| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Topoisomerase I
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在人乳腺癌 (MCF-7)、膀胱 (MGH-U1) 和结肠 (HT-29) 癌细胞系中,9-Aminocamptothecin 的细胞毒性随着药物浓度的增加和暴露时间的延长而增加。除非 9-氨基喜树碱的浓度超过 2.7 nm 的阈值,否则也会观察到最小的细胞杀伤作用[1]。药物暴露 96 小时后,PC-3、PC-3M、DU145 和 LNCaP 细胞被 9-Aminocamptothecin 抑制,IC50 值分别为 34.1、10、6.5 和 8.9 nM[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
9-氨基喜树碱 (9-Amino-CPT) 在最低口服剂量 0.35 mg/kg/天时可抑制肿瘤生长;皮下给药(4 mg/kg/周)和更高的口服剂量(0.75 和 1 mg/kg/天)可引起肿瘤消退。 9-氨基喜树碱的所有剂量均具有良好的耐受性,并且没有一组出现中毒性死亡或体重减轻超过 10% 的情况[2]。 9-氨基喜树碱在移植人骨髓性白血病的 SCID 小鼠中,55% 的小鼠得到完全缓解。静脉注射和口服途径同样有效。在一项涉及 AML 患者的 I 期试验中,9-氨基喜树碱作为抗白血病药物的评估得到了该临床前模型获得的结果的支持[3]。
将人类急性髓性白血病细胞系KBM-3静脉注射到严重联合免疫缺陷(SCID)小鼠体内,导致这些动物出现弥散性多器官人类疾病,并导致它们在一定时间内死亡。我们利用这种人白血病模型,研究了两种不同途径给药拓扑异构酶I抑制剂9-氨基amptothecin (9-AC)的体内治疗效果。将注射KBM-3的小鼠分为五组。组1只给予稀释液,作为对照组。其余4组均给予9-AC治疗,每周4天,连续3周:2组给予1.33 mg/kg/剂,静脉注射;第3组,1.33 mg/kg/剂,口服(口服);第4组静脉注射2.0 mg/kg/次,第5组静脉注射2.0 mg/kg/次。对照组所有动物在移植后第64天死于播散性人类白血病,中位生存期为59天。在20只接受治疗的小鼠中,有11只存活下来,没有疾病迹象,并在实验第128天结束时被处死。pcr辅助组织分析人类DNA的存在没有显示人类白血病的证据。综上所述,9-AC在移植人骨髓性白血病的SCID小鼠中是一种活性剂,应该在I-II期试验中进行探索。口服和静脉注射同样有效。[3] |
| 细胞实验 |
克隆形成试验用于评估 9-amino-CPT(9-amino-20(S)-camptothecin)的细胞毒性。将指数生长的细胞重悬于培养基中后,将 100–250 个细胞一式三份接种到 60 个 15 mm 培养皿中,培养皿中装有 5 mL 培养基,并使用电子计数器确定细胞数量。将 5 μL 9-氨基喜树碱储备液添加到培养皿中,孵育过夜后达到终浓度 137、274 nM、0.27、1.37、2.74、13.7、27.4 和 0.27 nM。将新鲜培养基添加到培养皿中,并在暴露 4、8、12、24、48、72 和 240 小时后通过抽吸除去培养基。药物处理样品中的结肠与对照(DMSO 载体处理)样品中的结肠比率用于计算每个药物浓度和暴露时间下的存活百分比[1]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Mice: On the seventh day following the KBM-3 cell inoculation, 9-Aminocamptothecin treatment is initiated. The following treatment is given to five groups of five mice each, with an average weight of 22 g, four days a week for three weeks: 1) PBS is IV injected into group 1 control mice; 2) group 2 mice receive 1.33 mg/kg Group 3 mice are given 1.33 mg/kg of 9-Aminocamptothecin IV. 4) Group 4 mice receive 2.0 mg/kg of 9-Aminocamptothecin IV; 5) Group 5 mice receive 2.0 mg/kg of 9-Aminocamptothecin orally by gavage. Gavage of 9-Aminocamptothecin orally[3].
The intravenous (i.v.) injection of the human acute myelogenous leukemia cell line KBM-3 into severe combined immune deficient (SCID) mice results in disseminated multi-organ human disease involvement in these animals which leads to their death over a defined period of time. We utilized this model of human leukemia to investigate the in vivo therapeutic efficacy of the topoisomerase I inhibitor 9-aminocamptothecin (9-AC) given by two different routes. Mice injected with KBM-3 were divided into five groups. Group 1 received only diluent and served as control. The four remaining groups were treated with 9-AC four days a week for three consecutive weeks as follows: group 2 received 1.33 mg/kg/dose, i.v.; group 3, 1.33 mg/kg/dose, orally (p.o.); group 4, 2.0 mg/kg/dose i.v. and group 5, 2.0 mg/kg/dose p.o.. All animals in the control group died from disseminated human leukemia by day 64 from grafting, with a median survival of 59 days. Eleven out of 20 treated mice survived with no evidence of disease and were sacrificed at the termination of the experiment on day 128. PCR-assisted tissue analysis for the presence of human DNA showed no evidence of human leukemia. In conclusion, 9-AC is an active agent in SCID mice engrafted with human myelogenous leukemia and should be explored in phase I-II trials. Oral and intravenous routes are equally effective.[3]
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
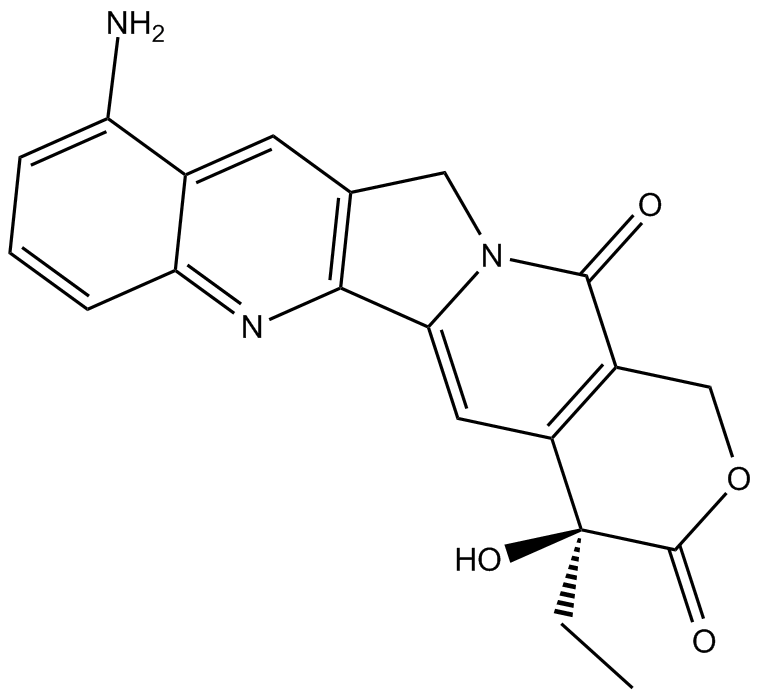
9-Aminocamptothecin is a pyranoindolizinoquinoline.
Aminocamptothecin has been used in trials studying the treatment of Lymphoma, Gastric Cancer, Ovarian Cancer, Esophageal Cancer, and Ovarian Neoplasms, among others. Aminocamptothecin is a water-insoluble camptothecin derivative. Aminocamptothecin binds to the nuclear enzyme topoisomerase I, thereby inhibiting repair of single-strand DNA breakages. Because the terminal lactone ring of aminocamptothecin required for the agent's antitumor activity spontaneously opens under physiological conditions to an inactive carboxy form, the drug must be administered over an extended period of time to achieve effective cytotoxicity. (NCI04) See also: 10-Aminocamptothecin (annotation moved to). The camptothecins are a group of anticancer agents with a unique mechanism of action: poisoning of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I. 9-aminocamptothecin (9-AC), a potent water-insoluble derivative of camptothecin, is currently undergoing clinical testing. The kinetics of the active derivative 9-AC lactone in cell culture media was defined, and then 9-AC cytotoxicity against human breast (MCF-7), bladder (MGH-U1), and colon (HT-29) cancer cell lines was studied. The relationship between cytotoxic effects, drug concentration, and exposure time was then explored. For all of the three cell lines, 9-AC cytotoxicity increased with both higher drug concentrations and longer exposure times. However, when the duration of exposure was less than 24 h, cytotoxicity was limited and less than 1 log of cell killing occurred, even with very high drug concentrations. Minimal cell killing was also observed unless 9-AC concentrations exceeded a threshold of 2.7 nM. No fixed relationship between the survival fraction and the area under the drug concentration-time curve could be modeled that would fit all of the three cell lines. However, data for the three cell lines from the multiple exposure time experiments were fitted very well to the pharmacodynamic model C(n)t = k (r2, 0.90-0.99), where C is the drug concentration, n is the drug concentration coefficient, and t is the exposure time. For the three cell lines, to kill 1 log of cells, 0.30 < n < 0.85, which indicated that duration of exposure was more important than concentration. Our data support the use of 9-AC by infusion for 24 h or longer in clinical studies providing target plasma concentrations can be achieved.[1] 9-Aminocamptothecin (9-AC) is a topoisomerase I inhibitor currently being developed as an antineoplastic agent. The aim of these preclinical studies was to assess the activity of 9-AC against prostate cancer, a malignancy notoriously insensitive to most cytotoxic agents in the clinic. The activity of 9-AC was first tested in vitro against one hormone-sensitive (LNCaP) and three hormone-resistant (PC-3, PC-3M, and DU145) human prostate cancer cell lines. After 96 h of drug exposure, concentrations required to inhibit cell viability to 50% of control values (IC50s) were 34.1, 10, 6.5, and 8.9 nm for PC-3, PC-3M, DU145, and LNCaP, respectively. Because 9-AC is known to undergo rapid hydrolysis, we assayed lactone levels in tissue culture medium over 24 h and found that the half-life was 20 min, with only 15%of the drug remaining as lactone at steady state. Consequently, the IC50s calculated from a single dose of the drug may represent overestimates. Subsequently, we tested the activity of a colloidal dispersion formulation of 9-AC against PC-3 implanted into flanks of nude mice. 9-AC was given for a total of 3 weeks by daily oral gavage (excluding weekends) or by twice weekly s.c. injections. 9-AC inhibited tumor growth at the lowest oral dose (0.35 mg/kg/day), whereas higher oral doses (0.75 and 1 mg/kg/day) and s.c. administration (4 mg/kg/week) caused tumor regression. 9-AC was well tolerated at all doses, with no toxic death or weight loss of more than 10% observed in any group. Finally, we considered that the activity of 9-AC seen in the mouse xenograft model might be explained, in part, by the relatively acidic tumor microenvironment, which would favor the formation of the more potent lactone. Simultaneous determination of plasma and tumor 9-AC lactone concentrations confirmed this hypothesis. Taken together, these studies suggest that 9-AC should be submitted for clinical trials in patients with prostate cancer.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C20H17N3O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
363.36668
|
| 精确质量 |
363.121
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 66.11; H, 4.72; N, 11.56; O, 17.61
|
| CAS号 |
91421-43-1
|
| PubChem CID |
72402
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to brown solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
819.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
449.5±34.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.771
|
| LogP |
0.44
|
| tPSA |
107.44
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
27
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
775
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
C([C@]1(C(=O)OCC2C(N3CC4C=C5C(N)=CC=CC5=NC=4C3=CC1=2)=O)O)C
|
| InChi Key |
FUXVKZWTXQUGMW-FQEVSTJZSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H17N3O4/c1-2-20(26)13-7-16-17-10(6-11-14(21)4-3-5-15(11)22-17)8-23(16)18(24)12(13)9-27-19(20)25/h3-7,26H,2,8-9,21H2,1H3/t20-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(19S)-8-amino-19-ethyl-19-hydroxy-17-oxa-3,13-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.02,11.04,9.015,20]henicosa-1(21),2,4,6,8,10,15(20)-heptaene-14,18-dione
|
| 别名 |
9AC; 9aminoCPT; 9-amino-20-camptothecin; 9-amino-camptothecin; 9-AC9-amino-CPT; 9-amino-20(S)-camptothecin; 9aminocamptothecin; Aminocamptothecin
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~3.3 mg/mL (~9.2 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.33 mg/mL (0.91 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 3.3 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.33 mg/mL (0.91 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 3.3 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入 900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.33 mg/mL (0.91 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7520 mL | 13.7601 mL | 27.5202 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5504 mL | 2.7520 mL | 5.5040 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2752 mL | 1.3760 mL | 2.7520 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00002671 | Completed | Drug: aminocamptothecin | Ovarian Cancer | Ovarian Cancer | December 1995 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00002635 | Completed | Drug: aminocamptothecin Biological: filgrastim |
Lymphoma | Yale University | May 1995 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00003192 | Completed | Drug: aminocamptothecin | Esophageal Cancer Gastric Cancer |
University of Chicago | March 1998 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00002745 | Completed | Drug: aminocamptothecin | Lymphoma | National Cancer Institute (NCI) | April 1996 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00003523 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: aminocamptothecin colloidal dispersion |
Primary Peritoneal Cavity Cancer Ovarian Cancer |
Gynecologic Oncology Group | January 1999 | Phase 2 |