| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 25g |
|
||
| 50g |
|
||
| 100g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
阿莫西林 (Amoxycillin)(1-100 µM;24 小时;嗜酸乳杆菌)以剂量依赖性方式减少活细胞并增加细胞壁破裂程度[1]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
当大鼠给予阿莫西林剂量为 7 毫克/公斤(ih;雌性 ICR/瑞士小鼠)时,大鼠存活率会增加,并且菌株数量受到抑制[2]。
给予阿莫西林(也称为阿莫西林)的瑞士白化小鼠阿莫西林)(1.6–9.5 mg/kg;口服;每天,持续 7 或 14 天)可预防沙眼衣原体感染[3]。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal Model: Female ICR/Swiss mice[2]
Dosage: 7 mg/kg Administration: Subcutaneous injection: every eight hours for a full day Result: exhibited a dose-dependent inhibition on the number of bacteria. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Amoxicillin is approximately 60% bioavailable. A 250mg dose of oral amoxicillin reaches a Cmax 3.93±1.13mg/L with a Tmax 1.31±0.33h and an AUC of 27.29±4.72mg\*h/L. A 875mg dose of oral amoxicillin reaches a Cmax 11.21±3.42mg/L with a Tmax 1.52±0.40h and an AUC of 55.04±12.68mg\*h/L. 125mg to 1g doses of amoxicillin are 70-78% eliminated in the urine after 6 hours. The central volume of distribution of amoxicillin is 27.7L. The mean clearance of amoxicillin is 21.3L/h. ... A 48 year-old woman was admitted because of pneumococcal meningitis. After 4 days on high-dose amoxicillin (320 mg/kg/day), she developed acute oliguric renal failure and amoxicillin crystallization was documented by infrared spectrometry. The outcome was favorable after amoxicillin dosage tapering, together with one single hemodialysis session and further hydratation. Amoxicillin is mainly excreted in the urine in its unchanged form. Amoxicillin diffuses readily into most body tissues and fluids, with the exception of brain and spinal fluid, except when meninges are inflamed. In blood serum, amoxicillin is approximately 20% protein-bound. Following a 1 gram dose and utilizing a special skin window technique to determine levels of the antibiotic, it was noted that therapeutic levels were found in the interstitial fluid. Although presence of food in the GI tract reportedly results in lower and delayed peak serum concentrations of amoxicillin, the total amount of drug absorbed does not appear to be affected. Amoxicillin was studied in normal subjects after intravenous, oral, and intramuscular administration of 250-, 500-, and 1,000-mg doses. Serum drug levels were analyzed using a two-compartment open model, as well as area under the curve (AUC) and urinary recovery. The variations of these pharmacokinetic parameters were then examined using the three-way analysis of variance and linear regression equations. These results confirmed nearly complete oral absorption: AUC was 93% of intravenous absorption, and urinary recovery was 86%. The intramuscular administration of amoxicillin results in complete and reliable absorption with peak drug levels, AUCs, and urinary recovery equivalent to oral dosage. The absorption of lyophilized amoxicillin after intramuscular injection resulted in an AUC that was 92% of intravenous absorption and urinary recovery of 91%. The peak serum levels, time to peak, and other pharmacokinetic parameters for intramuscular injection were nearly identical to those for oral administration. Kinetics of both intramuscular and oral administration exhibited dose-dependent absorption (absorption rate constant, 1.3/hr for 250 mg and 0.7/hr for 1,000 mg). This resulted in relatively later and lower peak serum levels for increasing dose. Total absorption, however, showed no dose dependence, as indicated by urinary recovery and AUC, which changed by less than 10%. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for AMOXICILLIN (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Incubation with human liver microsomes has lead to the detection of 7 metabolites. The M1 metabolite has undergone hydroxylation, M2 has undergone oxidative deamination, M3 to M5 have undergone oxidation of the aliphatic chain, M6 has undergone decarboxylation, and M7 has undergone glucuronidation. Biological Half-Life The half life of amoxicillin is 61.3 minutes. The half-life of amoxicillin is 61.3 minutes. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Amoxicillin is a semi-synthetic antibiotic related to penicillin. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported in patients on penicillin therapy including amoxicillin. Although anaphylaxis is more frequent following parenteral therapy, it has occurred in patients on oral penicillins. These reactions are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity and/or a history of sensitivity to multiple allergens. There have been reports of individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity who have experienced severe reactions when treated with cephalosporins. Before initiating therapy with amoxicillin, careful inquiry should be made regarding previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins, or other allergens. If an allergic reaction occurs, amoxicillin should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. There was no evidence of any association between use of these drugs and the incidence or type of congenital malformation. There was no association with use of these drugs and intrauterine growth retardation or perinatal death, but there was a significant difference in the rate of prematurity in the users (8.9%) compared with nonusers (6.5%). ANIMAL STUDIES: Reproduction studies have been performed in mice and rats at doses up to 2000 mg/kg. There was no evidence of harm to the fetus due to amoxicillin. However, 100 ug/mL amoxicillin altered rat renal development in vitro. Prolonged use of amoxicillin might have a negative effect on bone formation around implants. Studies to detect mutagenic potential of amoxicillin alone have not been conducted; however, the following information is available from tests on a 4:1 mixture of amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate. Amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate was non-mutagenic in the Ames bacterial mutation assay, and the yeast gene conversion assay. Amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate was weakly positive in the mouse lymphoma assay. Amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate was negative in the mouse micronucleus test and in the dominant lethal assay in mice. Interactions Amoxicillin may affect the gut flora, leading to lower estrogen reabsorption and reduced efficacy of combined oral estrogen/progesterone contraceptives. Concomitant use of penicillins (e.g., amoxicillin, carbenicillin) may decrease renal clearance of methotrexate, presumably by inhibiting renal tubular secretion of the drug. Increased serum concentrations of methotrexate, resulting in GI or hematologic toxicity, have been reported in patients receiving concomitant administration of low- or high-dose methotrexate therapy with penicillins. Patients receiving methotrexate and penicillins concomitantly should be monitored carefully. Chloramphenicol, macrolides, sulfonamides, and tetracyclines may interfere with the bactericidal effects of penicillin. This has been demonstrated in vitro; however, the clinical significance of this interaction is not well documented. Probenecid decreases the renal tubular secretion of amoxicillin. Concurrent use of amoxicillin and probenecid may result in increased and prolonged blood levels of amoxicillin. For more Interactions (Complete) data for AMOXICILLIN (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Anti-Bacterial Agents Infections of the Ear, Nose, and Throat: Amoxicillin capsules are indicated in the treatment of infections due to susceptible (ONLY beta-lactamase-negative) isolates of Streptococcus species. (alpha- and beta-hemolytic isolates only), Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus spp., or Haemophilus influenzae. /Included in US product labeling/ Infections of the Genitourinary Tract: Amoxicillin capsules are indicated in the treatment of infections due to susceptible (ONLY beta-lactamase-negative) isolates of Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, or Enterococcus faecalis. /Included in US product labeling/ Infections of the Skin and Skin Structure: Amoxicillin capsules are indicated in the treatment of infections due to susceptible (ONLY beta-lactamase-negative) isolates of Streptococcus spp. (alpha- and beta-hemolytic isolates only), Staphylococcus spp., or E. coli. /Included in US product labeling/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for AMOXICILLIN (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Reproduction studies have been performed in mice and rats /and/ there was no evidence of harm to the fetus due to amoxicillin. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, amoxicillin should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. A high percentage of patients with mononucleosis who receive amoxicillin develop an erythematous skin rash. Thus amoxicillin should not be administered to patients with mononucleosis. Oral ampicillin is poorly absorbed during labor. It is not known whether use of amoxicillin in humans during labor or delivery has immediate or delayed adverse effects on the fetus, prolongs the duration of labor, or increases the likelihood of the necessity for an obstetrical intervention. Because amoxicillin is distributed into milk and may lead to sensitization of infants, the drug should be used with caution in nursing women. Because of its general safety in infants, the CDC states that amoxicillin is an option for anti-infective prophylaxis in breast-feeding women when Bacillus anthracis is known to be penicillin susceptible and there is no contraindication to maternal amoxicillin use. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for AMOXICILLIN (21 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Amoxicillin competitively inhibit penicillin binding proteins, leading to upregulation of autolytic enzymes and inhibition of cell wall synthesis. Amoxicillin has a long duration of action as it is usually given twice daily. Amoxicillin has a wide therapeutic range as mild overdoses are not associated with significant toxicity. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of anaphylaxis, _Clostridium difficile_ infections, and bacterial resistance. |
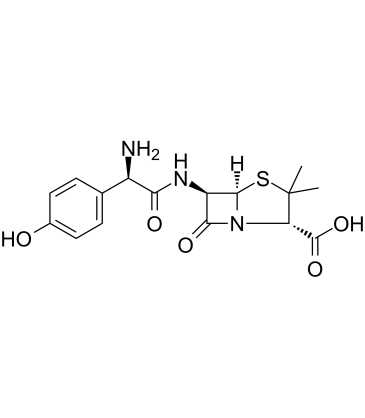
| 分子式 |
C16H19N3O5S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
365.4
|
| 精确质量 |
365.104
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 52.59; H, 5.24; N, 11.50; O, 21.89; S, 8.78
|
| CAS号 |
26787-78-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Amoxicillin sodium;34642-77-8;Amoxicillin trihydrate;61336-70-7;Amoxicillin-d4;2673270-36-3;Amoxicillin trihydrate mixture with potassium clavulanate (4:1);Amoxicillin-13C6;Amoxicillin arginine;59261-05-1
|
| PubChem CID |
33613
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder.
|
| 密度 |
1.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
701.8±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
378.2±35.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.745
|
| LogP |
0.92
|
| tPSA |
158.26
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
590
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
S1C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])[C@]([H])(C(=O)O[H])N2C([C@]([H])([C@@]12[H])N([H])C([C@@]([H])(C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])O[H])N([H])[H])=O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
LSQZJLSUYDQPKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H19N3O5S/c1-16(2)11(15(23)24)19-13(22)10(14(19)25-16)18-12(21)9(17)7-3-5-8(20)6-4-7/h3-6,9-11,14,20H,17H2,1-2H3,(H,18,21)(H,23,24)
|
| 化学名 |
(2S,5R,6R)-6-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid
|
| 别名 |
Amoxicilline Amoxicillin anhydrous Clamoxyl Amopenixin AmoxAmoxycillin; Amoxicilline; Amoxicillin anhydrous; Clamoxyl; Amopenixin; Amox
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : 73 ~83.33 mg/mL (228.05~199.78 mM)
H2O : ~2 mg/mL (~5.47 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.69 mM) 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7367 mL | 13.6836 mL | 27.3673 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5473 mL | 2.7367 mL | 5.4735 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2737 mL | 1.3684 mL | 2.7367 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Comparison of Twice- and Four-times-daily Amoxicillin Administration in 2-week Tegoprazan-based H. Pylori Eradication
CTID: NCT06431737
Phase: Status: Recruiting
Date: 2024-11-08
|
|
|