| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
HIV-1(EC50=0.03-6.92 nM);HIV-2(EC50=0.018-0.02 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Azvudine(RO-0622)对野生型 HIV-1IIIB 和 HIV-1RF 显示出强烈的抑制作用,EC50 范围为 30 至 110 pM。 Azvudine 针对 HIV-1KM018、HIV-1TC-1 和 HIV-1WAN T69N 的 EC50 值分别为 6.92、0.34 和 0.45 nM。 Azvudine 对 NRTIs 耐药株 HIV-174V、PIs 耐药株 HIV-1L10R/M46I/L63P/V82T/I84V 和 HIV-1RF V82F/184V 以及 FIs 耐药株 pNL4-3 gp41 (36G) V38A/N42T 敏感。 Azvudine 针对这些耐药菌株的 EC50 值分别为 0.11、0.14、0.37 和 0.36 nM[1]。
在细胞模型中,阿扎夫定(FNC)以剂量依赖的方式有效地抑制了HBV抗原的分泌,在第9天,乙肝表面抗原的50%有效浓度值为0.037μM,乙肝e抗原为0.044μM。与HBV抗原减少一致,阿扎夫定(FNC)也分别在细胞内和细胞外将HBV DNA水平降低了92.31%和93.90%。[2]
阿扎夫定(FNC)以剂量依赖的方式抑制野生型和拉米夫定耐药HBV临床分离株的复制,平均±SD EC(50)值分别为0.12±0.01μM和0.27±0.01μM。 结论:Azvudine(FNC)是一种潜在的抗病毒药物,可对抗野生型和拉米夫定耐药的HBV临床分离株,因此值得进一步评估其治疗HBV感染的效果。[3] Azvudine(FNC)以0.95-4.55μM的IC(50)有效抑制多种侵袭性人类癌症细胞系的细胞增殖,包括B细胞非霍奇金淋巴瘤、肺腺癌和急性髓系白血病。用阿扎夫定(FNC)处理的细胞在高剂量和低剂量下分别表现出G1和S细胞周期阻滞,这证实了核苷类似物的作用机制。FNC治疗B-NHL细胞系以剂量和时间依赖的方式诱导凋亡。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
体内抗病毒药效[2]
经0.5、1.0和2.0 mg/kg•天剂量的Azvudine (FNC) 治疗后,DHBV DNA水平显著降低。在第10天,2.0 mg/kg•d剂量的Azvudine (FNC) 在鸭血清和肝脏中的抑制率分别达到91.68%和81.96%。此外,通过组织病理学分析评估,观察到FNC治疗后肝脏组织学明显恢复。[2] 体内抗肿瘤药效[4] 最后,肝癌(H22)、肉瘤(S180)和胃癌(SGC7901)的小鼠异种移植物模型表明,Azvudine (FNC) 以剂量依赖的方式具有显著的肿瘤生长抑制活性,且毒性低[4]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
通过荧光定量PCR定量HBV[2]
DNA为了进一步证实FNC在HepG2.2.15细胞中的抗病毒活性,通过荧光定量(FQ)-PCR评估了细胞外和细胞内HBV DNA水平。从培养上清液和细胞中提取病毒DNA,然后根据制造商的方案,使用HBV荧光定量PCR检测试剂盒 在Light Cycler 1.5中进行实时定量PCR。循环程序如下:在初始变性(95°C下2分钟)后,样品经历了40个变性循环(94°C下5秒)和退火/延伸循环(每个循环在56°C下45秒)。 |
| 细胞实验 |
体外抗HIV活性[1]
C8166细胞感染了不同浓度的HIV-1或HIV-2实验室菌株和耐药菌株,感染复数(MOI)为0.075-0.6。PHA刺激的PBMC与不同临床菌株在RPMI-1640(含10%FBS、50 U/ml IL-2和2µg/ml聚异戊二烯)中以0.1的MOI孵育。在37°C的5%CO2中感染2小时后,将C8166细胞洗涤三次以去除游离病毒,并用RPMI-1640(含10%FBS)重新悬浮。将100µl 4×104个细胞(PBMC为5×105个细胞)接种在96孔板上,板上有梯度浓度的Azvudine (FNC) 。将平板置于37°C、5%CO2的加湿培养箱中。3TC和AZT作为对照。孵育3-7天后,对合胞体形成的抑制百分比进行评分,或通过ELISA测量p24水平[19],并计算50%有效浓度(EC50)。 细胞毒性试验[1] 简而言之,将连续浓度的FNC加入96孔板中,然后加入100µl 4×104 C8166细胞(PBMC为5×105细胞)。在37°C、5%CO2下孵育3天后(PBMC为7天),每孔加入20µl MTT。孵育4小时后,去除100µl上清液,加入100µl 20%SDS-50%DMF。将平板在37°C下孵育过夜。通过ELISA阅读器在570nm和630nm处测量吸光度,并计算50%细胞毒性浓度(CC50)。3TC和AZT作为对照。 |
| 动物实验 |
DHBV infection and drug treatment experiment[2]
Each duck, aged 1 day, was injected into its tibial vein with 0.2 ml of serum from ducks with positive DHBV serology on day 3. The drug treatment experiment was carried out 7 days after ducks were infected with DHBV. The DHBV-positive ducks were randomly divided into five groups with 16 ducks in each group. Azvudine (FNC) in differ- ent concentrations and 3TC control were given orally to DHBV-infected ducks, respectively. Five groups were observed: FNC 0.5 mg/kg•day, Azvudine (FNC) 1.0 mg/kg•day, Azvudine (FNC) 2.0 mg/kg•day and 3TC 20 mg/kg•day as a posi- tive control. Normal saline was used as a mock treat- ment for the negative control group. The drugs were given once daily for 10 days continuously. The blood was drawn from the leg vein of all ducks before treat- ment, after medicating for 5 days and 10 days, and after withdrawal of the drug for 3 days. The serum samples and livers were separated and stored at -80°C. Measurement of DHBV DNA by FQ-PCR[2] DHBV DNA was measured on day 0, days 5 and 10 during treatment, and day 13, that is day 3 after ces- sation of treatment on day 10 by FQ-PCR. For DHBV DNA, the DNA was extracted from serum using a DNA Extraction Kit, and FQ-PCR was performed in Light-cycler 1.5 using SYBR Green I. A pair of primers was designed based on the sequences from a previously published report, and used for amplifying the genome of DHBV, and the amplified PCR fragments were then cloned into pMD-18T. Based on the conserved sequences of DHBV S gene, another pair of primers for real-time PCR were designed and used to amplify the recombinant plasmid for constructing the standard curves. Meanwhile, the specificity, sensitivity and repeatability of the assay were tested. A rapid and specific SYBR Green I real-time PCR assay was estab- lished to detect DHBV. DHBV DNA from the serum and liver of experimentally infected ducklings was detected by this assay at different time points as indicated.[2] Mouse xenograft studies[4] All mice were maintained under barrier conditions and experiments were conducted using protocols and conditions approved by the institutional animal care. Kunming mice (including male and female, body weight 20 ± 2 g from Shanghai Sikelai Co., Shanghai, China) were injected with 1 × 107 sarcoma (S-180) and hepatoma (H22) cells subcutaneously into the right front flank and divided randomly into several different test groups with 8–10 mice per cohort. One day after implantation of tumor cells, the mice were treated daily by IV or IG with vehicle (saline) or 5-FU (15 mg/kg/day), cisplatin (1.0 mg/kg/day), capecitabine (400 or 600 mg/kg/day) and Azvudine (FNC) (0.5, 1.0, 2.0 mg/kg/day) formulated in saline or distilled water (for capecitabine) for 8 days. Then the mice were sacrificed and the tumors were excised and weighed for evaluating the tumor growth inhibition at 24 h after the end of treatment. BALB/c nu/nu mice were provided by Shanghai Sikelai Co. and human gastric cancer cells (SGC7901) were subcutaneously implanted in the right hind back using 200 μl of a 1 × 107 cell/ml suspension in PBS. When tumors reached an average diameter of 5–8 mm, mice were weighed, randomized by tumor size, assigned to the various study groups, and treated with vehicle (saline), capecitabine (600 mg/kg/day), or Azvudine (FNC) (0.5, 1.0, 2.0 mg/kg/day) by IG daily for 20 days. After treatment, mice were sacrificed and the tumors were excised and weighed for evaluating the tumor growth inhibition. All results are represented as mean ± SEM of eight or ten animals. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Azvudine is under investigation in clinical trial NCT04668235 (Study on Safety and Clinical Efficacy of AZVUDINE in COVID-19 Patients (Sars-cov-2 Infected)).
Mechanism of Action Azvudine is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor that acts against HIV, HBV, and HCV. Some studies also show that it is able to modulate the expression of proteins like P-glycoprotein (P-gp), MRP2, and BCRP; in one instance, it was also able to increase the activity of P-gp. In 2020, the compound was tested in numerous clinical trials for the treatment of mild and common COVID-19. Azvudine is a novel nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor with antiviral activity on human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus. Here we reported the in vitro activity of azvudine against HIV-1 and HIV-2 when used alone or in combination with other antiretroviral drugs and its drug resistance features. Azvudine exerted highly potent inhibition on HIV-1 (EC(50)s ranging from 0.03 to 6.92 nM) and HIV-2 (EC(50)s ranging from 0.018 to 0.025 nM). It also showed synergism in combination with six approved anti-HIV drugs on both C8166 and PBMC. In combination assay, the concentrations of azvudine used were 1000 or 500 fold lower than other drugs. Azvudine also showed potent inhibition on NRTI-resistant strains (L74V and T69N). Although M184V caused 250 fold reduction in susceptibility, azvudine remained active at nanomolar range. In in vitro induced resistant assay, the frequency of M184I mutation increased with induction time which suggests M184I as the key mutation in azvudine treatment. As control, lamivudine treatment resulted in a higher frequency of M184I/V given the same induction time and higher occurrence of M184V was found. Molecular modeling analysis suggests that steric hindrance is more pronounced in mutant M184I than M184V due to the azido group of azvudine. The present data demonstrates the potential of azvudine as a complementary drug to current anti-HIV drugs. M184I should be the key mutation, however, azvudine still remains active on HIV-1LAI-M184V at nanomolar range.[2] Novel nucleoside analogue FNC is effective against both wild-type and lamivudine-resistant HBV clinical isolates. HBV infection causes major public health problems worldwide. The clinical limitation of current antiviral drugs for HBV, such as lamivudine, is causing rapid emergence of drug-resistant viral strains during prolonged antiviral therapy. Therefore, new antiviral drugs are urgently needed to prevent or delay the selection of drug-resistant HBV mutants. A novel cytidine analogue, FNC (2'-deoxy-2'-β-fluoro-4'-azidocytidine), was recently shown to strongly inhibit human HBV and duck HBV (DHBV) replication in vitro and in vivo, respectively. The present study was designed to evaluate the in vitro antiviral activity of FNC against clinical wild-type and lamivudine-resistant HBV isolates in transiently transfected cells. Methods: HBV DNA was extracted from serum samples collected both before lamivudine therapy and at the time of viral breakthrough and was amplified by PCR. The amplicon was cloned into a novel expression vector, pHY106, which can initiate the intracellular HBV replication cycle after cell transfection. Following transfection of the cloned amplicon into HepG2 cells, a drug susceptibility assay was performed. Quantitative real-time PCR was used for determining the amount of intracellular HBV DNA, and the effective concentration required to reduce HBV replication by 50% (EC(50)) was calculated. Results: FNC inhibited the replication of both wild-type and lamivudine-resistant HBV clinical isolates in a dose-dependent manner, with mean ±SD EC(50) values of 0.12 ±0.01 μM and 0.27 ±0.01 μM, respectively. Conclusions: FNC is a potential antiviral agent against both wild-type and lamivudine-resistant HBV clinical isolates, and therefore deserves further evaluation for the treatment of HBV infection.[3] Azvudine/FNC, a novel nucleoside analogue inhibits cell proliferation and tumor growth in a variety of human cancer cells. Inhibition of cellular DNA synthesis is a strategy to block cancer cell division. Nucleoside analogues can incorporate into DNA and terminate DNA strand elongation. So far, several nucleoside analogues have been successfully used as anticancer drugs. FNC, 2'-deoxy-2'-β-fluoro-4'-azidocytidine is a novel cytidine analogue which demonstrated potent activity against hepatitis C virus (HCV). To investigate the therapeutic potential of FNC in human cancers we studied its activity in a number of cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. [4] |
| 分子式 |
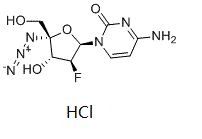
C9H12CLFN6O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
322.68078327179
|
| 精确质量 |
322.059
|
| CAS号 |
1333126-31-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Azvudine;1011529-10-4
|
| PubChem CID |
54579399
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to khaki solid powder
|
| tPSA |
123Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
21
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
533
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
Cl.F[C@@H]1[C@H](N2C(N=C(C=C2)N)=O)O[C@](CO)([C@H]1O)N=[N+]=[N-]
|
| InChi Key |
MKMLHJHSIBILJH-DBSFTZRASA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C9H11FN6O4.ClH/c10-5-6(18)9(3-17,14-15-12)20-7(5)16-2-1-4(11)13-8(16)19;/h1-2,5-7,17-18H,3H2,(H2,11,13,19);1H/t5-,6-,7+,9+;/m0./s1
|
| 化学名 |
4-amino-1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-azido-3-fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]pyrimidin-2-one;hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
Azvudine HCl; RO-0622; FNC; RO0622; Azvudine (hydrochloride); Azvudine hydrochloride; 1333126-31-0; 4-amino-1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-azido-3-fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]pyrimidin-2-one;hydrochloride; CHEMBL1822611;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~125 mg/mL (~387.38 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 14.29 mg/mL (44.29 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。 (<60°C).
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0990 mL | 15.4952 mL | 30.9905 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6198 mL | 3.0990 mL | 6.1981 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3099 mL | 1.5495 mL | 3.0990 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。