| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Myosin II[1]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
para-aminoblebbistatin[1]的体外和体内抑制特性
在对para-aminoblebbistatin进行物理化学表征后,我们将其体外和体内抑制性能与博来司他的和对硝基博来司的进行了比较。我们测量了兔骨骼肌肌球蛋白S1(SkS1)和盘基网柄菌肌球蛋白II运动结构域(DdMD)在对氨基博来司他丁、对硝基博来司他的丁或博来司的浓度增加时的基础和肌动蛋白激活的ATP酶活性(图3a,b)。所有三种肌球蛋白II抑制剂都在最大程度上降低了SkS1的基础ATP酶和肌动蛋白激活的ATP酶活性(~98-100%),产生了半最大抑制浓度值IC50,AmBleb=1.3±0.1μM,IC50,NBleb=0.3±0.04μM和IC50,Bleb=0.3±0.03μM用于SkS1的基底ATP酶和IC50,AmBlenb=0.47±0.06μM,IC50,NBleb=0.1±0.004μM和IC50,Bleb=0.11±0.009μM用于SkS1的肌动蛋白激活ATP酶活性。对硝基博来司他丁和博来司他汀对DdMD也有最大的抑制作用(~100%),而AmBleb对DdMD的基础和肌动蛋白激活的ATP酶活性分别达到90%和80%的抑制作用,产生IC50的一半最大抑制浓度值,AmBleb=6.6±2μM,IC50,NBleb=5.3±1.6μM和IC50,Bleb=4.4±0.3μM用于基础ATP酶和IC50,AmBleb=6.7±1.9μM,IC50,NBleb=3.4±0.3μM和IC50,Blenb=3.9±0.3μM.用于DdMD的肌动蛋白激活ATP酶活性。值得注意的是,AmBleb对SkS1和DdMD的IC50分别高出4.3倍和1.7倍。[1] 接下来,我们比较了para-aminoblebbistatin、对硝基布司他汀和布司他汀对人黑色素瘤(M2)和HeLa细胞中非肌肉肌球蛋白II的抑制作用。由于博来司他丁因其阻断M2细胞起泡的能力而得名1,我们比较了在不同浓度的三种不同肌球蛋白II抑制剂中孵育的M2细胞的起泡指数17(图3c-e)。即使5μM浓度的肌球蛋白II抑制剂在一小时内也能显著降低细胞的起泡指数,而更高浓度的抑制剂在>40-60分钟(10μM)或>20分钟(25和50μM)内完全停止了细胞的起泡。在5μM抑制剂浓度下抑制M2细胞起泡的速率常数相似,而在10和25μM浓度下,para-aminoblebbistatin的速率常数略慢于对硝基博来司他的速率常数或博来司的速率常数(表1)。[1] 非光毒性和非细胞毒性para-aminoblebbistatin增强成像。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在活斑马鱼胚胎试验中,在孵育24小时后,布来司他丁对肌球蛋白II的抑制被证明具有高度毒性,而使用对硝基布来司他的细胞毒性作用可以忽略不计8。为了比较para-aminoblebbistatin和布司他汀的细胞毒性,我们用不同浓度的抑制剂处理斑马鱼胚胎,并跟踪其发育72小时,确定其寿命(图4b)。40小时后,经布来司他丁处理的斑马鱼胚胎开始死亡,69小时后,所有胚胎在所有布来司他的浓度下都死亡。相比之下,即使在高浓度下,用para-aminoblebbistatin处理的胚胎也没有显示出任何细胞毒性的迹象,它们的适应性与未处理的对照胚胎相当[1]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
稳态ATP酶测量[1]
在不存在或存在45μM肌动蛋白或15μM肌动蛋白的情况下,在增加的博来司他丁、对硝基博来司他的或para-aminoblebbistatin的浓度下,测量了500 nM(用于基础ATP酶)或50 nM(对于肌动蛋白激活的ATP酶)SkS1(兔骨骼S1片段)和1μM(用于基础ATPase)或300 nM(针对肌动蛋白激活的ATPase)DdMD的MgATP酶活性。在SkS1或DdMD的情况下,分别在25°C或20°C下使用丙酮酸激酶/乳酸脱氢酶偶联试验(NADH偶联试验)进行测量。将肌球蛋白和肌动蛋白与指定浓度的抑制剂在室温下预孵育5分钟,并用1 mM ATP开始测量。数据已针对肌动蛋白的背景ATP酶活性进行了校正。相应地,从兔骨骼肌制备G-肌动蛋白24,并在室温下用2mM MgCl2聚合1小时。在pH 7.2的含有5 mM HEPES、2 mM MgCl2、0.1 mM EGTA和2 mM DTT的低盐缓冲液中,或在pH 7.3的含有20 mM HEPES,40 mM NaCl,4 mM MgCl2的测定缓冲液中进行测量,以用DdMD进行基础ATP酶活性测量。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞检测条件[1]
为了测定起泡指数,在每种情况下,在添加抑制剂之前,将M2细胞在PBS中孵育30分钟,以引发广泛的起泡。在向细胞添加抑制剂之前和之后监测细胞的起泡情况。在所有实验中,DMSO浓度为0.1体积/体积%。起泡指数是通过在给定的标准区域17(大小相似的全细胞,直径=12±1μm)上以5分钟的间隔(从指定的时间点开始)对开始的起泡进行求和,并将其归一化为抑制剂治疗前的起泡指数来计算的。[1] 对于伤口愈合试验,将200μl HeLa细胞以300000个细胞/ml的浓度镀在35mm硼硅酸盐玻璃成像皿上,并孵育24小时。在受伤前1小时,将细胞在20μM的不同肌球蛋白II抑制剂中孵育。一小时后,在单层培养中用移液管尖端进行划痕,并用Foculus数码相机(IEEE1394)监测占据伤口的细胞运动24小时。ImageJ通过测量移液管尖端产生的接近细胞边缘两侧的两条线之间的距离来分析细胞运动。[1] 对于细胞生长测定,HeLa Kyoto H2B mCherry eGFP-α-微管蛋白细胞在八室Lab Tek硼硅酸盐盖玻片系统上生长,初始细胞浓度为100000个细胞/ml。细胞附着在表面后,立即用0、2、5、10、25或50μM浓度的para-aminoblebbistatin、对硝基或博来司他的处理。细胞在指定抑制剂浓度下生长三天,每天定量细胞数量。所有实验中DMSO的最终体积百分比为0.1。数据分析由斐济软件进行。在实验的第三天,使用蔡司LSM 710和Plan Apo 20x/0.8物镜对多核细胞进行可视化。对于光毒性实验,在进一步补充25 mM HEPES的DMEM中对HeLa Kyoto H2B mCherry eGFP-α-微管蛋白细胞进行12小时的共聚焦延时成像,以实现CO2非依赖性培养基。使用Plan Apo 20x/0.8物镜在蔡司LSM 710上进行共聚焦延时成像,参数如下:λexc=488 nm时为2%激光强度,λexc=543 nm时为3%激光强度,1.2倍变焦,平均4,线步1,1000×1000像素,0.35μm像素大小,0.65μs停留时间,3层/z堆叠,每10分钟切片之间为7μm[1]。 |
| 动物实验 |
Conditions of assays with zebrafish embryos
For the fast escape response experiments, 6 dpf embryos were placed in 50 μl drops of E3 medium on a plastic plate. They were treated with 0, 2, 5, 10 or 20 μM of the inhibitors. 10 taps were carried out with 1 minute intervals every hour for 4 hours. The tapping force was standardized. The videos were recorded by a Ximea Camera (MQ003MG-CM) at 500 fps for 2 s. Data were analyzed by Flote software version 2.1 and maximal angular velocity parameters of C-start reflex were quantified. For the experiments investigating the effect of the inhibitors on the heart muscle of zebrafish, 6 dpf larvae were embedded in 1% agarose and kept in E3 in the presence of 20 μM concentrations of the inhibitors. Videos were taken at 15.1 fps before and after inhibitor treatment every hour for 3 hours. For the cytotoxicity assay, zebrafish embryos were incubated in E3 medium containing 0 μM (Control), 5 μM, 10 μM or 20 μM of para-aminoblebbistatin, para-nitroblebbistatin or blebbistatin in 0.1 vol/vol% final concentration of DMSO and monitored for 70 hours. Embryos were considered to be dead when the whole body became necrotic and the heart stopped beating. Dead embryos were removed from the experiment to prevent contamination. Images of zebrafish were captured with a Zeiss Stereo Lumar V12 microscope using a NeoLumar S 0.8x FWD 80mm objective at 50× zoom.
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Blebbistatin is a commonly used molecular tool for the specific inhibition of various myosin II isoforms both in vitro and in vivo. Despite its popularity, the use of blebbistatin is hindered by its poor water-solubility (below 10 micromolar in aqueous buffer) and blue-light sensitivity, resulting in the photoconversion of the molecule, causing severe cellular phototoxicity in addition to its cytotoxicity. Furthermore, blebbistatin forms insoluble aggregates in water-based media above 10 micromolar with extremely high fluorescence and also high adherence to different types of surfaces, which biases its experimental usage. Here, we report a highly soluble (440 micromolar in aqueous buffer), non-fluorescent and photostable C15 amino-substituted derivative of blebbistatin, called para-aminoblebbistatin. Importantly, it is neither photo- nor cytotoxic, as demonstrated on HeLa cells and zebrafish embryos. Additionally, para-aminoblebbistatin bears similar myosin II inhibitory properties to blebbistatin or para-nitroblebbistatin (not to be confused with the C7 substituted nitroblebbistatin), tested on rabbit skeletal muscle myosin S1 and on M2 and HeLa cells. Due to its drastically improved solubility and photochemical feature, as well as lack of photo- or cytotoxicity, para-aminoblebbistatin may become a feasible replacement for blebbistatin, especially at applications when high concentrations of the inhibitor or blue light irradiation is required.[1]
Blebbistatin, the best characterized myosin II-inhibitor, is commonly used to study the biological roles of various myosin II isoforms. Despite its popularity, the use of blebbistatin is greatly hindered by its blue-light sensitivity, resulting in phototoxicity and photoconversion of the molecule. Additionally, blebbistatin has serious cytotoxic side effects even in the absence of irradiation, which may easily lead to the misinterpretation of experimental results since the cytotoxicity-derived phenotype could be attributed to the inhibition of the myosin II function. Here we report the synthesis as well as the in vitro and in vivo characterization of a photostable, C15 nitro derivative of blebbistatin with unaffected myosin II inhibitory properties. Importantly, para-nitroblebbistatin is neither phototoxic nor cytotoxic, as shown by cellular and animal tests; therefore it can serve as an unrestricted and complete replacement of blebbistatin both in vitro and in vivo.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C18H17N3O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
307.35
|
| 精确质量 |
307.132
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 70.34; H, 5.58; N, 13.67; O, 10.41
|
| CAS号 |
2097734-03-5
|
| PubChem CID |
129626534
|
| 外观&性状 |
Orange to red solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
571.3±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
299.3±32.9 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.715
|
| LogP |
0.34
|
| tPSA |
78.9
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
23
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
526
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
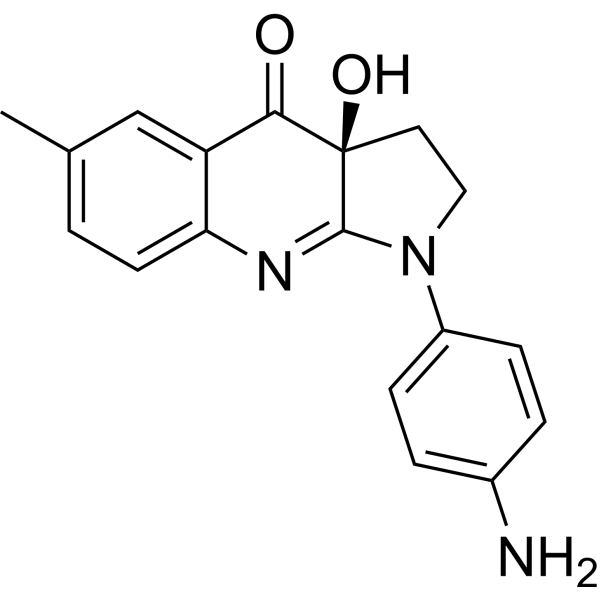
| SMILES |
CC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N=C3[C@](C2=O)(CCN3C4=CC=C(C=C4)N)O
|
| InChi Key |
LYWLZINJPRNWFF-GOSISDBHSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H17N3O2/c1-11-2-7-15-14(10-11)16(22)18(23)8-9-21(17(18)20-15)13-5-3-12(19)4-6-13/h2-7,10,23H,8-9,19H2,1H3/t18-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(3aS)-1-(4-aminophenyl)-3a-hydroxy-6-methyl-2,3-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-b]quinolin-4-one
|
| 别名 |
para-amino-Blebbistatin; para-aminoblebbistatin; 2097734-03-5; (3aS)-1-(4-aminophenyl)-3a-hydroxy-6-methyl-2,3-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-b]quinolin-4-one; p-aminoblebbistatin; CHEMBL4164044; SCHEMBL22512479; TQR0309;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMF: ~20 mg/mL (65.1 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2536 mL | 16.2681 mL | 32.5362 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6507 mL | 3.2536 mL | 6.5072 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3254 mL | 1.6268 mL | 3.2536 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。