| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
5-HT1A Receptor; 5-HT2A Receptor; 5-HT2B Receptor; 5-HT2C Receptor; D2 Receptor; D3 Receptor; D4 Receptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
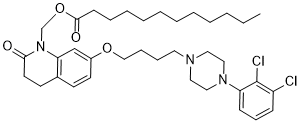
阿立哌唑月桂醇是由十二烷酸的羧基与7-{4-[4-(2,3-二氯苯基)哌嗪-1-基]丁氧基}-2-氧-3,4-二氢喹啉-1(2H)-基]甲醇的羟基缩合而成的十二烷酸酯。它是阿立哌唑的前药,用于治疗精神分裂症。它具有h1受体拮抗剂、第二代抗精神病药、血清素激动剂和前药的作用。它是十二烷酸酯、喹诺酮、二氯苯、n -芳基哌嗪、n -烷基哌嗪、芳香醚和-内酰胺。[1]
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
中间体 N-对应的阿立哌唑参与月桂酰阿立哌唑(车载产品;1.87 mg/mL)的体内生物转化。因此,根据外围数据,月桂酰阿立哌唑具有高生物转化率,导致观察到的N-对应甲基阿立哌唑的合成。当动物服用月桂酰亚立曲唑时,亚立曲唑的浓度非常高[1]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
缓冲液中体外转化[2]
为了使n -羟甲基阿立哌唑/aripiprazole lauroxil自发转化为阿立哌唑,制备了DMSO-d6的原液,将原液加入pH为7.4的磷酸盐缓冲液中,即含有0.5% v/v DMSO-d6,即可开始反应。缓冲液中n -羟甲基阿立哌唑/aripiprazole lauroxil的最终浓度为9µM,等于阿立哌唑在水中的溶解度。在25°C和37°C的连续测量中,[2] 1H NMR波谱在600.163 MHz下在配备5 mm TCI CryoProbe的Bruker AV-III-600上测量。参照DMSO-d6 (2.51 ppm)。溶剂抑制与激发雕刻使用方形180脉冲的4毫秒应用于水溶液。采集时间为1.7 s,重复延迟为3 s,傅里叶变换前进行1.0 Hz的洛伦兹线展宽,积分前对芳香区进行4次多项式拟合的基线校正。 血浆中体外转化[2] 体外实验采用三次重复,将30µL 1µM aripiprazole lauroxil溶解于乙醇中,加入雌性Sprague Dawley大鼠1.47 mL血浆中,37℃。加峰血浆在37℃下保存,在加峰后0.5和1.0 h取50µL。等分液立即用含有0.4%柠檬酸的200µL冷乙腈处理,保存在-80°C,直到按照第2.7节的描述进行分析。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Female SD (SD (Sprague-Dawley)) rats[1]
Doses: 1.87 mg/ml Route of Administration: Blood samples were collected at 5, 15, 30 minutes and 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 24 hrs (hrs (hours)) after administration. Experimental Results: Displayed clearance: 0.32 ± 0.11 L/h/kg. Formulations for the in vivo study [2] An emulsion for intravenous administration containing each of the three compounds (i.e., aripiprazole, N-hydroxymethyl-aripiprazole or aripiprazole lauroxil) in equimolar concentrations equivalent to 1 mg aripiprazole was produced. The emulsions consisted of compound, 20% w/w fractionated coconut oil, 1.2% w/w lecithin, 2% w/w glycerol and q.s. water. The amount of each compound added was 1 mg aripiprazole/mL, 1.2 mg N-hydroxymethyl-aripiprazole/mL or 1.87 mg aripiprazole lauroxil/mL, i.e., equimolar. Each of the three compounds was dissolved in the oil together with lecithin and gently heated to 50 °C with continuous stirring. Glycerol was added to the aqueous phase as an isotonic agent and the aqueous phase was heated to 50 °C. The two phases were mixed and homogenised to a pre-emulsion by rapid stirring for 1 min. The pre-emulsion was placed on ice and the droplet size was further reduced by means of a homogeniser equipped with a standard microtip at a power output of 5 (Sonifier Cell Disruptor, Model B15, Branson, Pusan, Korea) for 10 min. The formulation was then filtered through a 0.45 µm sterile filter into a sterilised glass bottle with a rubber membrane and a crimped lid. In vivo study[2] The protocol used for the in vivo study in rats was approved by the institutional animal ethics committee in accordance with Danish law regulating experiments on animals and in compliance with EC directive 2010/63/EU, and the NIH guidelines on animal welfare. Female Sprague Dawley rats, weighing 248–276 g on the day of administration, were used for the pharmacokinetic studies (n = 6 per group). The animals were acclimatised for a minimum of 5 days in groups of 2 on wooden bedding in plastic cages, 595 × 380 × 200 mm3, with a stainless steel lid in humidity- and temperature-controlled ventilation cupboards, relative humidity 40–60%, temperature 20 ± 1 °C, light from 6:00–18:00 h. The animals had free access to a standard rodent diet and water ad libitum during the study.[2] The animals were randomly assigned to three groups (n = 6 per group) receiving either aripiprazole, N-hydroxymethyl-aripiprazole or aripiprazole lauroxil molar equivalent to 5 mg aripiprazole/kg. The animals were dosed by injection into the tail vein with a submicron emulsion containing a molar concentration equivalent to 1 mg aripiprazole/mL. Blood samples of 100 µL were obtained from the lateral tail vein by individual vein puncture and collected into potassium–EDTA tubes. Samples was taken at 5, 15, 30 min and 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 24 h after administration. Plasma was harvested immediately by 10 min of centrifugation at 4 °C, 2765g and stored at -80 °C until analysed. At the end of the experiment, the animals were sacrificed. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following a single extended-release intramuscular injection of aripiprazole lauroxil, aripiprazole can be detected in the systemic circulation from 5 to 6 days and is continued to be released for an additional 36 days. The concentrations of aripiprazole increases with consecutive doses of aripiprazole lauroxil and the steady state is reached following the fourth monthly injection. The systemic exposure to aripiprazole was similar when comparing deltoid and gluteal intramuscular injections. Based on the pharmacokinetic study for aripiprazole, less than 1% of unchanged aripiprazole was excreted in the urine and approximately 18% of the oral dose was recovered unchanged in the feces. Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis, the apparent volume of distribution of aripiprazole following intramuscular injection of aripiprazole lauroxil was 268 L, indicating extensive extravascular distribution following absorption. Health human volunteer study indicates that aripiprazole crosses the blood-brain barrier. In rats, the clearance for aripiprazole lauroxil was 0.32 ± 0.11 L/h/kg following injection of aripiprazole lauroxil molar equivalent to 5 mg aripiprazole/kg. Metabolism / Metabolites Aripiprazole lauroxil is hydrolyzed to form N-hydroxymethyl-aripiprazole via esterases. N-hydroxymethyl-aripiprazole undergoes a rapid, nonenzymatic spontaneous cleavage, or water-mediated hydrolysis, to form aripiprazole, which mainly contributes to the pharmacological actions of aripiprazole lauroxil. Aripiprazole is further metabolized by hepatic CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 to form dehydro-aripiprazole, which retains some pharmacological activity. Dehydro-aripiprazole displays affinities for D2 receptors similar to aripiprazole and represents 30-40% of the aripiprazole exposure in plasma. Cytochrome P450 2D6 is subject to genetic polymorphism, which results in pharmacokinetic differences among CYP2D6 metabolizer phenotypes and dosage adjustments accordingly. Biological Half-Life The mean aripiprazole terminal elimination half-life ranged from 29.2 days to 34.9 days after every 4-week injection of aripiprazole lauroxil 441, 662 and 882 mg. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Serum protein binding of aripiprazole and its major metabolite is >99% at therapeutic concentrations, where they are primarily bound to albumin. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Aripiprazole lauroxil is a dodecanoate ester obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of dodecanoic acid with the hydroxy group of 7-{4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]butoxy}-2-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinolin-1(2H)-yl]methanol. A prodrug for aripiprazole, it is used for treatment of schizophrenia. It has a role as a H1-receptor antagonist, a second generation antipsychotic, a serotonergic agonist and a prodrug. It is a dodecanoate ester, a quinolone, a dichlorobenzene, a N-arylpiperazine, a N-alkylpiperazine, an aromatic ether and a delta-lactam.
Aripiprazole lauroxil is a long-acting injectable atypical antipsychotic drug used in the treatment of schizophrenia in adult patients. It is a prodrug of [aripiprazole], which acts as a partial agonist at the D2 and 5-HT1A receptors, and as an antagonist at the 5-HT2A receptors. Affecting about 1% of the adult population in the United States and approximately 26 million people worldwide, schizophrenia is a chronic neurological disorder that may result in impairments in cognition and executive functions. The quality of life in patients is greatly reduced due to negative health outcomes, and oftentimes the patients are faced with social stigma and discriminations. Schizophrenia is characterized by positive symptoms such as delusions, hallucinations, thought disorders, and catanoia, and negative symptoms that include social withdrawal, anhedonia, and flattening of emotional responses. D2 receptors have been the most common target for antipsychotic agents used in the treatment of schizophrenia: the positive symptoms are thought to arise from overactivity in the mesolimbic dopaminergic pathway activating D2 receptors, whereas negative symptoms may result from a decreased activity in the mesocortical dopaminergic pathway with D1 receptors predominating. In a randomized, double-blind clinical trial, treatment of aripiprazole lauroxil in adult patients with schizophrenia resulted in improvement of positive and negative symptoms scores at day 85 of treatment. Aripiprazole lauroxil was initially approved by the FDA in October 2015 under the market name Aristada for the treatment of schizophrenia. It is administered via intramuscular injection, and requires the establishment of tolerability prior to dosing in treatment-naïve patients. On July 2nd, a different formulation of aripiprazole lauroxil marketed as Aristada Initio was FDA-approved for immediate initiation of Aristada at any dose. The patients may receive Aristada Initio in combination with a single 30 mg oral dose of aripiprazole to achieve appropriate levels of aripiprazole more rapidly. Long-acting injectable aripiprazole lauroxil displayed comparable efficacy and safety to aripiprazole, and reduced dosing frequency improves patient adherence. See also: Aripiprazole (has active moiety). Drug Indication Aripiprazole lauroxil is indicated for the treatment of schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders. FDA Label Mechanism of Action The pharmacological activity of aripiprazole lauroxil is thought to be mainly mediated by its metabolite aripiprazole, and to a lesser extent, dehydro-aripiprazole. Aripiprazole functions as a partial agonist at the dopamine D2 and the serotonin 5-HT1A receptors, and as an antagonist at the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor. The desired outcome of antipsuchotic agents in schizophrenia is to inhibit dopaminergic transmission in the limbic system and enhance dopaminergic transmission in the prefrontal cortex. As a partial agonist at D2 receptors in the mesolimbic dopaminergic pathway, aripiprazole acts as a functional antagonist in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway and reduces the extent of dopaminergic pathway activity. This results in reduced positive symptoms in schizophrenia and extrapyramidal motor side effects. In contrast, aripiprazole is thought to act as a functional agonist in the mesocortical pathway, where reduced dopamine activity is seen in association with negative symptoms and cognitive impairment. Antagonism at 5-HT2A receptors by aripiprazole alleviates the negative symptoms and cognitive impairment of schizophrenia. 5-HT2A receptors are Gi/Go-coupled that upon activation, produce neuronal inhibition via decreased neuronal excitability and decreased transmitter release at the nerve terminals. In the nigrostriatal pathway, 5-HT2A regulates the release of dopamine. Through antagonism of 5-HT2A receptors, aripiprazole disinhibits the release of dopamine in the striatum and enhance the levels of the transmitters at the nerve terminals. The combined effects of D2 and 5-HT2A antagonism are thought to counteract the increased dopamine function causing increased extrapyramidal side effects. Blocking 5-HT2A receptors may also lead to the modulation of glutamate release in the mesocortical circuit, which is a transmitter that plays a role in schizophrenia. 5-HT1A receptors are autoreceptors that inhibit 5-HT release upon activation. Aripiprazole is a partial agonist at theses receptors and reduces 5-HT release; this results in potentiated dopamine release in the striatum and prefrontal cortex. It is reported that therapeutic doses of aripiprazole occupies up to 90% of brain D2 receptors in a dose-dependent manner. Apripiprazole targets different receptors that lead to drug-related adverse reactions; for example, the antagonist activity at the alpha-1 adrenergic receptors results in orthostatic hypotension. Aripiprazole's antagonism of histamine H1 receptors may explain the somnolence observed with this drug. Schizophrenia is a chronic medical condition with periods of remission and relapses over a patient's lifetime. Antipsychotic medications represent the mainstay of treatment for this disease. Long-acting injectable (LAI) formulations of antipsychotics are an attractive alternative to their oral counterparts, as they enhance patient adherence. A number of second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) are available in LAI formulations. These include paliperidone, aripiprazole, olanzapine, and risperidone. This article reviews the most recently developed and approved of these formulations-aripiprazole monohydrate, aripiprazole lauroxil, and paliperidone palmitate. While all were initially available as once-monthly formulations, a paliperidone palmitate 3-monthly injection formulation has been approved and is the first LAI agent to extend the dosing administration beyond the typical monthly time period. In addition, aripiprazole lauroxil every 6-week and 8-week administration preparations have been developed. LAI preparations of the SGAs have all demonstrated superiority over placebo and are comparable to their oral counterparts in terms of safety and tolerability, if injection site reactions are not taken into account. First-generation antipsychotic LAI preparations (e.g., haloperidol decanoate) have recently been compared with SGA LAI agents, and both formulations demonstrated comparable efficacy with the expected adverse events seen with each drug. Despite their availability, barriers to the use of LAIs remain. Education of both patients and clinicians on the use of LAI formulations and the continued development of these agents are important steps in ensuring these medications are available to the patients they would be most likely to benefit. [1] |
| 精确质量 |
659.326
|
|---|---|
| 元素分析 |
C, 65.44; H, 7.78; Cl, 10.73; N, 6.36; O, 9.69
|
| CAS号 |
1259305-29-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
129722-12-9;851220-85-4 (hydrate);1259305-26-4 (cavoxil);1259305-29-7 (lauroxil);
|
| PubChem CID |
49831411
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 熔点 |
81-83
|
| LogP |
8.743
|
| tPSA |
62.32
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
20
|
| 重原子数目 |
45
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
858
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCN1C2=C(C=CC(=C2)OCCCCN3CCN(CC3)C4=CC=CC(=C4Cl)Cl)CCC1=O
|
| InChi Key |
DDINXHAORAAYAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C36H51Cl2N3O4/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-16-35(43)45-28-41-33-27-30(19-17-29(33)18-20-34(41)42)44-26-12-11-21-39-22-24-40(25-23-39)32-15-13-14-31(37)36(32)38/h13-15,17,19,27H,2-12,16,18,20-26,28H2,1H3
|
| 化学名 |
[7-[4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]butoxy]-2-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinolin-1-yl]methyl dodecanoate
|
| 别名 |
Aripiprazole lauroxil; 1259305-29-7; Aristada; RDC-3317; ALKS 9072; Aristada initio; ALKS 9070; RDC 3317;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~8.33 mg/mL (~12.61 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.83 mg/mL (1.26 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 8.3 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04203056 | TERMINATEDWITH RESULTS | Drug: Aripiprazole Lauroxil Drug: ARI-ORAL Drug: AL-NCD |
Schizoaffective Disorder, Depressive Type Schizophrenia Schizophreniform Disorder |
University of California, Los Angeles | 2019-12-16 | Phase 4 |
| NCT02634320 | COMPLETEDWITH RESULTS | Drug: Aripiprazole Lauroxil | Schizophrenia | Alkermes, Inc | 2015-12 | Phase 4 |
| NCT02320032 | COMPLETED | Drug: Aripiprazole Lauroxil | Schizophrenia | Alkermes, Inc | 2014-12 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02636842 | COMPLETED | Drug: Aripiprazole Lauroxil | Schizoaffective Disorder Schizophrenia |
Alkermes, Inc | 2015-12 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03345979 | COMPLETEDWITH RESULTS | Combination Product: Aripiprazole Lauroxil Drug: Paliperidone Palmitate |
Schizophrenia | Alkermes, Inc | 2017-11-15 | Phase 3 |
|
|