ng/mL)诱导的STAT3磷酸化。 细胞凋亡分析 [2] 细胞类型: Capan-1 细胞、BxPC-3 细胞、HPAF-II 细胞、HPAC 细胞 测试浓度: 10μM、20μM(Capan-1); 5μM、10μM(BxPC-3); 10 μM、20 μM (HPAF-II); 10 μM、15 μM (HPAC) 孵育时间:过夜 实验结果:诱导细胞凋亡。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: 6weeks old female athymic nude mice [2]
Doses: 5 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage), daily, for 18 days. Experimental Results: Inhibited the growth of pancreatic cancer xenograft tumors and induced tumor cell apoptosis. Vasomotor instability (hot flush)[1] Ovariectomized female (60 d) rats were obtained after surgery. The surgeries were performed minimally 7 d before initiation of any experiment. Vehicle and ethinyl estradiol (0.3 mg/kg) were included in each replicate. Bazedoxifene was administered orally in a saline, Tween-80, methylcellulose vehicle. A detailed description of methodology for evaluating vasomotor instability in rats has been published (21). Briefly, compound treatment (17β-estradiol, ethinyl estradiol, or bazedoxifene) is initiated, and on the third day of treatment each animal receives a morphine pellet sc. This is followed by two more pellets on the fifth day of treatment. On the eighth day, a thermistor is taped to the animal’s tail to measure tail skin temperature for 15 min (to obtain baseline temperature) followed by a sc injection of naloxone (1 mg/kg). Tail skin temperature readings continue for 1 h after naloxone injection. All animal studies were conducted in accordance with the principles and standard procedures approved by IACUC of the Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital. Capan-1 (3 × 106) and HPAF-II (3 × 106) cells in Matrigel were injected subcutaneously into the both side of flank area of 6-week-old female athymic nude mice which were purchased from Harlan. After Capan-1 tumor development, which was 1 week after initial implantation, mice were divided into two treatment groups consisting of four mice (tumors: n = 8): DMSO vehicle control and gavage injection of Bazedoxifene (5 mg/kg/d). Mice bearing HPAF-II tumor were irrigated with Bazedoxifene(5 mg/kg/d) and/or injected via abdomen with paclitaxel (15 mg/kg, 2/w). Tumor growth was determined by measured the length (L) and width (W) of the tumor every other day with a caliper, and tumor volume was calculated on the basis of the following formula: volume = 0.52 × LW2. After 21 days of treatment, tumors were harvested, snap-frozen in dry ice, and stored at −80°C. Tumors tissue homogenates were lysed and separated by SDS-PAGE to examine the expression of STAT3 phosphorylation, P-ERK1/2, P-AKT (Ser473), and cleaved caspase-3.[2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Bazedoxifene is rapidly absorbed with a tmax of approximately 2 hours and exhibits a linear increase in plasma concentrations for single doses from 0.5 mg up to 120 mg and multiple daily doses from 1 mg to 80 mg. The absolute bioavailability of bazedoxifene is approximately 6%. The major route of elimination of radio-labelled bazedoxifene is the faeces, and less than 1% of the dose is eliminated in urine. Following intravenous administration of a 3 mg dose of bazedoxifene, the volume of distribution is 14.7 ± 3.9 l/kg. The apparent oral clearance of bazedoxifene is approximately 4 to 5 l/h/kg. Metabolism / Metabolites Glucuronidation is the major metabolic pathway. After peroral application, bazedoxifene is metabolized by UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) to bazedoxifene-4'-glucuronide (M4) and bazedoxifene-5-glucuronide (M5).Little or no cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism is evident. The concentrations of this glucuronide are approximately 10-fold higher than those of unchanged active substance in plasma. Biological Half-Life ~30 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
98-99%. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Bazedoxifene is a phenylindole.
Bazedoxifene is a third generation selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM), developed by Pfizer following the completion of their takeover of Wyeth Pharmaceuticals. In late 2013, Pfizer received approval for bazedoxifene as part of the combination drug DUAVEE in the prevention (not treatment) of postmenopausal osteoporosis. It is approved in the European Union (marketed in Italy and Spain) and Japan as monotherapy. In 2013, the combination product containing conjugated estrogens and bazedoxifene was approved by the FDA for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause, as well as the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis in women. Bazedoxifene is an Estrogen Agonist/Antagonist. The mechanism of action of bazedoxifene is as a Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator. Bazedoxifene is an indole derivative and third-generation selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon administration, bazedoxifene specifically binds to estrogen receptors in responsive tissues, including liver, bone, breast, and endometrium. The resulting ligand-receptor complex is translocated to the nucleus where, depending on the tissue type, it either promotes or suppresses the transcription of estrogen-regulated genes. Bazedoxifene acts as an estrogen antagonist in uterine and breast tissue, thereby blocking the proliferative effects of estrogen-binding to ER-positive cells in these tissues. Bazedoxifene functions as an estrogen agonist in lipid metabolism, thereby decreasing total and LDL cholesterol levels. In bone, it decreases bone resorption and bone turnover and increases bone mineral density. Drug Indication Indicated for following conditions alone or in combination with conjugated estrogens in women with a uterus: - Treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause - Prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis FDA Label Conbriza is indicated for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis in women at increased risk of fracture. A significant reduction in the incidence of vertebral fractures has been demonstrated; efficacy on hip fractures has not been established. When determining the choice of Conbriza or other therapies, including oestrogens, for an individual postmenopausal woman, consideration should be given to menopausal symptoms, effects on uterine and breast tissues, and cardiovascular risks and benefits. Mechanism of Action Bazedoxifene belongs to a class of compounds known as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs). Bazedoxifene acts as both an oestrogen-receptor agonist and/or antagonist, depending upon the cell and tissue type and target genes. Bazedoxifene decreases bone resorption and reduces biochemical markers of bone turnover to the premenopausal range. These effects on bone remodelling lead to an increase in bone mineral density (BMD), which in turn contributes to a reduction in the risk of fractures. Bazedoxifene functions primarily as an oestrogen-receptor antagonist in uterine and breast tissues. |
| 分子式 |
C30H34N2O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
470.6
|
| 精确质量 |
470.256
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 76.57; H, 7.28; N, 5.95; O, 10.20
|
| CAS号 |
198481-32-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Bazedoxifene acetate;198481-33-3;Bazedoxifene hydrochloride;198480-56-7;Bazedoxifene-d4;1133695-49-4;Bazedoxifene-d4 acetate;1795027-71-2
|
| PubChem CID |
154257
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
694.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
373.8±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.622
|
| LogP |
6.59
|
| tPSA |
57.86
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
623
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
UCJGJABZCDBEDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C30H34N2O3/c1-22-28-20-26(34)12-15-29(28)32(30(22)24-8-10-25(33)11-9-24)21-23-6-13-27(14-7-23)35-19-18-31-16-4-2-3-5-17-31/h6-15,20,33-34H,2-5,16-19,21H2,1H3
|
| 化学名 |
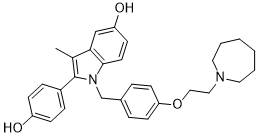
1-(4-(2-(azepan-1-yl)ethoxy)benzyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1H-indol-5-ol
|
| 别名 |
WAY-140424; WAY140424; WAY 140424; TSE 424; Bazedoxifene [INN]; 1H-Indol-5-ol, 1-[[4-[2-(hexahydro-1H-azepin-1-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-; Bazedoxifene free base; Q16TT9C5BK; 1-(4-(2-(azepan-1-yl)ethoxy)benzyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1H-indol-5-ol; TSE424; TSE-424 Viviant.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~212.49 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.31 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.31 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.31 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1249 mL | 10.6247 mL | 21.2495 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4250 mL | 2.1249 mL | 4.2499 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2125 mL | 1.0625 mL | 2.1249 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。