| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
angrelide 可有效抑制骨髓巨核细胞的形成 (IC50=26 nM) [1]。一种防止骨髓巨核细胞生成的特殊药物是阿那格雷。 angrelide(0.05、0.3 和 1 µM)仅抑制巨核细胞增殖,但不抑制非巨核细胞增殖。阿那格雷导致细胞增殖重新定位到非巨核细胞区室的事实表明它不具有细胞毒性特性[2]。尽管阿那格雷仅在 GIST48 细胞系中表现出温和的作用,但它在亚微摩尔浓度 (IC50= 16 nM) 下可在 GIST882 细胞系中引起细胞毒性 [3]。在体外,阿那格雷可以减少胃肠道间质瘤(GIST)细胞的生长并增加细胞凋亡[3]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
阿那格雷在具有 KIT 外显子 9 突变的 GIST 异种移植小鼠模型中有效,这可能代表治疗问题,因为这些 GIST 需要每日大剂量的伊马替尼 [3]。阿那格雷在源自患者的小鼠异种移植模型中抑制 GIST 的发展。阿那格雷在治疗 GIST 方面具有治疗潜力。阿那格雷在胃肠道间质瘤异种移植模型中表现出抗癌功效[3]。阿那格雷(5 mg/kg/bid)可抑制或减少 GIST2B、GIST9 和 GIST882 模型中的肿瘤生长 [3]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖测定[2]
细胞类型:巨核细胞和非巨核细胞 测试浓度: 0.05、0.3、1 µM 孵育持续时间:12天 实验结果:仅在每个测试浓度下抑制巨核细胞生长 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Adult female athymic mouse GIST2B, GIST3, GIST9, GIST882 model [3]
Doses: 5 mg/kg/bid Route of Administration: 5 mg/kg/bid or combined with anagrelide and imatinib ( given simultaneously) dose and schedule as a single agent); for 10 days Experimental Results: Three of the four models (GIST2B, GIST9, GIST882) inhibited or diminished tumor growth. The most potent effect was observed in the GIST2B model, which contains the KIT exon 9 mutation leading to the p.A502_Y503 duplication. The tumor volume of this model diminished by 68% after 10 days of treatment. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following oral administration, the bioavailability of anagrelide is approximately 70%. Given on an empty stomach, the Cmax is reached within 1 hour (Tmax) of administration. Co-administration with food slightly lowers the Cmax and increases the AUC, but not to a clinically significant extent. Following metabolism, urinary excretion of metabolites appears to be the primary means of anagrelide elimination. Less than 1% of an administered dose is recovered in the urine as unchanged parent drug, while approximately 3% and 16-20% of the administered dose is recovered as 3-hydroxy anagrelide and RL603, respectively. Following oral administration of 14C-anagrelide in people, more than 70% of radioactivity was recovered in urine. The available plasma concentration time data at steady state in patients showed that anagrelide does not accumulate in plasma after repeated administration. The volume of distribution (VolD) is 12 L/kg of body weight. Limited data indicate probable dose linearly between doses of 500 mg (0.5 mg) and 2 mg. Bioavailability was found to be modestly reduced by an average of 13.8% when anagrelide was administered after food. The peak plasma level was lowered by an average of 45% and delayed by 2 hours ... when a 0.5 mg dose of anagrelide was taken after food ... For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ANAGRELIDE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Anagrelide is extensively metabolized, primarily in the liver by cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2), into two major metabolites: 6,7-dichloro-3-hydroxy-1,5 dihydro-imidazo[2,1-b]quinazolin-2-one (3-hydroxy anagrelide) and 2-amino-5,6-dichloro-3,4,-dihydroquinazoline (RL603). The 3-hydroxy metabolite is considered pharmacologically active and carries a similar potency and efficacy in regards to its platelet-lowering effects, but inhibits PDE3 with a potency 40x greater than that of the parent drug. Anagrelide is extensively metabolized; less than 1% is recovered unchanged in the urine. Biological Half-Life The t1/2 of anagrelide and its active metabolite, 3-hydroxy anagrelide, are approximately 1.5 hours and 2.5 hours, respectively. At fasting and at a dose of 0.5 mg, the plasma half-life is 1.3 hours ... . Elimination: Plasma 1.3 hours (at a dose of 0.5 mg while fasting). Note: Plasma half life was found to be increased (to 1.8 hours) when anagrelide was taken after food. Steady state plasma concentration measurements show no accumulation of anagrelide in plasma with repeated administration. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In preregistration studies, anagrelide was not associated with serum enzyme elevations or with episodes of clinically apparent liver injury. Since its approval, there has been a single published abstract reporting progressive, ultimately fatal cholestasis after liver transplantation and use of anagrelide, but there have been no other published reports of anagrelide hepatotoxicity in the literature. In large, long term follow up studies there have been occasional instances of transient serum enzyme elevations without jaundice or symptoms. The product label for anagrelide mentions abnormal enzymes as an adverse event but not clinically apparent liver injury, hepatitis or jaundice. However, the general clinical experience with anagrelide has been limited. Likelihood score: E* (unlikely, but suspected rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of anagrelide during breastfeeding. The manufacturer recommends that the drug not be used during breastfeeding and for 1 week after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Interactions Bioavailability studies evaluating possible interactions between anagrelide and other drugs have not been conducted. The most common medications used concomitantly with anagrelide have been aspirin, acetaminophen, furosemide, iron, ranitidine, hydroxyurea, and allopurinol. The most frequently used concomitant cardiac medication has been digoxin. Although drug-to-drug interaction studies have not been conducted, there is no clinical evidence to suggest that anagrelide interacts with any of these compounds. A case report has suggested that sucralfate may interfere with anagrelide absorption. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Antithrombocythemic Anagrelide is indicated for reduction of elevated platelet counts and of the risk of thrombosis, as well as for amelioration of symptoms, in patients with thrombocythemia secondary to myeloproliferative disorders. /Included in US product labeling/ Drug Warnings While most reported adverse events during anagrelide therapy have been mild in intensity and have decreased in frequency with continued therapy, serious adverse events were reported in patients with myeloproliferative diseases of varying etiology. These include the following: congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, cardiomegaly, complete heart block, atrial fibrillation, cerebrovascular accident, pericarditis, pulmonary infiltrates, pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension, pancreatitis, gastric/duodenal ulceration, and seizure. The most frequently reported adverse reactions to anagrelide (in 5% or greater of 942 patients with myeloproliferative disease) in clinical trials were: headache 43.5%; palpitations 26.1%; diarrhea 25.7%; asthenia 23.1%; edema, other 20.6%; nausea 17.1%; abdominal pain 16.4%; dizziness 15.4%; pain, other 15.0%; dyspnea 11.9%; flatulence 10.2%; vomiting 9.7%; fever 8.9%; peripheral edema 8.5%; rash, including urticaria 8.3%; chest pain 7.8%; anorexia 7.7%; tachycardia 7.5%; pharyngitis 6.8%; malaise 6.4%; cough 6.3%; paresthesia 5.9%; back pain 5.9%; pruritus 5.5%; dyspepsia 5.2%. It is recommended that patients with renal insufficiency (creatinine 2 mg/dL or greater) receive anagrelide when the potential benefits of therapy outweigh the potential risks. Monitor patients closely for signs of renal toxicity while receiving anagrelide. Use with caution in patients with known or suspected heart disease only if the potential benefits outweigh the potential risks. Because of the positive inotropic effects and side effects of anagrelide, a pretreatment cardiovascular examination is recommended along with careful monitoring during treatment. Therapeutic doses of anagrelide may cause cardiovascular effects, including vasodilation, tachycardia, palpitations, and congestive heart failure. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ANAGRELIDE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Anagrelide decreases platelet counts by suppressing transcription factors necessary for the synthesis and maturation of platelet-producing cells. The drug itself appears to have a relatively short residence time in the body necessitating twice or four times daily dosing. However, given that the pharmacological effect of anagrelide therapy is reliant on a gradual suppression of platelet-producing cells, it may take 7 to 14 days for its administration to be reflected in reduced platelet counts - for this reason any changes to anagrelide doses should not exceed 0.5 mg/day in any one week. Evidence from animal studies suggests anagrelide may impair female fertility. Female patients of reproductive age should be advised of the potential for adverse effects on fertility prior to initiating therapy. |
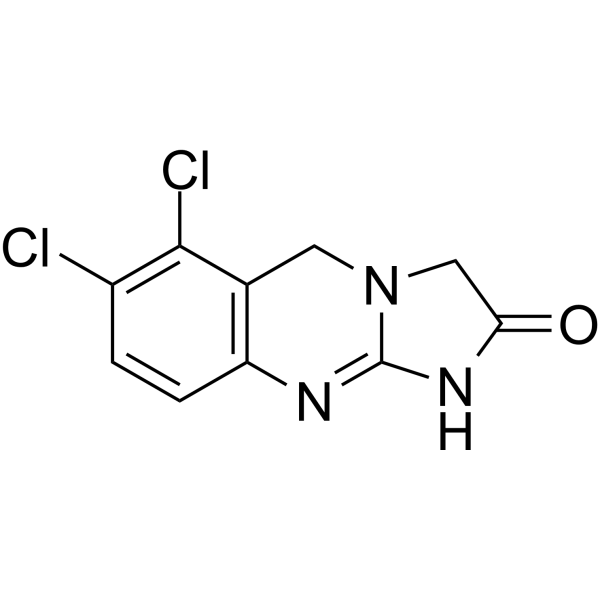
| 分子式 |
C10H7N3OCL2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
256.08808
|
| 精确质量 |
254.996
|
| CAS号 |
68475-42-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Anagrelide hydrochloride;58579-51-4;Anagrelide hydrochloride monohydrate;823178-43-4
|
| PubChem CID |
135409400
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.8±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
376.5±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
280 °C
|
| 闪点 |
181.5±30.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.791
|
| LogP |
1.96
|
| tPSA |
44.7
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
0
|
| 重原子数目 |
16
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
360
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C1N=C2NC3=C(C(Cl)=C(Cl)C=C3)CN2C1
|
| InChi Key |
OTBXOEAOVRKTNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C10H7Cl2N3O/c11-6-1-2-7-5(9(6)12)3-15-4-8(16)14-10(15)13-7/h1-2H,3-4H2,(H,13,14,16)
|
| 化学名 |
6,7-dichloro-3,5-dihydro-1H-imidazo[2,1-b]quinazolin-2-one
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.9049 mL | 19.5244 mL | 39.0488 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7810 mL | 3.9049 mL | 7.8098 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3905 mL | 1.9524 mL | 3.9049 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。