| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
HSP90 (IC50 = 62 nM); GRP94 (IC50 = 65 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Alvespimycin (17-DMAG) 的 EC50 为 62 nM,使其成为 Hsp90 的有效抑制剂。过度表达 Hsp90 客户蛋白 Her2 的人类癌细胞系 SKBR3 和 SKOV3 的生长会受到阿维斯匹霉素 (17-DMAG) 的抑制。这导致 Her2 下调和 Hsp70 诱导,这与 Hsp90 抑制一致。在 SKBR3 和 SKOV3 细胞中,Her2 降解的 EC50 值分别为 8 ± 4 nM 和 46 ± 24 nM,而 Hsp70 诱导的 EC50 值分别为 4 ± 2 nM 和 14 ± 7 nM[1]。与载体对照相比,在浓度范围为 50 nM 至 500 nM(对应于药理学可达到的剂量)时,Alvespimycin (17-DMAG) 显示剂量依赖性细胞凋亡(24 小时和 48 小时时间点的平均值 P<0.001)。在长期暴露 24 至 48 小时后,Alvespimycin (17-DMAG) 在慢性淋巴细胞白血病 (CLL) 细胞中表现出时间依赖性细胞凋亡(P <0.001,所有剂量的平均值),这与许多其他药物的效果相当。治疗 24 小时和 48 小时后,Alvespimycin (17-DMAG) 的效力也显着高于 17-AAG[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
肿瘤生长两个月,然后开始腹膜内注射 (ip),持续一个月,使用 0、5、10 和 20 mg/kg Alvespimycin (17-DMAG) 或 0、50、100 和200 mg/kg 二棕榈酰根自由基。尽管样本异质性,但接受 HSP90 抑制剂治疗的动物的肿瘤体积比接受载体对照治疗的动物小得多。在胃肠道癌症动物模型中,HSP90 抑制剂已被证明会引起肝毒性。然而,在 100 mg/kg 剂量下,二棕榈酰根赤霉素以统计学上显着的方式减小了肿瘤大小,而在 10 或 20 mg/kg 剂量下,阿维螺旋霉素 (17-DMAG) 也显着减小了肿瘤大小[3]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
竞争结合测定。[1]
从HeLa细胞(SPP-770)和重组犬Grp94(SPP-766)中分离的天然人Hsp90蛋白(α+β异构体)购自Stressgen Biotechnologies。基于FP的结合测定的程序改编自Chiosis及其同事所描述的程序。42,43 BODIPY-AG溶液在FP测定缓冲液(20mM HEPES−KOH,pH 7.3,1.0mM EDTA,100mM KCl,5.0mM MgCl2,0.01%NP-40,0.1mg/mL新鲜牛γ-球蛋白(BGG),1.0mM新鲜DTT和完全蛋白酶抑制剂)中从DMSO的储备溶液中新鲜制备。通过在384孔微孔板中混合等体积(10μL)的BODIPY-AG溶液和连续稀释的人Hsp90(或Grp94)溶液获得结合曲线,得到10nM的BODIPY-AG、不同浓度的Hsp90和0.05%DMSO。在30°C下孵育3小时后,在EnVision 2100多标签板读取器上测量荧光各向异性(λEx=485 nm,λEm=535 nm)。通过混合每种含有BODIPY-AG和Hsp90(或Grp94)的溶液10μL,以及从DMSO中的储备溶液在FP测定缓冲液中新制备的每种化合物的连续稀释,获得竞争曲线。最终浓度为10 nM BODIPY-AG、40或60 nM Hsp90(或Grp94)、不同浓度的每种化合物(0.10 nM−10μM)和≤0.25%二甲基亚砜。由于化合物(1−3)a在中性pH下易于氧化,因此在氮气氛下,在LabMaster手套箱(M.Braun,Stratham,NH)中与醌类化合物(1–3)b平行进行这些化合物的测定。通常,将Hsp90蛋白溶液和化合物储备溶液作为冷冻液体放入手套箱中,并在FP测定缓冲液中制备结合混合物,该缓冲液通过重复的抽空和氩气冲洗循环脱氧。孵育后,将微孔板从手套箱中取出,并立即测量荧光各向异性。有趣的是,BODIPY-AG与Hsp90的结合导致荧光各向异性(FA)和强度的同时增加,而与Grp94的结合使荧光强度的变化相对较小。为每个结合或竞争曲线收集三份数据点。竞争结合曲线由四参数逻辑函数拟合[1]。 17-AAG与Hsp90(配合物)的分离。[1] 使用旋转柱测定法测定1b在细胞裂解物中从纯化的人Hsp90蛋白或Hsp90复合物的解离速率。[烯丙基氨基-3H]-17-AAG(20 Ci/mmol,HPLC纯度≥97%)购自商业。在真空下干燥200μCi(10nmol)的[3H]-17-AAG在乙醇中,并与30nmole的未标记1b在DMSO中混合,得到1mM[3H]-17AAG的储备溶液,SA为3×106−4×106 cpm/nmol。结合反应在测定缓冲液(20mM HEPES−KOH,pH 7.3,1.0mM EDTA,100mM KCl,5.0mM MgCl2,0.01%NP-40,1.0mM新鲜DTT和完全蛋白酶抑制剂)中含有400 nM Hsp90、4.0μM[3H]-17-AAG和0.38 mg/mL BGG。牛γ-球蛋白仅作为纯化的Hsp90蛋白的载体蛋白。或者,使用来自正常人真皮成纤维细胞(NHDF,5.0mg/mL总蛋白)或乳腺癌症细胞系SKBR3(1.5mg/mL)的细胞裂解物(如Kamal等人20所述制备)代替纯化的Hsp90蛋白。在37°C下孵育≥2小时后,将65μL的结合反应依次通过两个Zeba脱盐旋转柱以去除未结合的配体。在解离反应(650μL)中,用未标记的1b稀释含有结合[3H]-17-AAG的脱盐蛋白质溶液,以在测定缓冲液中得到约40 nM Hsp90、40μM 17-AAG和0.48 mg/mL BGG的最终浓度。类似地,用最终浓度为20μM的1b将脱盐的细胞裂解物稀释10倍。未标记的17-AAG以超过Hsp90≥1000倍的量存在,以确保[3H]-17-AAG的解离实际上是不可逆的。在不同的孵育时间(37°C),取出60μL的解离反应,并依次通过两个Zeba旋转柱。在MicroBeta微板闪烁计数器上分析流通部分。离解动力学用单指数函数a=A0×exp-kt+a∞拟合,得到一阶速率常数k。 |
| 细胞实验 |
MTT 测定用于测量细胞毒性。将阿维斯匹霉素、17-AAG 或载体与来自 CLL 患者的总共 1×106 CD19 选择的 B 细胞一起孵育 24 或 48 小时。添加MTT试剂后,将板再孵育24小时,然后进行分光光度测量。使用碘化丙啶 (PI) 和膜联蛋白 V-异硫氰酸荧光素染色可鉴定细胞凋亡。将细胞暴露于药物中,然后在磷酸盐缓冲盐水中清洗,并在结合缓冲液中染色一次。使用流式细胞术评估细胞死亡。 System II 软件包用于分析数据。对于每个样本,计数一万个细胞。通过用亲脂性阳离子染料 JC-1 染色并使用流式细胞术分析结果来评估线粒体膜电位的变化[2]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Mice: The mice used are CB-17/IcrHsd-Prkdc-SCID young male mice. A collagen solution is mixed with 1×105 BPH1 cells and 2.5×105 CAF per graft to create recombinant xenografts, which are then left to gel, covered with medium, and cultured for an entire night. The tumors are given eight weeks to form before being treated for four weeks with intraperitoneal injections of compounds in sesame oil every four days. The three different doses of dipalmitoyl-radicicol (50, 100, and 200 mg/kg) and Alvespimycin (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg) are administered. The mice are killed after a total of 12 weeks, their kidneys removed, the grafts cut in half, and their photos taken before the tissue is processed for histology. The measurements of the graft are taken, and the volume of the resulting tumor is computed using the formula volume=width × length × depth × π/6. This formula understates the volume of large, invasive tumors when compared to smaller, non-invasive tumors, suggesting a cautious approach to evaluating tumor volumes. Grafts that have been removed are embedded in paraffin, fixed in 10% formalin, and then subjected to immunohistochemistry.
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Increasing concentration of the drug results in dose-proportional increase in the plasma concentration. At the maximum tolerated dose of 80mg/m^2, the plasma concentration exceeded 63nM (mean IC50 for 17-DMAG in the NCI 60 human tumor cell line panel) for less than 24 hours in all patients. The mean peak concentration (Cmax) reached 2680 nmol/L at this dose. Mainly renal and biliary elimination pathways. In a mice study, the excreted urine 24 hours post-dose recovered 10.6–14.8% of delivered dose unchanged. At the maximum tolerated dose of 80mg/m^2, the mean Vd value is 385 L. The mean clearance is 18.9 L/hr at the dose of 80mg/m^2. Metabolism / Metabolites Alvespimycin demonstrates redox cycling catalyzed by purified human cytochrome P450 reductase (CYP3A4/3A5) to quinones and hydroquinones. It could also form glutathione conjugates at the 19-position on the quinone ring. However in vivo and in vitro studies suggest that weak metabolism of alvespimysin occurs in humans. Biological Half-Life The half-life across all dose levels ranged from 9.9 to 54.1 h (median, 18.2 h). |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Reported to be minimal. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
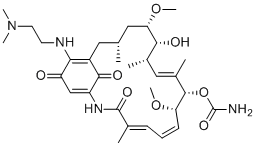
Alvespimycin is a 19-membered macrocyle that is geldanamycin in which the methoxy group attached to the benzoquinone moiety has been replaced by a 2-(N,N-dimethylamino)ethylamino group. It has a role as a Hsp90 inhibitor. It is a secondary amino compound, a tertiary amino compound, an ansamycin, a member of 1,4-benzoquinones and a carbamate ester. It is functionally related to a geldanamycin.
Alvespimycin is a derivative of geldanamycin and heat shock protein (HSP) 90 inhibitor. It has been used in trials studying the treatment of solid tumor in various cancer as an antitumor agent. In comparison to the first HSP90 inhibitor tanespimycin, it exhibits some pharmacologically desirable properties such as reduced metabolic liability, lower plasma protein binding, increased water solubility, higher oral bioavailability, reduced hepatotoxicity and superior antitumor activity. Alvespimycin has been reported in Cullen corylifolium and Trichosanthes kirilowii with data available. Alvespimycin is an analogue of the antineoplastic benzoquinone antibiotic geldanamycin. Alvespimycin binds to HSP90, a chaperone protein that aids in the assembly, maturation and folding of proteins. Subsequently, the function of Hsp90 is inhibited, leading to the degradation and depletion of its client proteins such as kinases and transcription factors involved with cell cycle regulation and signal transduction. Drug Indication Investigated for use as an antineoplastic agent for solid tumors, advanced solid tumours or acute myeloid leukaemia. Mechanism of Action Alvespimycin inhibits HSP90 and its regulation of correct folding and function of many cellular signalling proteins, which are referred to as Hsp90 client proteins. These client proteins are also referred to as oncoproteins and include Her-2, EGFR, Akt, Raf-1, p53, Bcr-Abl, Cdk4, Cdk6 and steroid receptors that are involved in cellular signalling pathways that drive cellular proliferation and counteract apoptosis. They are often over-expressed or mutated in tumors, and contribute to cancer progression and therapy resistance. Alvespimycin promotes an anticancer activity by disrupting Hsp90's chaperone function and inducing the proteasomal degradation of oncoproteins. It is shown to reduce the levels of CDK4 and ERBB2. Pharmacodynamics Alvespimycin mediates an antitumor activity through HSP90 inhibition that targets client proteins for proteasomal destruction, including oncogenic kinases such as BRAF. The administration of the drug is shown to result in the depletion of client proteins that have oncogenic activity and potential induction of HSP70 (HSP72). It is more selective for tumors over normal tissue. A study also reports that alvespimycin enhances the potency of telomerase inhibition by imetelstat in pre-clinical models of human osteosarcoma. |
| 分子式 |
C32H48N4O8
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
616.756
|
| 精确质量 |
616.347
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 62.32; H, 7.84; N, 9.08; O, 20.75
|
| CAS号 |
467214-20-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Alvespimycin hydrochloride;467214-21-7
|
| PubChem CID |
5288674
|
| 外观&性状 |
Pale purple to purple solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
810.5±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
444.0±34.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±6.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.566
|
| LogP |
2.07
|
| tPSA |
169.52
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
44
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1230
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
6
|
| SMILES |
O(C([H])([H])[H])[C@]1([H])[C@@]([H])([C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])=C(C([H])([H])[H])[C@@]([H])([C@]([H])(C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])([H])[H])C(N([H])C2=C([H])C(C(=C(C2=O)C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C1([H])[H])N([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)=O)OC([H])([H])[H])OC(N([H])[H])=O)O[H] |c:16,31,t:27|
|
| InChi Key |
KUFRQPKVAWMTJO-LMZWQJSESA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C32H48N4O8/c1-18-14-22-27(34-12-13-36(5)6)24(37)17-23(29(22)39)35-31(40)19(2)10-9-11-25(42-7)30(44-32(33)41)21(4)16-20(3)28(38)26(15-18)43-8/h9-11,16-18,20,25-26,28,30,34,38H,12-15H2,1-8H3,(H2,33,41)(H,35,40)/b11-9-,19-10+,21-16+/t18-,20+,25+,26+,28-,30+/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
[(4E,6Z,8S,9S,10E,12S,13R,14S,16R)-19-[2-(dimethylamino)ethylamino]-13-hydroxy-8,14-dimethoxy-4,10,12,16-tetramethyl-3,20,22-trioxo-2-azabicyclo[16.3.1]docosa-1(21),4,6,10,18-pentaen-9-yl] carbamate
|
| 别名 |
17-DMAG; KOS 1022; KOS-1022; KOS1022; Alvespimycin
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.03.00
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~100 mg/mL (~162.1 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 +5% Tween-80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80+,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6214 mL | 8.1069 mL | 16.2138 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3243 mL | 1.6214 mL | 3.2428 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1621 mL | 0.8107 mL | 1.6214 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00089362 | Completed | Other: pharmacological study Other: laboratory biomarker analysis |
Male Breast Cancer Recurrent Melanoma |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
July 2004 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00089271 | Completed | Other: laboratory biomarker analysis Drug: alvespimycin hydrochloride |
Intraocular Lymphoma Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
July 2004 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00803556 | Completed | Drug: Alvespimycin Drug: Trastuzumab |
Solid Tumor Breast Cancer |
Bristol-Myers Squibb | January 2006 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00088868 | Completed | Drug: alvespimycin hydrochloride | Lymphoma Small Intestine Cancer |
National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
June 2004 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00780000 | Terminated | Drug: Alvespimycin | Breast Cancer | Bristol-Myers Squibb | April 2008 | Phase 2 |