| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
阿托西班通过催产素阻止子宫肌层释放 IP3。子宫肌层细胞骶浆网释放的细胞内钙和通过电压门控通道的外部 Ca2+ 流入均减少。此外,当催产素存在时,阿托西班可以阻止蜕膜释放 PGE 和 PGF [1]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
阿托西班影响精氨酸加压素对胎儿-母体心血管和肾脏系统的生理作用。垂体后叶激素催产素和精氨酸加压素在结构上仅存在两个氨基酸的差异。一项使用阿托西班一小时的试验并未对妊娠晚期绵羊的母亲或胎儿的心血管系统造成任何变化[1]。在小鼠的臂旁核中,阿托西班抑制表达催产素受体的神经元的激活[2]。
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
In women receiving 300 μg/min by infusion for 6-12 h, average steady state concentrations of 442 ng/mL were reached within 1 h. Steady state concentrations increase proportionally to dosage. Small amounts of atosiban are found in the urine with 50 times the amount appearing as the large fragment metabolite (des-(Orn⁸, Gly⁹-NH2)-[Mpa¹, D-Tyr(Et)², Thr⁴]-oxytocin. The amount of drug excreted in the feces is not known. Atosiban has a mean volume of distribution of 41.8 L. Atosiban crosses the placenta and, at a dose of 300 μg/min, was found to have a 0.12 maternal/fetal concentration ratio. Atosiban has a mean clearance rate of 41.8 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites There are two metabolites of atosiban created through the cleavage of the peptide bond between ornithine and proline which is thought to be facilitated by prior cleavage of the disulfide bridge. The larger fragment remains active as an antagonist of oxytocin receptors but is 10 times less potent than the parent molecule. At a dosage of 300 μg/min the ratio of parent molecule to the main metabolite was observed to be 1.4 at the second hour and 2.8 at the end of infusion. Biological Half-Life Atosiban does not conform to either 1-compartment or 2-compartment kinetics. It has been determined to have an initial half life (tα) of 0.21 h and a terminal half life (tβ) of 1.7 h. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Atosiban is 46-48% bound to plasma proteins in pregnant women. It is not known to partition into red blood cells. Differences in the free fraction of drug between maternal and fetal compartments are unknown. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Sanu O, et al. Critical appraisal and clinical utility of atosiban in the management of preterm labor. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2010 Apr 26;6:191-9.
[2]. Philip J Ryan, et al. Oxytocin-receptor-expressing Neurons in the Parabrachial Nucleus Regulate Fluid Intake. Nat Neurosci. 2017 Dec;20(12):1722-1733. |
| 其他信息 |
Atosiban is an oligopeptide.
Atosiban is an inhibitor of the hormones oxytocin and vasopressin. It is used intravenously to halt premature labor. Although initial studies suggested it could be used as a nasal spray and hence would not require hospital admission, it is not used in that form. Atobisan was developed by the Swedish company Ferring Pharmaceuticals. It was first reported in the literature in 1985. Atosiban is licensed in proprietary and generic forms for the delay of imminent pre-term birth in pregnant adult women. Drug Indication Atosiban is indicated for use in delaying imminent pre-term birth in pregnant adult women with: - regular uterine contractions of at least 30 s duration at a rate of at least 4 per 30 min - a cervical dilation of 1-3cm (0-3cm for nulliparas) and effacement of at least 50% - a gestational age of 24-33 weeks - a normal fetal heart rate Tractotile is indicated to delay imminent pre-term birth in pregnant adult women with: regular uterine contractions of at least 30 seconds duration at a rate of ⥠4 per 30 minutes; a cervical dilation of 1 to 3 cm (0-3 for nulliparas) and effacement of ⥠50%; a gestational age from 24 until 33 completed weeks; a normal foetal heart rate. Atosiban is indicated to delay imminent pre-term birth in pregnant adult women with: regular uterine contractions of at least 30 seconds' duration at a rate of ⥠4 per 30 minutes; a cervical dilation of 1 to 3 cm (0-3 for nulliparas) and effacement of ⥠50%; a gestational age from 24 until 33 completed weeks; a normal foetal heart rate. Mechanism of Action Atosiban is a synthetic peptide oxytocin antagonist. It resembles oxytocin with has modifications at the 1, 2, 4, and 8 positions. The N-terminus of the cysteine residue is deaminated to form 3-mercaptopropanic acid at position 1, at position 2 L-tyrosine is modified to D-tyrosine with an ethoxy group replacing the phenol , threonine replaces glutamine at postion 4, and ornithine replaces leucine at position 8. It binds to membrane bound oxytocin receptors on the myometrium and prevents oxytocin-stimulated increases in inositol triphosphate production. This ultimately prevents release of stored calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and subsequent opening of voltage gated calcium channels. This shutdown of cytosolic calcium increase prevents contractions of the uterine muscle, reducing the frequency of contractions and inducing uterine quiescence. Atosiban has more recently been found to act as a biased ligand at oxytocin receptors. It acts as an antagonist of Gq coupling, explaining the inhibition of the inositol triphosphate pathway thought to be responsible for the effect on uterine contraction, but acts as an agonist of Gi coupling. This agonism produces a pro-inflammatory effect in the human amnion, activating pro-inflammatory signal tranducer NF-κB. It is thought that this reduces atosiban's effectiveness compared to agents which do not produce inflammation as inflammatory mediators are known to play a role in the induction of labour. Pharmacodynamics Atosiban reduces the frequency of uterine contractions to delay pre-term birth in adult females and induces uterine quiescence. |
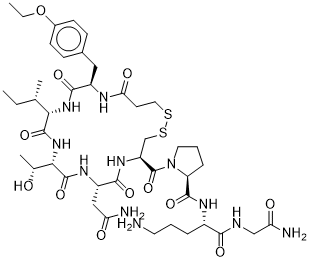
| 分子式 |
C43H67N11O12S2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
994.19
|
| 精确质量 |
993.441
|
| CAS号 |
90779-69-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Atosiban acetate;914453-95-5
|
| PubChem CID |
5311010
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
1469.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
842.2±34.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.549
|
| LogP |
-3.41
|
| tPSA |
416.27
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
11
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
15
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
18
|
| 重原子数目 |
68
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1770
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
9
|
| SMILES |
CC[C@H](C)[C@H]1C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](CSSCCC(=O)N[C@@H](C(=O)N1)CC2=CC=C(C=C2)OCC)C(=O)N3CCC[C@H]3C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCN)C(=O)NCC(=O)N)CC(=O)N)[C@@H](C)O
|
| InChi Key |
VWXRQYYUEIYXCZ-OBIMUBPZSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C43H67N11O12S2/c1-5-23(3)35-41(63)53-36(24(4)55)42(64)50-29(20-32(45)56)38(60)51-30(43(65)54-17-8-10-31(54)40(62)49-27(9-7-16-44)37(59)47-21-33(46)57)22-68-67-18-15-34(58)48-28(39(61)52-35)19-25-11-13-26(14-12-25)66-6-2/h11-14,23-24,27-31,35-36,55H,5-10,15-22,44H2,1-4H3,(H2,45,56)(H2,46,57)(H,47,59)(H,48,58)(H,49,62)(H,50,64)(H,51,60)(H,52,61)(H,53,63)/t23-,24+,27-,28+,29-,30-,31-,35-,36-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2S)-N-[(2S)-5-amino-1-[(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]-1-[(4R,7S,10S,13S,16R)-7-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-13-[(2S)-butan-2-yl]-16-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]-10-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-6,9,12,15,18-pentaoxo-1,2-dithia-5,8,11,14,17-pentazacycloicosane-4-carbonyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
Atosiban RWJ-22164 RW22164 TractocileRWJ22164 RW-22164 TractocileRWJ 22164
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~16.67 mg/mL (~16.77 mM)
DMSO : ≥ 16.67 mg/mL (~16.77 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 1.67 mg/mL (1.68 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 16.7 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 1.67 mg/mL (1.68 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 16.7mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 1.67 mg/mL (1.68 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.0058 mL | 5.0292 mL | 10.0584 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2012 mL | 1.0058 mL | 2.0117 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1006 mL | 0.5029 mL | 1.0058 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05693688 | COMPLETED | Drug: Atosiban | Preterm Birth | Academisch Medisch Centrum - Universiteit van Amsterdam (AMC-UvA) | 2017-12-01 | Phase 4 |
| NCT03570294 | COMPLETED | Drug: Atosiban | Premature Birth | Polish Mother Memorial Hospital Research Institute | 2014-02-01 | Not Applicable |
| NCT01493440 | COMPLETED | Drug: atosiban | Repeated Implantation Failure | An Sinh Hospital | 2011-03 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05382143 | UNKNOWN STATUS | Drug: Atosiban | Endometriosis | Radboud University Medical Center | 2022-02-01 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03904745 | UNKNOWN STATUS | Drug: Atosiban | Infertility, Female | Bezmialem Vakif University | 2020-12-21 | Not Applicable |
|
|