| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Antibiotic/antibacterial
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
庆大霉素 C1a 的 IC50 值为 1 mg/mL,抑制大肠杆菌、铜绿假单胞菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的生长[2]。 OC-k3 细胞活力不受庆大霉素 C1a(2 mM,48 小时)的影响 [2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
庆大霉素C1a(4 mg/kg,静脉推注剂量,单剂量)在比格犬中的平均滞留时间为84分钟,CL值为1.81 mL/min/kg[3]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
庆大霉素C1a是半合成抗生素依替米星的前体,在临床上重要的庆大霉素C混合物中具有最高的抗菌活性。为了获得庆大霉素C1a高产菌株,我们灭活了紫色小单孢菌中的gacD基因。通过序列分析推测gacD编码C6'甲基转移酶,并在庆大霉素中间体X2转化为G418中发挥作用。因此,gacD的失活阻断了X2到G418的代谢途径,导致庆大霉素C1a的积累。与野生型菌株相比,所得重组菌株产生的庆大霉素C1a是野生型菌株的10倍以上。此外,野生型菌株产生4种主要生产成分C1a、C2、C2a和C1,而重组菌株仅产生2种成分C1a和C2b,使庆大霉素C1a的纯化更容易。重组菌株遗传稳定,可用于庆大霉素C1a的工业生产。[1]
|
| 细胞实验 |
抗菌素耐药性的蔓延和新型抗生素的短缺导致了对新型抗菌药物的迫切需求。尽管氨基糖苷类抗生素(AG)是非常有效的抗感染药物,但由于严重的副作用,主要是肾毒性和耳毒性,它们的使用在很大程度上受到限制。我们根据其对ESKAPE小组多重耐药临床分离株(庆大霉素、庆大霉素C1a、阿普霉素、巴龙霉素和新霉素)的强抗菌活性,评估了从一组较大的AGs中选择的各种AGs的耳毒性。在局部圆窗应用后,AGs对外毛细胞存活和复合动作电位的剂量依赖性影响表明庆大霉素C1a和阿普霉素的毒性最小。值得注意的是,尽管在用低浓度新霉素、庆大霉素和巴龙霉素治疗后,复合动作电位阈值和外毛细胞存活率没有变化,但内毛细胞突触带的数量和复合动作电位振幅都有所减少。在这种浓度下,庆大霉素C1a或阿普霉素没有观察到这种隐性听力损失的迹象。这些发现将内毛细胞确定为AG治疗中最脆弱的元素,表明庆大霉素C1a和阿普霉素是开发临床有用抗生素的有前景的基础[2]。
|
| 动物实验 |
The pharmacokinetics of gentamicin C(1), C(2), and C(1a) were studied in six beagles after administration of gentamicin at 4 mg/kg of body weight as a single intravenous bolus dose. Plasma concentrations of the gentamicin components were analyzed with a novel high-performance liquid chromatography method capable of identifying and quantifying each of the components. The pharmacokinetic analysis of the plasma concentration-versus-time data was performed using the noncompartmental approach. The results indicated significant differences in the pharmacokinetic characteristics between the gentamicin components C(1), C(1a), and C(2). The mean residence times of gentamicin C(1), C(1a), and C(2) were 81+/-13, 84+/-12, and 79+/-13 min (mean +/- standard deviation), respectively. The half-lives of the respective components were 64+/-12, 66+/-12 and 63+/-12 min. Clearance (CL) of gentamicin C(1), 4.62+/-0.71 ml min(-1) kg(-1), was significantly higher (P = 0.0156) than CL of gentamicin C(1a), 1.81+/-0.26 ml min(-1) kg(-1), and C(2), 1.82+/-0.25 ml min(-1) kg(-1). Similarly, the volume of distribution at steady state (V(ss)) of gentamicin C(1), 0.36+/-0.04 liter kg(-1), was significantly higher (P = 0.0156) than the V(ss) of gentamicin C(1a), 0.14+/-0.01 liter kg(-1), and C(2), 0.15+/-0.02 liter kg(-1). Tissue binding was considered the most likely cause for the difference. The difference may have clinical and toxicological significance.[3]
|
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Li D, et al. Construction of a gentamicin C1a-overproducing strain of Micromonospora purpurea by inactivation of the gacD gene. Microbiol Res. 2013 Jun 12;168(5):263-7.
[2]. Ishikawa M, et al. Lower ototoxicity and absence of hidden hearing loss point to gentamicin C1a and apramycin as promising antibiotics for clinical use. Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 20;9(1):2410. [3]. Isoherranen N, et al. Pharmacokinetics of gentamicin C(1), C(1a), and C(2) in beagles after a single intravenous dose. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000 Jun;44(6):1443-7. |
| 其他信息 |
Gentamycin C1a is a gentamycin C. It is a conjugate base of a gentamycin C1a(5+).
Gentamicin C1a has been reported in Cordyceps farinosa, Serratia plymuthica, and other organisms with data available. Gentamicin C1a is one of the major components of the gentamicin complex. Gentamicin C1a lacks methyl groups on the 2-amino-hexose ring and has a free amine at the 6' position. |
| 分子式 |
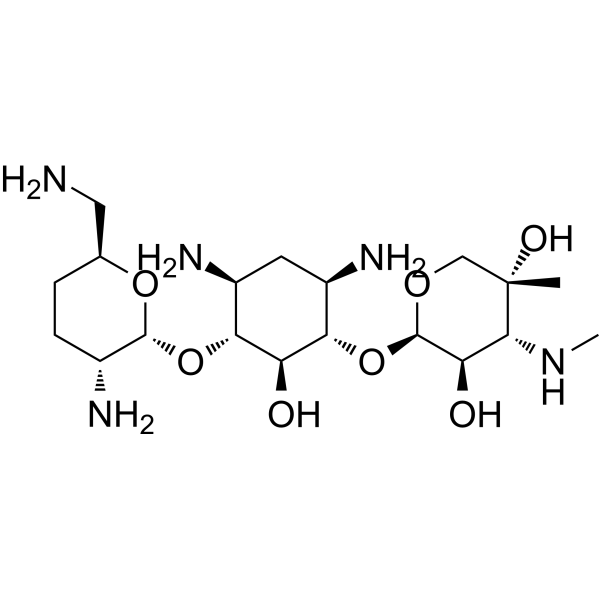
C19H39N5O7
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
449.54
|
| 精确质量 |
449.285
|
| CAS号 |
26098-04-4
|
| PubChem CID |
72396
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as
White to off-white solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.36g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
675.2ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
102-108ºC
|
| 闪点 |
362.1ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
3.97E-21mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.603
|
| LogP |
-5
|
| tPSA |
213.72
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
8
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
592
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
12
|
| SMILES |
[NH3+]CC1CCC([NH3+])C(OC2C([NH3+])CC([NH3+])C(OC3OCC(C)(O)C([NH2+]C)C3O)C2O)O1
|
| InChi Key |
VEGXETMJINRLTH-BOZYPMBZSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H39N5O7/c1-19(27)7-28-18(13(26)16(19)24-2)31-15-11(23)5-10(22)14(12(15)25)30-17-9(21)4-3-8(6-20)29-17/h8-18,24-27H,3-7,20-23H2,1-2H3/t8-,9+,10-,11+,12-,13+,14+,15-,16+,17+,18+,19-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-[(1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4,6-diamino-3-[(2R,3R,6S)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol
|
| 别名 |
Gentamycin C1A; Gentamycin C12; Gentamicin Cla; AV4A72IATD; CHEBI:27784; (2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-[(1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4,6-diamino-3-[(2R,3R,6S)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : 250 mg/mL (556.12 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2245 mL | 11.1225 mL | 22.2450 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4449 mL | 2.2245 mL | 4.4490 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2224 mL | 1.1122 mL | 2.2245 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。