| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Rapidly absorbed orally with greater than 60% bioavailability. Peak plasma levels are attained 1 to 3 hours following oral administration. Mostly via the kidney as metabolites The volume of distribution at steady-state appeared to be significantly dose dependent: 78 ml/kg for doses < or = 20 microg/kg and 88 ml/kg for doses > 20 microg/kg respectively ACENOCOUMAROL IS LARGELY EXCRETED BY KIDNEYS, IN UNCHANGED FORM. Rats received sc 1 mg doses of the R- or S-enantiomers of acenocoumarol and biliary and urinary excretion patterns were studied. In 24 hr, 50% biliary and 20% urinary excretion was observed with no gross differences in metabolic pattern or amount of metabolites. Slight differences due to stereochemistry are /noted/. Metabolism / Metabolites Extensively metabolized in the liver via oxidation forming two hydroxy metabolites and keto reduction producing two alcohol metabolites. Reduction of the nitro group produces an amino metabolite which is further transformed to an acetoamido metabolite. Metabolites do not appear to be pharmacologically active. Extensively metabolized in the liver via oxidation forming two hydroxy metabolites and keto reduction producing two alcohol metabolites. Reduction of the nitro group produces an amino metabolite which is further transformed to an acetoamido metabolite. Metabolites do not appear to be pharmacologically active. Route of Elimination: Mostly via the kidney as metabolites Half Life: 8 to 11 hours. Biological Half-Life 8 to 11 hours. 8 to 11 hours. Acenocoumarol has a short half-life of 10 to 24 hours. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Acenocoumarol is not approved for marketing in the United States by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, but is available in Canada and other countries. Because of the low levels of acenocoumarol in breastmilk, amounts ingested by the infant are small. No changes in coagulation measurements or adverse reactions in breastfed infants have been reported from maternal acenocoumarol use during lactation. There is a consensus that maternal acenocoumarol therapy during breastfeeding poses little risk to the breastfed infant. No special precautions are necessary. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Nineteen infants were breastfed (extent not stated) while their mothers were anticoagulated with acenocoumarol immediately postpartum. Despite not receiving prophylactic vitamin K at birth, none of the infants had abnormal blood clotting as measured by the Thrombotest after at least 5 days of maternal therapy. Seven infants were exclusively breastfed by mothers who were receiving long-term anticoagulation with acenocoumarol for thromboprophylaxis following heart valve replacement. All women were therapeutically anticoagulated and receiving an average of 21 mg of acenocoumarol per week (range 12 to 45 mg per week). Each infant received 1 mg of vitamin K prophylactically at birth and had their prothrombin time measured after at least 7 days of breastfeeding. The prothrombin times of the infants was not different from those of a control group of 42 breastfed infants whose mothers were not anticoagulated. No instances of bleeding were reported. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding 98.7% protein bound, mainly to albumin |
| 其他信息 |
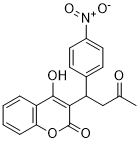
Acenocoumarol is a hydroxycoumarin that is warfarin in which the hydrogen at position 4 of the phenyl substituent is replaced by a nitro group. It has a role as an anticoagulant and an EC 1.6.5.2 [NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone)] inhibitor. It is a C-nitro compound, a hydroxycoumarin and a methyl ketone.
Acenocoumarol is a coumarin derivative used as an anticoagulant. Coumarin derivatives inhibit the reduction of vitamin K by vitamin K reductase. This prevents carboxylation of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, II, VII, IX and X, and interferes with coagulation. Hematocrit, hemoglobin, international normalized ratio and liver panel should be monitored. Patients on acenocoumarol are prohibited from giving blood. Acenocoumarol is a 4-hydroxycoumarin derivative with anticoagulant activity. As a vitamin K antagonist, acenocoumarol inhibits vitamin K epoxide reductase, thereby inhibiting the reduction of vitamin K and the availability of vitamin KH2. This prevents gamma carboxylation of glutamic acid residues near the N-terminals of the vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, including factor II, VII, IX, and X and anticoagulant proteins C and S. This prevents their activity and thus thrombin formation. Compared to other coumarin derivatives, acenocoumarol has a short half-life. Acenocoumarol is a coumarin derivative used as an anticoagulant. Coumarin derivatives inhibit the reduction of vitamin K by vitamin K reductase. This prevents carboxylation of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, II, VII, XI and X, and interferes with coagulation. Hematocrit, hemoglobin, international normalized ratio and liver panel should be monitored. Patients on acenocoumarol are prohibited from giving blood. A coumarin that is used as an anticoagulant. Its actions and uses are similar to those of WARFARIN. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p233) Drug Indication For the treatment and prevention of thromboembolic diseases. More specifically, it is indicated for the prevention of cerebral embolism, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, thromboembolism in infarction and transient ischemic attacks. It is used for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and myocardial infarction. Mechanism of Action Acenocoumarol inhibits vitamin K reductase, resulting in depletion of the reduced form of vitamin K (vitamin KH2). As vitamin K is a cofactor for the carboxylation of glutamate residues on the N-terminal regions of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, this limits the gamma-carboxylation and subsequent activation of the vitamin K-dependent coagulant proteins. The synthesis of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors II, VII, IX, and X and anticoagulant proteins C and S is inhibited resulting in decreased prothrombin levels and a decrease in the amount of thrombin generated and bound to fibrin. This reduces the thrombogenicity of clots. The oral anticoagulants block the regeneration of reduced vitamin K and thereby induce a state of functional vitamin K deficiency. The mechanism of the inhibition of reductase(s) by the coumarin drugs is not known. There exist reductases that are less sensitive to these drugs but that act only at relatively high concentrations of oxidized vitamin K; this property may explain the observation that administration of sufficient vitamin K can counteract even large doses of oral anticoagulants. /Oral Anticoagulants/ Both 4-hydroxycoumarin derivatives and indandiones (also known as oral anticoagulants) are antagonists of vitamin K. Their use as rodenticides is based on the inhibition of the vitamin K-dependent step in the synthesis of a number of blood coagulation factors. The vitamin K-dependent proteins ...in the coagulation cascade... are the procoagulant factors II (prothrombin), VII (proconvertin), IX (Christmas factor) and X (Stuart-Prower factor), and the coagulation-inhibiting proteins C and S. All these proteins are synthesized in the liver. Before they are released into the circulation the various precursor proteins undergo substantial (intracellular) post-translational modification. Vitamin K functions as a co-enzyme in one of these modifications, namely the carboxylation at well-defined positions of 10-12 glutamate residues into gamma-carboxyglutamate (Gla). The presence of these Gla residues is essential for the procoagulant activity of the various coagulations factors. Vitamin K hydroquinone (KH2) is the active co-enzyme, and its oxidation to vitamin K 2,3-epoxide (KO) provides the energy required for the carboxylation reaction. The epoxide is than recycled in two reduction steps mediated by the enzyme KO reductase... . The latter enzyme is the target enzyme for coumarin anticoagulants. Their blocking of the KO reductase leads to a rapid exhaustion of the supply of KH2, and thus to an effective prevention of the formation of Gla residues. This leads to an accumulation of non-carboxylated coagulation factor precursors in the liver. In some cases these precursors are processed further without being carboxylated, and (depending on the species) may appear in the circulation. At that stage the under-carboxylated proteins are designated as descarboxy coagulation factors. Normal coagulation factors circulate in the form of zymogens, which can only participate in the coagulation cascade after being activated by limited proteolytic degradation. Descarboxy coagulation factors have no procoagulant activity (i.e. they cannot be activated) and neither they can be converted into the active zymogens by vitamin K action. Whereas in anticoagulated humans high levels of circulating descarboxy coagulation factors are detectable, these levels are negligible in warfarin-treated rats and mice. /Anticoagulant rodenticides/ |
| 分子式 |
C19H15NO6
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
353.33
|
| 精确质量 |
353.089
|
| CAS号 |
152-72-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Acenocoumarol-d5;1185071-64-0;Acenocoumarol-d4
|
| PubChem CID |
54676537
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
592.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
196-199ºC
|
| 闪点 |
312.3±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.656
|
| LogP |
3.15
|
| tPSA |
113.33
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
614
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
VABCILAOYCMVPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H15NO6/c1-11(21)10-15(12-6-8-13(9-7-12)20(24)25)17-18(22)14-4-2-3-5-16(14)26-19(17)23/h2-9,15,22H,10H2,1H3
|
| 化学名 |
4-hydroxy-3-[1-(4-nitrophenyl)-3-oxobutyl]chromen-2-one
|
| 别名 |
SintromG-23350SinthromeAcenocoumarinNicoumalone
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~283.02 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.08 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.08 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.89 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8302 mL | 14.1511 mL | 28.3022 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5660 mL | 2.8302 mL | 5.6604 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2830 mL | 1.4151 mL | 2.8302 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03015025 | Completed | Genetic: Acenocoumarol | Atrial Fibrillation Venous Thromboses |
Instituto de Investigación Hospital Universitario La Paz |
October 2011 | |
| NCT01851824 | Completed | Drug: acenocoumarol Drug: vemurafenib |
Malignant Melanoma, Neoplasms | Hoffmann-La Roche | August 2013 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01631877 | Withdrawn | Drug: Enoxaparin with acenocoumarol Other: placebo |
Portal Vein Thrombosis | Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences, India |
June 2012 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05515120 | Completed | Drug: Aspirin 300mg Drug: Acenocoumarol Oral Tablet |
Venous Thromboembolism Anticoagulant-induced Bleeding |
Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social | January 3, 2021 | Phase 2 Phase 3 |