| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Bcl-xL (Ki = 0.01 nM); Bcl-W (Ki = 4 nM); Bcl-2 (Ki = 6 nM); Mcl-1 (Ki = 142 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
A-1331852 作为单一药物以及与 TKI 联合使用,在杀死原代 CD34+ CML 细胞方面均表现出显着的效力。此外,它在低纳摩尔浓度处理后 1 小时内就具有诱导这些细胞凋亡的显着能力[2]。
在这项研究中,研究人员描述了A-1331852的发现,这是一种一流的口服活性BCL-XL抑制剂,可选择性和有效地诱导BCL-XL依赖性肿瘤细胞的凋亡。该分子是通过使用基于结构的药物设计重新设计我们之前报道的BCL-XL抑制剂A-1155463而产生的。关键的设计元素包括A-1155463药效团的刚性化,以及在BCL-XL的关键P4口袋内引入能够产生高效相互作用的富含sp3的部分。此后,A-1331852被用作进一步探索BCL-2家族蛋白质生物学的关键工具分子,同时也是药物发现计划的一个有吸引力的入口 A-1331852(13)对MOLT-4细胞的杀伤效力相对于环己烷12提高了10至30倍,同时保持了对RS4的选择性;11细胞系。因此,A-1331852(13)对MOLT-4细胞系表现出6nM的EC50,其体外疗效水平比我们之前公开的工具化合物A-1155463(1)强20倍。Reference: ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020 Oct 8; 11(10): 1829–1836. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7549103/ |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
作为单一药物,A-1331852 在 Molt-4 异种移植模型中诱导肿瘤消退,证明了抗肿瘤功效[1]。
口服生物可利用的BCL-XL选择性抑制剂A-1331852可增强多西他赛的体内疗效[1] 研究人员评估了选择性BCL-XL抑制剂在体内增强多西他赛疗效的能力。为此,我们使用基于结构的设计来产生A-1331852(图4A),这是一种具有口服生物利用度的BCL-XL选择性抑制剂。A-1331852是一种强效的BCL-XL抑制剂,结合BCL-XL的Ki值<0.010 nM,其细胞活性分别比A-1155463和navitoclax强10至50倍(表1)。该分子选择性地破坏BCL-XL-BIM复合物,并诱导BCL-XL-依赖性Molt-4细胞凋亡的标志,其中位抑制浓度(IC50)值在低纳摩尔范围内(图4,B至E和表1),但不影响缺乏BAK或BAX的MEF细胞(图S5)。此外,A-1331852在Molt-4异种移植物模型中显示出抗肿瘤功效,作为单一药物诱导肿瘤消退(图4F)。此外,A-1331852与venetoclax联合使用,概括了navitoclax在NCI-H1963.FP5小细胞肺癌异种移植物模型中的疗效(图4G),从而为图2(B和D)所示的联合研究提供了体内证实。[1] 在包括乳腺癌症、NSCLC和癌症在内的七种实体瘤皮下异种移植模型中测定了A-1331852与多烯紫杉醇联合对肿瘤生长的抑制作用。作为单一药物,a-1331852在所有七种模型中均显著抑制了肿瘤生长(P<0.05)(表4)。尽管其单药活性适中(七种模型中有五种的TGImax<60%),但A-1331852在所有七种模型上都提高了多西他赛的疗效。如表4所示,A-1331852作为单一药物的最大肿瘤生长抑制率(TGImax)在34%(OVCAR-5)和67%(A549-FP3)之间。对A-1331852的最持久反应是在A549-FP3模型中观察到的108%的肿瘤生长延迟(TGD)。这表明,与假治疗对照组相比,用a-1331852治疗时肿瘤达到1cm3体积所需的中位时间大约是其两倍。当将联合治疗与最有效的单一药物治疗进行比较时,在七个模型中的五个模型中,反应的幅度和持久性的增加具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。在MDA-MB-231 LC3转移性乳腺癌症模型(图5A)和NSCLC模型NCI-H1650(图5B)和NCI-H358(表4)中效果最为显著。总体而言,小鼠对单一药物和联合治疗具有良好的耐受性,没有明显的毒性或体重减轻>9%的迹象。这些数据表明,单独抑制BCL-XL可以增强多西他赛在各种实体瘤模型中的疗效。 在这项研究中,研究人员首先开始了体内疗效研究,其中A-1331852作为单一疗法或与多西他赛联合给药,13其结果最近已有报道。我们还利用A-1331852在体内评估了BCL-XL抑制与标准化疗的其他组合。我们最近报道,BCL2L1(BCL-XL)扩增是癌症(CRC)细胞系亚群的特征,包括Colo205细胞系。16此外,反义寡核苷酸体外敲低CRC细胞中BCL-XL蛋白表达可以增强对拓扑异构酶I(Topo I)抑制剂的凋亡反应,24从而表明小分子BCL-XL抑制剂与Topo I抑制剂(如伊立替康)的潜在联合治疗。Reference: ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020 Oct 8; 11(10): 1829–1836. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7549103/ 为了评估这种组合在体内环境中的潜力,评估了A-1331852作为单剂和与伊立替康组合在人结直肠癌癌症的Colo205小鼠异种移植物模型中的疗效,如图55所示。用Colo205细胞接种SCID/米黄色小鼠,并将其尺寸匹配至约220mm3的肿瘤体积,之后将A-1331852以单剂或与伊立替康组合口服给药。用A-1331852(25mg/kg/天,QD×14)或伊立替康(30mg/kg/天、Q3D×4)治疗后的TGImax值分别为35%或75%。a-1331852和伊立替康联合治疗导致TGImax值为92%。因此,联合治疗后的肿瘤生长抑制明显(p<0.001)高于单独使用伊立替康治疗后。此外,与单独使用伊立替康(TGD=162%)治疗后观察到的结果相比,该组合还显著(p<0.001)提高了反应的持久性(TGD=254%)。Reference: ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020 Oct 8; 11(10): 1829–1836. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7549103/ |
| 酶活实验 |
结合亲和力测定[1]
如前所述,对BCL-2、BCL-XL和MCL-1进行了时间分辨荧光共振能量转移(TR-FRET)结合亲和力测定。使用帝肯Gemini机器人从500μM开始在DMSO中连续稀释化合物。使用帝肯Temo在测定缓冲液中进行1:10的中间稀释,并将10μL转移到白色384孔低容量Corning#3673测定板上(2×起始浓度;10%DMSO)。然后将10μL的蛋白质/探针/抗体混合物添加到每个孔中,最终浓度如下:1 nM GST标记的蛋白质、1 nM铽抗GST抗体和100 nM俄勒冈绿标记的BAK肽。然后将样品在室温下平衡1小时。对于每种测定,探针/抗体和蛋白质/探针/抗体分别作为阴性和阳性对照包含在每个测定板上。在Envision平板阅读器上使用340nm激发滤光片和520nm(f-BAK)和495nm(Tb标记的抗His抗体)发射滤光片测量时间分辨荧光。离解常数(Ki)使用王方程[1]确定。 |
| 细胞实验 |
BCL-XL 的免疫沉淀在 K562 细胞中进行,暴露于 A-1331852 (100 nM) 0-2 小时,并对洗脱的复合物进行免疫印迹以检测指定的蛋白质。为了评估免疫沉淀的有效性,对输入的细胞裂解物和免疫耗竭的上清液(标记为流穿液)进行免疫印迹。
细胞增殖和存活率测定[1] 将癌症乳腺细胞系以每孔5000个细胞接种在96细胞板中,并用9×3剂量基质中的化合物组合处理,其中以三倍步骤(20-0.001μM)稀释的navitoclax、venetoclax和a-1155463,以及50、5.0或0.5 nM的多烯紫杉醇。在评估存活率之前,将细胞孵育72小时。NSCLC细胞系在5×5剂量基质中用化合物组合治疗72小时,并如前所述进行评估[1]。将卵巢癌症细胞系以每孔10000个细胞接种在96细胞板中,并在9×3剂量的基质中用化合物组合处理48小时。以三倍的步骤稀释多西他赛(10-1.1 nM)。Navitoclax、venetoclax和A-1155463分两步稀释(20-0.08μM)。[1] 菌落形成试验[1] 来源于正常人骨髓(BM)的造血前体细胞在添加了30 ng mL-1重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子(rhGCSF)的MethoCult 4230甲基纤维素基培养基中与不同浓度的navitoclax、venetoclax或A-1155463±5 nM多西他赛孵育。DMSO用于制备所有测试化合物的储备溶液,并在所有孔中以<0.002%的终浓度存在。将来自三个不同批次(BM07B21195、BM0080512A和BM5H09)的冷冻BM光密度细胞在37°C下快速解冻,在补充了2%胎牛血清(IMDM+2%FBS)的10 mL Iscove改良Dulbecco's培养基(IMDM)中洗涤一次,然后重新悬浮在IMDM+2%FBS中。将2.4-4.3×104个活细胞接种在6孔板的每个孔中,并在37°C(5%CO2)下在试验化合物的存在下孵育14-16天。由训练有素的技术人员使用光学显微镜计数包含至少30个粒细胞的集落形成单元。每种条件都进行了三次测试,以确定平均菌落数+/-一个标准差。 |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: SCID-bg mice are used to study the tumors' ability to grow. A-1331852 is given intravenously at 7.5 mg/kg every day for 14 days, while RP-56976 is given orally at 25 mg/kg daily. Every day, the tumor's volume change is tracked.
Compounds and Formulations [1] For administration in vivo, A-1331852 was formulated in 60% Phosal 50 PG, 27.5 % PEG 400, 10% ethanol, and 2.5 % DMSO. First, A-1331852 was suspended in DMSO and ethanol until a uniform cloudy suspension was obtained. PEG 400 and Phosal were then added and the solution was mixed by vortexing. Allowing the solution to sit for approximately 30 min after adding all the excipients helped to achieve a clear solution. A probe sonicator was also used for less than 10 min. Formulated compound was stored in an amber bottle at room temperature to protect it from light. A-1331852 was administered per os (PO) in this formulation. Docetaxel (DTX, Taxotere, Sanofi) in a solution of 50/50 (v/v) ratio polysorbate 80/dehydrated alcohol was diluted with saline prior to intravenous (IV) injection. When combined, DTX was given 1 h after A-1331852. Rat studies [1] Three separate rat studies were conducted using male Sprague Dawley rats (Crl:CD). Each study consisted of four arms, with 10 rats per arm: vehicle control PO daily for 5 consecutive days, docetaxel dosed IV as a single dose on day 1, BCL-XL, BCL-2, or BCLXL/ BCL-2 inhibitors dosed PO daily for 5 consecutive days, and BCL-XL, BCL-2, or BCLXL/ BCL-2 inhibitors in combination with docetaxel (docetaxel was dosed as a single dose on day 1, followed immediately by a dose of BCL-2 family inhibitor, and continued daily doses of inhibitor on days 2-5). Control rats were dosed with vehicle: 80% PEG/20% TPGS at 2 mL/kg for the study with BCL-XL inhibitor A-1331852, a 20/80 mixture of Vitamin E TPGS/PEG400 and 0.9% Phosphate Buffered Saline at 5 mL/kg for the study with BCL-2 inhibitor A-1211212, and 10% ethanol/30% PEG-400/60% Phosal 50 PG for the study with the BCL-2/BCL-XL dual inhibitor A-874009. In each study, rats were dosed with docetaxel as a single agent, via intravenous (IV) bolus at a dose of 5 mg kg-1 (10 mL kg-1 volume) or with the inhibitors as single agents at 7 mg kg-1 (2 mL kg-1 volume) of A-1331852, 50 mg kg-1 (5 mL kg-1 volume) of A- 1211212, or 30 mg kg-1 (5 mL kg-1 volume) of A-874009. For the combination dosing, an IV bolus of 5 mg kg-1 of docetaxel was immediately followed by a dose of 7 mg kg-1 of A-1331852, 50 mg kg-1 of A-1211212, or 30 mg kg-1 of A-874009. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
The BCL-2/BCL-XL/BCL-W inhibitor ABT-263 (navitoclax) has shown promising clinical activity in lymphoid malignancies such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia. However, its efficacy in these settings is limited by thrombocytopenia caused by BCL-XL inhibition. This prompted the generation of the BCL-2-selective inhibitor venetoclax (ABT-199/GDC-0199), which demonstrates robust activity in these cancers but spares platelets. Navitoclax has also been shown to enhance the efficacy of docetaxel in preclinical models of solid tumors, but clinical use of this combination has been limited by neutropenia. We used venetoclax and the BCL-XL-selective inhibitors A-1155463 and A-1331852 to assess the relative contributions of inhibiting BCL-2 or BCL-XL to the efficacy and toxicity of the navitoclax-docetaxel combination. Selective BCL-2 inhibition suppressed granulopoiesis in vitro and in vivo, potentially accounting for the exacerbated neutropenia observed when navitoclax was combined with docetaxel clinically. By contrast, selectively inhibiting BCL-XL did not suppress granulopoiesis but was highly efficacious in combination with docetaxel when tested against a range of solid tumors. Therefore, BCL-XL-selective inhibitors have the potential to enhance the efficacy of docetaxel in solid tumors and avoid the exacerbation of neutropenia observed with navitoclax. These studies demonstrate the translational utility of this toolkit of selective BCL-2 family inhibitors and highlight their potential as improved cancer therapeutics.[1]
Cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (CIP2A) is a predictive biomarker of disease progression in many malignancies, including imatinib-treated chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Although high CIP2A levels correlate with disease progression in CML, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain elusive. In a screen of diagnostic chronic phase samples from patients with high and low CIP2A protein levels, high CIP2A levels correlate with an antiapoptotic phenotype, characterized by downregulation of proapoptotic BCL-2 family members, including BIM, PUMA and HRK, and upregulation of the antiapoptotic protein BCL-XL. These results suggest that the poor prognosis of patients with high CIP2A levels is due to an antiapoptotic phenotype. Disrupting this antiapoptotic phenotype by inhibition of BCL-XL via RNA interference or A-1331852, a novel, potent and BCL-XL-selective inhibitor, resulted in extensive apoptosis either alone or in combination with imatinib, dasatinib or nilotinib, both in cell lines and in primary CD34(+) cells from patients with high levels of CIP2A. These results demonstrate that BCL-XL is the major antiapoptotic survival protein and may be a novel therapeutic target in CML.[2] |
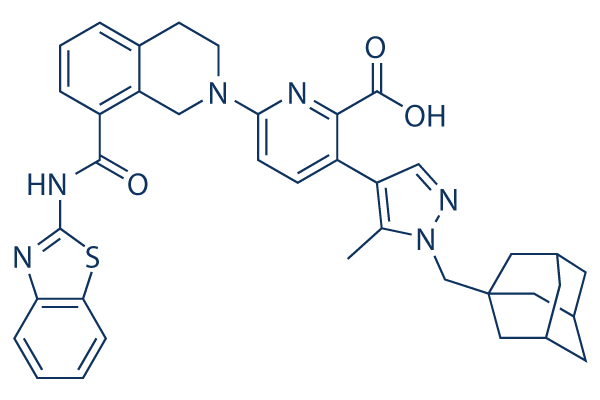
| 分子式 |
C38H38N6O3S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
658.81
|
|
| 精确质量 |
658.272
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 69.28; H, 5.81; N, 12.76; O, 7.29; S, 4.87
|
|
| CAS号 |
1430844-80-6
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
71565985
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.792
|
|
| LogP |
6.67
|
|
| tPSA |
142Ų
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
48
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1180
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
S1C2=CC=CC=C2N=C1NC(C1=CC=CC2=C1CN(CC2)C1C=CC(=C(C(=O)O)N=1)C1C=NN(C=1C)CC12CC3CC(CC(C3)C1)C2)=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
QCQQONWEDCOTBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C38H38N6O3S/c1-22-29(19-39-44(22)21-38-16-23-13-24(17-38)15-25(14-23)18-38)27-9-10-33(41-34(27)36(46)47)43-12-11-26-5-4-6-28(30(26)20-43)35(45)42-37-40-31-7-2-3-8-32(31)48-37/h2-10,19,23-25H,11-18,20-21H2,1H3,(H,46,47)(H,40,42,45)
|
|
| 化学名 |
3-[1-(1-adamantylmethyl)-5-methylpyrazol-4-yl]-6-[8-(1,3-benzothiazol-2-ylcarbamoyl)-3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-2-yl]pyridine-2-carboxylic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
A1331852; A-1331852; 3-[1-(1-adamantylmethyl)-5-methylpyrazol-4-yl]-6-[8-(1,3-benzothiazol-2-ylcarbamoyl)-3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-2-yl]pyridine-2-carboxylic acid; CHEMBL3793424; 3-(1-(((3r,5r,7r)-adamantan-1-yl)methyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-6-(8-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-ylcarbamoyl)-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)picolinic acid; A1331852; A 1331852
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.08 mg/mL (3.16 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.08 mg/mL (3.16 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.16 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.79 mM) (饱和度未知) in 2.5% DMSO 10% ethanol 27.5% PEG 300 60% Phosal 50 PG (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5179 mL | 7.5894 mL | 15.1789 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3036 mL | 1.5179 mL | 3.0358 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1518 mL | 0.7589 mL | 1.5179 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|---|